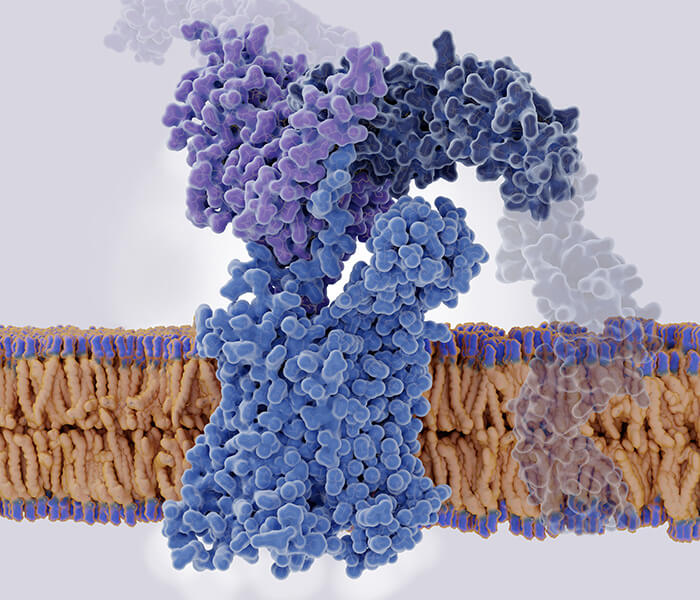
Protein palmitoylation serves as a reversible molecular switch that dynamically controls protein localization, stability, and interaction networks. This widespread lipid modification plays a crucial role in essential biological processes, including cellular signaling and membrane trafficking. Understanding its dynamic nature requires carefully selected detection methods aligned with specific research objectives.
Researchers now have access to a range of established and emerging techniques for studying this modification. Each approach provides unique strengths depending on whether your priority is mapping modification sites, measuring modification levels, or monitoring dynamic changes over time. Selecting the appropriate method relies heavily on your specific experimental questions and available technical resources.
In the following sections, we will examine the core principles, optimization strategies, and practical applications of major detection platforms. This includes chemical biology methods, mass spectrometry techniques, and biochemical assays that collectively offer a comprehensive understanding of palmitoylation dynamics.
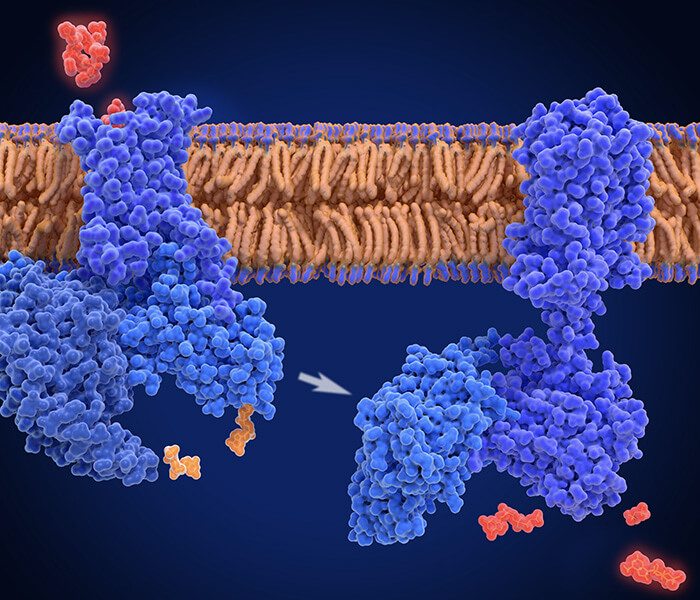
 The biochemistry of protein palmitoylation (Ko PJ et al., 2018)
The biochemistry of protein palmitoylation (Ko PJ et al., 2018)
Services you may be interested in:
Optimizing the Acyl-Biotin Exchange Assay: A Smarter Cleanup Strategy
A crucial advancement addresses a significant constraint in the conventional Acyl-Biotin Exchange (ABE) technique. Standard procedures involve repeated precipitation steps to eliminate surplus N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) following thiol blocking, frequently resulting in considerable sample reduction and protein clumping. This proves especially challenging when handling limited or sensitive protein specimens.
