The increasing usage of glycoproteins in biopharmaceutical products requires rapid and efficient analytical techniques for glycosylation analysis. The characterization of protein glycosylation needs the identification of intact glycopeptides. Different identified glycopeptides associated to the same glycosylation site on the same peptide backbone can be characterized due to the microheterogeneity. The full characterization of a glycopeptide includes identification of the peptide sequence, assignment of glycosylation sites, and glycan chain sequencing.
The glycan structure analysis includes monosaccharide composition, glycosidic linkage, and attachment to aglycones. Glycan structures remain very challenging to characterize owing to their diverse and heterogeneous nature. Mass spectrometry has become a routine experimental tool to obtain primary connectivity and glycosidic linkage information. The glycans can be released, purified and derivated by enzymatic or chemical methods prior to MS Profiling.
The highly specific exoglycosidases are generally used for the determination the sequence and structure of glycans. These specific Exoglycosidases remove terminal sugar groups from the non-reducing end of a glycan, but do not cleave internal bonds between monosaccharides. The glycosidic linkage and sugar groups of the removed glycan residues can be characterized and identified by using different linkage-specific exoglycosidases.
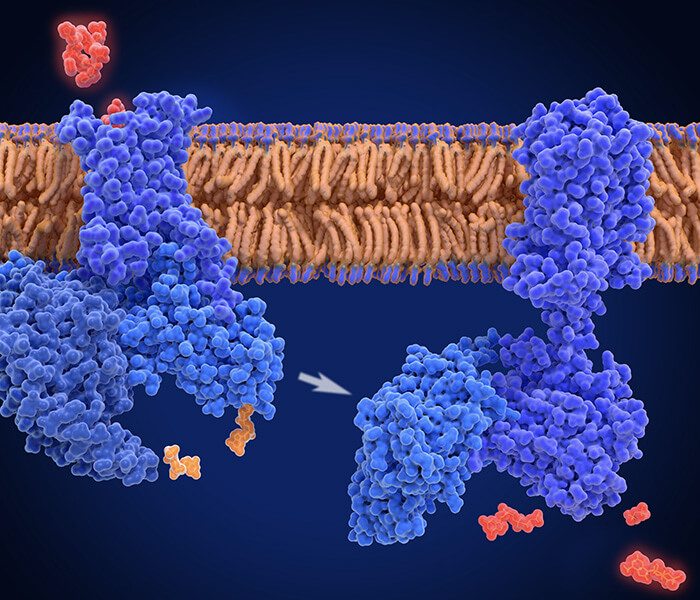
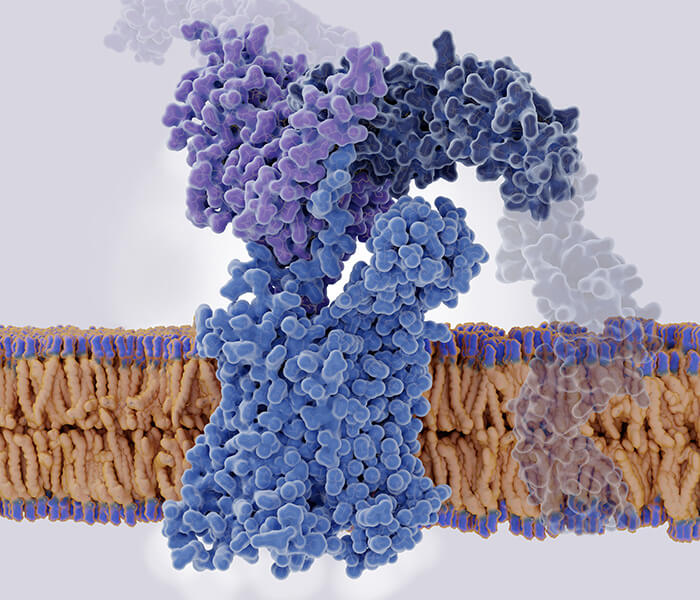
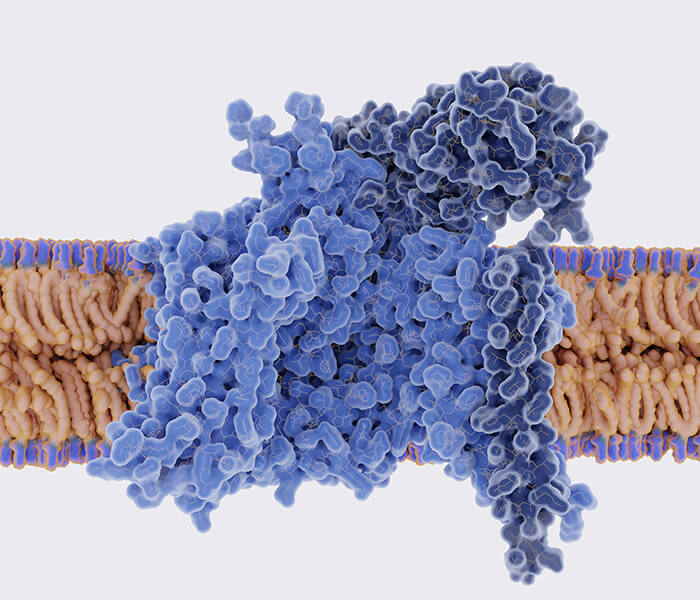
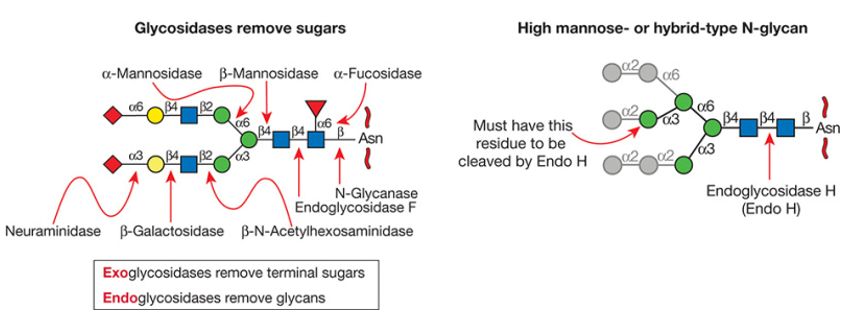 Figure 1. Glycosidases used for glycan structural analysis
Figure 1. Glycosidases used for glycan structural analysis
The exoglycosidase digestion coupled with high-performance separation techniques such as liquid chromatography is an efficient and fast approach for the structural characterization of glycans.
