LC-MS/MS Untargeted Metabolomics
Creative proteomics offers comprehensive metabolomics services designed to unlock the full potential of your biological samples. For LC-MS/MS untargeted metabolomics, our state-of-the-art technology and expertise enable the unbiased detection and analysis of a wide range of metabolites, providing valuable insights into disease mechanisms, biomarker discovery, and therapeutic efficacy. Enrich and progress your metabolomics research.
Submit Your Request Now
×- What is
- Workflow
- Applications
- Advantages
- Sample Requirements
- FAQs
- Case Study
- Publication
LC-MS/MS Untargeted Metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics is a technical method for comprehensive and unbiased analysis of all small molecule metabolites (usually with a molecular weight <1000 Da) in biological samples. The core goal is to "panoramic scan" metabolite composition and reveal changes in the metabolic state of biological systems. It is widely used in disease mechanisms, drug development, nutrition and other fields.
There are mainstream platforms for untargeted metabolomics:
LC-MS/MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry): Suitable for polar/non-polar metabolites.
GC-MS/MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry): Suitable for volatile/derivatized metabolites.
LC-MS/MS can provide a more comprehensive metabolic profile compare with GC-MS/MS, which shows higher sensitivity and resolution, detect even trace amounts of metabolites, with detection limits down to ppb level.
Data analysis:
Peak extraction (such as XCMS, MS-DIAL).
Metabolite annotation (based on databases such as HMDB, METLIN, etc.).
Multivariate statistics (PCA, PLS-DA) to screen differential metabolites.
General Workflow
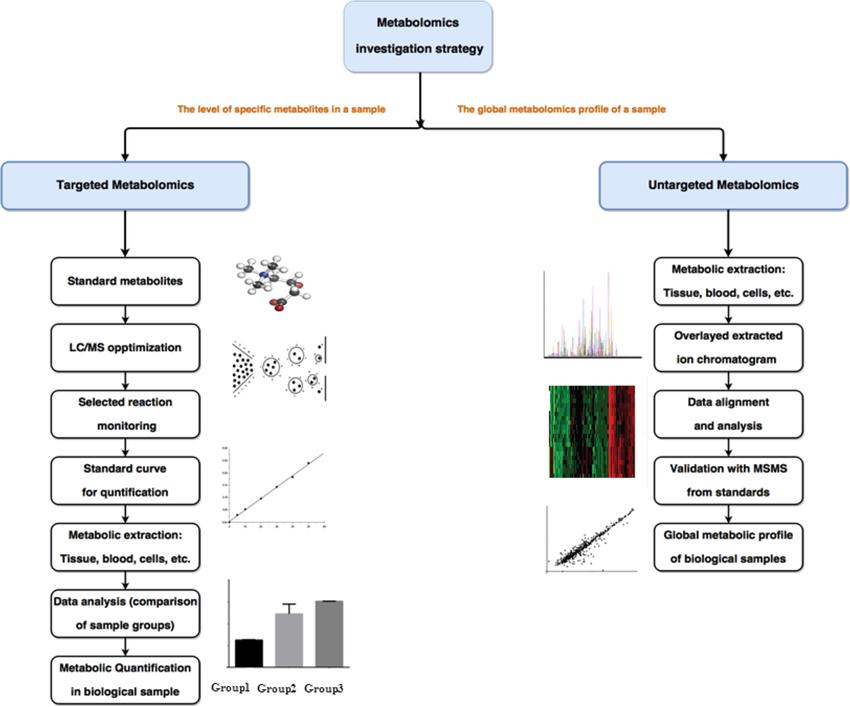 Figure 1. The targeted and untargeted workflow for LC-MS based metabolomics [1]
Figure 1. The targeted and untargeted workflow for LC-MS based metabolomics [1]
Applications
Basic medicine, clinical diagnosis: biomarker, disease mechanism, disease typing, personalized treatment, etc.
Biomedicine: drug mechanism of action, drug efficacy evaluation, drug development, etc.
Microbiology: pathogenesis, drug resistance mechanism, pathogen-host interaction research, etc.
Marine aquaculture: fishery resources, mariculture, fishery environment and aquatic product safety, etc.
Bioenergy and environmental science: fermentation process optimization, biofuel production, environmental risk assessment, etc.
Plant and agricultural Sciences: plant stress resistance mechanism, crop quality improvement, plant growth and development research.
Food nutrition: food storage and processing conditions optimization, food components and quality identification, functional food development, food safety monitoring and testing, etc.
Our Advantages
Detect up to 3000+ metabolites
Equipped with high-resolution, high-sensitivity mass spectrometry platform
Flexibility ion source choosing
Powerful database support
Advanced software tools and automated analysis
Platform:
Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Exploris 240, Thermo Scientific Q ExactiveTM HF-X MS, TripleTOF® 6600 System, Sciex
Sample Requirements
Our LC-MS/MS untargeted metabolomics platforms can offer broad coverage of sample type. For other sample types, please inquire us.
| Sample type | Minimum amount |
|---|---|
| Serum, plasma, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. | 200 μL |
| Brain, lung, kidney, liver, etc. | 200 mg |
| Cell supernatant, cell pellet, cell lysates, etc. | 200 μL, 10^7 cells |
| Roots, stems, leaves, fruits, seeds, etc. | 200 mg |
| Feces, bacteria, fungi, etc. | 200 mg |
FAQs
What is the difference between untargeted and targeted metabolomics?
Targeted metabolomics: Focuses on the quantitative analysis of specific metabolites or metabolic pathways, usually calibrated using known metabolite standards.
Untargeted metabolomics: Comprehensively detects all metabolites in a sample, not relying on a pre-defined list of metabolites.
Are biological replicates recommended?
It is recommended to have 6 to 10 biological replicates per group (to reduce the impact of individual differences).
How to ensure quality control in LC-MS/MS non-targeted metabolomics experiments?
QC samples: Use pooled QC samples to monitor variation during the experiment.
Regular calibration: Inject QC samples at the beginning and end of the experiment and after every 10 samples to calibrate the system.
Should I choose positive ion mode (ESI+) or negative ion mode (ESI-) for LC-MS/MS?
ESI+: Detects alkaline/neutral metabolites (such as amino acids, choline).
ESI-: Detects acidic metabolites (such as organic acids, fatty acids).
Suggestion: Switch between positive and negative modes or run in two times.
How to verify non-targeted results?
Targeted verification: Quantify key metabolites using MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) mode.
Standard comparison: Use the standards to verify retention time and MS/MS spectra.
Learn about other Q&A about other technologies.
LC-MS/MS Untargeted Metabolomics Case Study
Publications
Here are some publications in Metabolomics research from our clients:

- Effect of arabinogalactan on the gut microbiome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial in healthy adults. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111273
- Effects of microbial phytase on mucin synthesis, gastric protein hydrolysis, and degradation of phytate along the gastrointestinal tract of growing pigs. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky439
- NUDT22 promotes cancer growth through pyrimidine salvage and the TCA cycle. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1491465/v1
- Novakomyces olei sp. nov., the First Member of a Novel Taphrinomycotina Lineage. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020301
- WI12 Rhg1 interacts with DELLAs and mediates soybean cyst nematode resistance through hormone pathways. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13709
Reference
- Jacob M.; et al. Metabolomics toward personalized medicine. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019, 38(3):221-238 https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mas.21548