Scientists have introduced a novel chemical approach employing a Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction. Introducing a ten-fold molar surplus of 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene directly into the reaction solution effectively removes unreacted NEM. This method lowers NEM concentration from 10 mM to imperceptible concentrations in under sixty minutes.
This procedural refinement delivers notable benefits:
- Completely removes precipitation requirements
- Maintains sample quality and amount
- Enhances detection precision and signal reliability
- Especially useful for difficult-to-study proteins including receptor kinases
Research groups implementing this methodology observe approximately 40% superior signal reliability and significantly enhanced detection accuracy compared to conventional ABE methods.
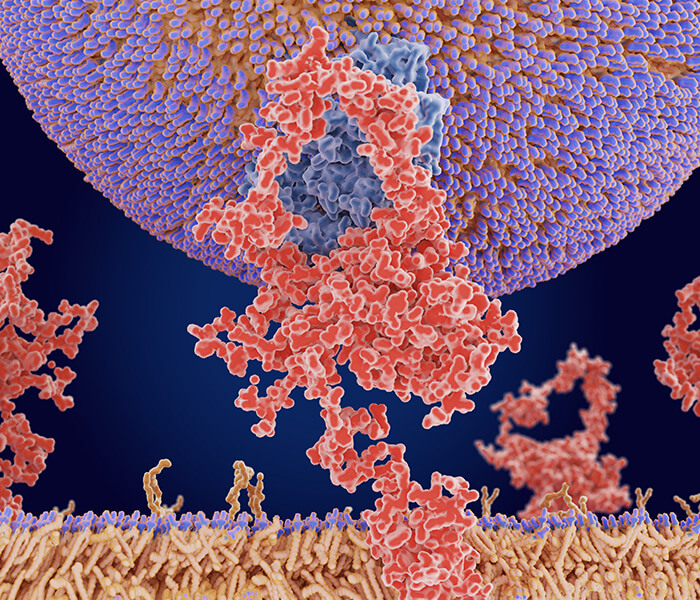
 ABE reaction scheme (Hurst CH et al., 2017)
ABE reaction scheme (Hurst CH et al., 2017)
Advancing Palmitoylation Proteomics with Nanomaterial Enrichment
The landscape of large-scale protein palmitoylation analysis has been revolutionized by advanced nanomaterial platforms. Contemporary technological platforms now enable researchers to characterize dynamic protein modifications with remarkable resolution and accuracy, bypassing previous methodological constraints that hindered comprehensive analysis.
Novel enrichment methodologies employing designed nanostructures have substantially enhanced our capacity to isolate and examine lipid-modified proteins. These developments facilitate extensive mapping of post-translational modifications, which was previously limited by technical challenges. The improved target selectivity of these systems minimizes non-specific background while boosting detection capabilities for rare molecular targets.
These technical innovations prove especially beneficial for:
- Comprehensive analysis of modification dynamics throughout complete proteomes
- Discovery of previously undetectable modification positions
- Precise measurement of alteration patterns under varying biological conditions
Through delivering purified samples and enhanced yield efficiency, nanomaterial-enhanced methods have accelerated discovery timelines in lipid modification studies, creating new opportunities for deciphering cellular communication systems.
A breakthrough approach utilizes magnetic microspheres functionalized with 2,2'-dithiodipyridine (Fe₃O₄/SiO₂-SSPy), which offer several distinct advantages for system-wide profiling:
- Rapid and Specific Capture: The magnetic core facilitates easy separation, while the high surface area and abundant reactive functional groups enable the highly specific capture of palmitoylated peptides directly from complex biological mixtures.
- Exceptional Sensitivity: This technology demonstrates remarkable performance even in challenging samples, effectively purifying target peptides from mixtures where palmitoylated to non-palmitoylated peptides are present at a 1:500 molar ratio, achieving detection limits at the femtomolar level.