Glycans with free-reducing termini can be chemically labeled with fluorescent tags, such as 2-amino-pyridine (2-AP), 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB), 2-aminobenzoic acid (2-AA), 2-aminonaphthalene trisulfonic acid (ANTS), or 1-aminopyrene-3,6,8-trisulfonic acid (APTS), providing detection sensitivity and feasible separation. Monosaccharide composition analysis and linkage analysis are used for the determination of the absolute configuration of each monosaccharide and the occurrence of linkage and branching point.
Due to the stereochemical complexity of glycans, multiple technologies must be combined to provide full unambiguous structural information. Liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry are currently the most useful and powerful techniques for high-throughput analysis of glycans. The emerging MS-hybridized analytical technique ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) coupled to MS facilitates the separation and characterization of isobaric glycans. Structural information can be ascertained through computational calculations.
As one of the leading companies in the omics field with over years of experience in omics study, Creative Proteomics provides glycomics analysis service customized to your needs. Contact us to discuss your project.
How to place an order

*If your organization requires signing of a confidentiality agreement, please contact us by email.
Reference
- Barbara Mulloy, Anne Dell, Pamela Stanley, and James H. Prestegard., Essentials of Glycobiology. 3rd edition.
- Christopher J. Gray, Lukasz G. Migas, Perdita E. Barran, Kevin Pagel, etc. (2019) Advancing Solutions to the Carbohydrate Sequencing Challenge, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 37, 14463-14479.