The practical power of this method is demonstrated by its application in neural tissue. In a landmark study, researchers applied this advanced enrichment strategy to analyze mouse brain tissue. The results were groundbreaking—they identified 1,304 potential palmitoylated proteins, creating the most extensive map of mouse protein palmitoylation ever compiled.
This comprehensive dataset revealed numerous previously unknown palmitoylation-regulated proteins and biological pathways. These findings provide crucial insights into brain function and the molecular mechanisms underlying neurological diseases, paving the way for new therapeutic developments.
Services you may be interested in:
Thiopropyl Capture Method: From Principle to Biological Insight
The Thiopropyl Capture (TPC) method provides a dependable biochemical approach for detecting protein palmitoylation through targeted molecular exchange. This technique utilizes sequential chemical reactions to isolate palmitoylated proteins from complex biological samples specifically.
Standard TPC Procedure:
- Initial Blocking: Free cysteine residues are covalently blocked using MMTS reagent
- Selective Cleavage: Hydroxylamine treatment specifically breaks palmitoyl-thioester bonds, generating new reactive thiol groups
- Specific Capture: Newly exposed thiols are captured via disulfide exchange using thiopropyl-sepharose beads
- Downstream Analysis: Captured proteins are eluted for identification through Western blot or mass spectrometry
This methodology has demonstrated particular value in metabolic studies. The application of TPC in adipocytes and adipose tissue has revealed numerous palmitoylated proteins involved in metabolic regulation. Seminal work by Ren W. et al. established that both the insulin-responsive glucose transporter GLUT4 and its adaptor protein IRAP undergo palmitoylation.
Notably, this modification intensifies under high glucose conditions and in obese mouse models, indicating a potential role in maintaining glucose homeostasis. These findings illustrate how TPC enables researchers to bridge specific protein modifications with systemic metabolic control mechanisms.
Decoding the Palmitoylome: A Systems-Level Workflow
Current palmitoylome profiling employs a sophisticated three-stage methodology that transforms complex protein mixtures into functional insights. This systematic framework—encompassing enrichment, identification, and quantification—has revolutionized our ability to study protein lipid modifications through a systems biology lens.
The integrated approach provides:
- Comprehensive mapping of dynamic modification networks
- Transition from basic detection to mechanistic understanding
- Quantitative assessment of modification changes across conditions
This methodological evolution enables researchers to move beyond simple cataloging of modification sites toward understanding the functional significance of palmitoylation in cellular regulation and disease mechanisms. The structured workflow ensures reproducible results while accommodating both discovery-phase and targeted investigation approaches.
Targeted Enrichment: Isolating the Signal
The foundational stage of palmitoylome analysis centers on precise isolation of palmitoylated peptides from complex protein mixtures. The optimized acyl-biotin exchange method serves as the cornerstone technique for this essential enrichment process. This chemical biology strategy proceeds through three well-defined operational stages:
- Block: Irreversibly cap all accessible thiol groups using N-ethylmaleimide
- Cleave: Specifically hydrolyze palmitoyl-thioester linkages with hydroxylamine to generate novel reactive thiols
- Tag: Efficiently capture these newly accessible thiols using biotin-conjugated reagents for subsequent purification
This targeted enrichment methodology successfully separates the typically scarce palmitoylated peptides from the predominant population of unmodified proteins. This crucial separation step establishes the foundation for the detailed analytical phases in comprehensive palmitoylome profiling, enabling highly specific capture of low-abundance targets while minimizing background interference for downstream analysis.
Advanced Mass Spectrometry Identification
Following successful enrichment, high-resolution mass spectrometry provides the analytical power required for comprehensive characterization. Modern platforms utilizing data-independent acquisition (DIA) methodologies, coupled with advanced instrumentation like the Astral analyzer, deliver systematic and complete peptide profiling.
This technological evolution has substantially improved both detection coverage and quantitative accuracy. The integration of these sophisticated systems enables:
- Unprecedented depth in modification site identification
- Enhanced measurement precision across multiple samples
- Robust reproducibility for longitudinal studies
Current experimental setups now routinely identify over 14,000 distinct palmitoylation sites in single analyses. This capacity represents a quantum leap beyond what was previously attainable, highlighting the remarkable acceleration in proteomic technology development. The expanded detection boundaries are reshaping our understanding of palmitoylation's regulatory scope and biological significance.
Intelligent Bioinformatics Interpretation
The essential final phase transforms raw spectral information into biological understanding through advanced computational processing. Sophisticated bioinformatics workflows manage these substantial datasets to reveal significant patterns and biological connections.
These computational systems execute several critical operations:
Pinpointing significant alterations in modification abundance across different experimental groups
- Connecting modification profiles to particular biological functions and signaling cascades
- Deciphering conserved sequence motifs surrounding modification positions
- Charting palmitoylation's impact on protein interaction networks
This integrated analytical approach reveals the organizational logic through which palmitoylation directs cellular functions. The methodology delivers a systems-wide viewpoint that moves beyond single-protein analysis, providing comprehensive understanding of regulatory architecture and how lipid modifications collectively influence cellular behavior.
Advanced Proteomic Strategies for System-Wide Palmitoylation Analysis
State-of-the-art mass spectrometry systems are fundamentally reshaping our investigation of protein palmitoylation throughout biological systems. These integrated analytical methodologies now provide unparalleled analytical power across three critical dimensions:
- Quantitative Accuracy: Contemporary instrumentation enables precise measurement of modification intensity across numerous sites concurrently
- Temporal Resolution: These systems monitor how palmitoylation dynamics shift in response to intracellular signaling and external stimuli
- Functional Correlation: They establish connections between distinct modification profiles and physiological consequences or pathological states
This methodological convergence revolutionizes our comprehension of how lipid-based modifications orchestrate cellular behavior, transitioning from isolated protein examinations to comprehensive understanding of regulatory networks. The integrated perspective enables researchers to connect molecular-level modifications with organism-level physiological responses, ultimately advancing our ability to decipher disease mechanisms and identify therapeutic opportunities.
Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Approaches
Researchers now combine stable isotope labeling with advanced enrichment techniques for precise quantification. The SILAC-ABE integration strategy allows absolute quantification of palmitoylation changes by comparing light/heavy labeled cells from different conditions. After mixing samples, researchers analyze peptide ion intensity ratios to calculate precise modification level differences.
For dynamic studies, the combination of 17-ODYA pulse-chase labeling with SILAC enables researchers to track modification turnover rates. This approach revealed that only specific protein classes—including Ras GTPases and Gα proteins—undergo rapid palmitoylation cycling, primarily regulated by thioesterases like LYPLA1/APT1.
Large-Scale Profiling and Validation
Researchers now achieve precise measurement of palmitoylation dynamics by integrating stable isotope labeling with advanced enrichment methods. The SILAC-ABE approach enables absolute quantification by comparing protein samples from different experimental conditions. Scientists analyze the intensity ratios between light and heavy labeled peptides to calculate exact differences in modification levels.
For rapid validation, researchers employ an in-gel fluorescence platform using click chemistry with fluorescent azide dyes. This method directly visualizes candidate proteins on SDS-PAGE gels with exceptional specificity, achieving false-positive rates as low as 10%. This validation step has become crucial for confirming discoveries from large-scale screening efforts before investing in functional studies.
Summary and Comparison of Detection Methods
The table below summarizes the key characteristics of the primary methods discussed to help guide your selection:
| Detection Method | Core Principle | Key Advantages | Key Limitations | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABE Method (Optimized) | Acyl-biotin exchange | No radioactivity; detects endogenous proteins; reduced sample loss after optimization | Multi-step protocol; potential for non-specific background | Measuring cumulative palmitoylation levels in tissues and cells |
| Metabolic Labeling (e.g., 17-ODYA) | Metabolic incorporation of alkyne-fatty acid analogs & click chemistry | Enables dynamic analysis (pulse-chase); high sensitivity | Requires live cells for label uptake | Real-time palmitoylation activity and dynamics in cultured cells |
| TPC Method | Acyl exchange & thiopropyl resin capture | Effectively enriches palmitoylated proteins for downstream analysis | - | Proteome-wide identification and validation of palmitoylated proteins |
| Novel Nanomaterial Enrichment | Direct capture of palmitoylated peptides by magnetic materials | Exceptional sensitivity and enrichment efficiency; ideal for omics studies | Requires specialized materials and MS platform | Ultra-deep palmitoylome profiling studies |
Core Differences Between Traditional and Modern Omics Strategies
| Feature Dimension | Traditional Biochemical Methods (e.g., ABE, Radioactive Labeling) | Modern Omics Strategies (e.g., MS-based Palmitoylome Analysis) |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Scale | Typically focuses on single or a few pre-defined target proteins | Global, unbiased identification of thousands of modification sites |
| Information Depth | Primarily confirms whether a protein is modified; difficult to pinpoint exact sites | Precisely identifies specific cysteine modification sites |
| Throughput & Efficiency | Low; limited information per experiment | High-throughput; enables simultaneous comparison of multiple sample states |
| Primary Application | Target verification; mechanistic exploration | Discovery of new targets; mapping modification networks; biomarker identification |
For information on how to detect palmitoylated proteins, see How to "Detect Palmitoylated Proteins: Methods and Best Practices".
Significant Discoveries in Omics Applications
Palmitoylomics has been applied to the study of various disease models and biological processes, yielding a series of groundbreaking discoveries.
- Applications in Cancer Research: In a study of hepatocellular carcinoma, Mo Y et al., using palmitoylomics, discovered that knockout of the palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC20 significantly reduced palmitoylation levels at 123 cysteine sites across 97 proteins, with fatty acid synthase being one of the most significantly altered substrates. Subsequent mechanistic studies revealed that ZDHHC20-mediated palmitoylation of FASN stabilizes FASN and promotes liver cancer development by competitively inhibiting its ubiquitination and degradation. This finding suggests that the ZDHHC20-FASN axis is a potential therapeutic target for liver cancer.
- Applications in Neuroscience and Disease: In a study of glioblastoma, Zhao C et al., through screening for palmitoylation substrates, identified the protein kinase GSK3β as a key substrate. Its palmitoylation is catalyzed by the enzyme ZDHHC4, a process that plays a crucial role in glioma stem cell self-renewal and chemotherapy resistance, making ZDHHC4 a potential chemosensitizer.
- Applications in Metabolic Disease Research: Palmitoylomics has helped reveal its role in type 2 diabetes. Dong G et al. found that under high glucose stimulation, the activity of the depalmitoylation enzyme APT1 in pancreatic β-cells is inhibited, leading to increased palmitoylation of its substrate protein SCAMP1, which in turn causes excessive insulin secretion and, in the long term, β-cell failure. This provides new insights into the pathogenesis of diabetes.
- Applications in Plant Science Research: Kumar M et al. used acyl-resin affinity chromatography combined with mass spectrometry to generate the first plant palmitoylation map in Arabidopsis thaliana. A total of 1,849 modification sites were identified, involving 1,094 proteins, indicating that at least 6% of Arabidopsis proteins may be regulated by palmitoylation, providing new insights into plant cell organization and function.
To learn more about the role of protein Palmitoylation in diseases, please refer to "Protein Palmitoylation: Role in Diseases, Research Methods, and Therapeutic Implications".
To see how large-scale analysis of protein palmitoylation can be achieved in drug discovery, see "Large-Scale Profiling of Protein Palmitoylation in Drug Discovery".
Therapeutic Horizons: From Palmitoylome Insights to Treatment Strategies
Palmitoylome profiling is rapidly transitioning from a basic research tool to a engine for therapeutic discovery. By systematically mapping this dynamic modification landscape, researchers are identifying novel drug targets and developing innovative treatment strategies with significant clinical potential. This approach is revealing entirely new avenues for intervention across multiple disease areas.
Discovering Novel Therapeutic Targets
Comparative analysis of palmitoylation patterns between diseased and normal states systematically reveals crucial dysregulated modification events. This enables identification of key "writer-enzyme-substrate" regulatory axes that drive pathology, uncovering promising drug targets that would remain hidden through conventional approaches.
Informing Strategic Drug Development
Current therapeutic strategies targeting palmitoylation primarily focus on two complementary approaches:
- Developing inhibitors against ZDHHC palmitoyltransferases ("writers")
- Creating compounds that target depalmitoylating enzymes ("erasers")
Notably, drug repurposing efforts have shown particular promise. The FDA-approved drug disulfiram has been found to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome palmitoylation, demonstrating anti-inflammatory effects and highlighting the potential of existing compounds for new therapeutic applications.
Advancing Precision Medicine Applications
Palmitoylome profiling is increasingly guiding personalized therapeutic approaches. In cancer immunotherapy, research has revealed that PD-L1 checkpoint protein stability depends critically on its palmitoylation status. Inhibiting this modification enhances T-cell mediated antitumor immunity, suggesting combination strategies that could improve response rates to existing immunotherapies. This emerging understanding of modification-specific regulatory mechanisms opens new possibilities for patient stratification and targeted intervention.
Conclusion: The Evolving Frontier of Palmitoylation Analysis
The field of protein palmitoylation analysis has decisively shifted toward highly sensitive, dynamic, and proteome-wide profiling platforms. Modern methods now capture the transient nature of this modification across entire cellular systems, providing unprecedented insights into its regulatory roles.
Looking ahead, two technological frontiers appear particularly promising. The development of selective thioesterase inhibitors will enable precise manipulation of palmitoylation dynamics, while the adaptation of single-cell analysis techniques will reveal cell-to-cell heterogeneity in modification patterns. These advances promise to illuminate the intricate spatiotemporal control mechanisms governing this essential post-translational modification, potentially unlocking new therapeutic strategies for related diseases.
References
- Ren W, Jhala US, Du K. Proteomic analysis of protein palmitoylation in adipocytes. Adipocyte. 2013;2(1):17-28.
- Mo Y, Han Y, Chen Y, Fu C, Li Q, Liu Z, Xiao M, Xu B. ZDHHC20 mediated S-palmitoylation of fatty acid synthase (FASN) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 19;23(1):274.
- Zhao C, Yu H, Fan X, Niu W, Fan J, Sun S, Gong M, Zhao B, Fang Z, Chen X. GSK3β palmitoylation mediated by ZDHHC4 promotes tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem cells in temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma through the EZH2-STAT3 axis. Oncogenesis. 2022 May 23;11(1):28.
- Hernandez JL, Majmudar JD, Martin BR. Profiling and inhibiting reversible palmitoylation. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013 Feb;17(1):20-6.
- Martin BR, Cravatt BF. Large-scale profiling of protein palmitoylation in mammalian cells. Nat Methods. 2009 Feb;6(2):135-8.
- Dong G, Adak S, Spyropoulos G, Zhang Q, Feng C, Yin L, Speck SL, Shyr Z, Morikawa S, Kitamura RA, Kathayat RS, Dickinson BC, Ng XW, Piston DW, Urano F, Remedi MS, Wei X, Semenkovich CF. Palmitoylation couples insulin hypersecretion with β cell failure in diabetes. Cell Metab. 2023 Feb 7;35(2):332-344.e7.
- Kumar M, Carr P, Turner SR. An atlas of Arabidopsis protein S-acylation reveals its widespread role in plant cell organization and function. Nat Plants. 2022 Jun;8(6):670-681.
- Zhang X, Zhang Y, Fang C, Zhang L, Yang P, Wang C, Lu H. Ultradeep Palmitoylomics Enabled by Dithiodipyridine-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2018 May 15;90(10):6161-6168.
- Hurst CH, Turnbull D, Plain F, Fuller W, Hemsley PA. Maleimide scavenging enhances determination of protein S-palmitoylation state in acyl-exchange methods. Biotechniques. 2017 Feb 1;62(2):69-75.