Accurate Polysaccharide MW Determination Services
Polysaccharide molecular weight analysis plays a critical role in both scientific research and industrial applications. From functional food ingredients to drug development, knowing the molecular weight and distribution of polysaccharides is essential for understanding their biological activities, structural properties, and commercial value.
Unlike small molecules, polysaccharides don't have a fixed molecular weight. Instead, they exist as complex mixtures of molecules of varying sizes. This diversity is known as polydispersity and makes accurate measurement both essential and technically challenging.
At Creative Proteomics, we offer a comprehensive glycomics analysis service tailored to these challenges. Our platform integrates advanced instrumentation and multiple analytical methods, providing clients with reliable, detailed insights into polysaccharide structure and properties.
Submit Your Request Now
×
Reliable Molecular Weight Analysis for Complex Polysaccharides
Unlock precise insights into your polysaccharides' size, structure, and bioactivity. Our advanced SEC-MALS and HPGPC services deliver accurate data you can trust for research, development, and quality control.
- What is
- Available Methods
- Advantages
- Sample Requirement
- FAQ
- Demo
- Publication
Why Polysaccharide Molecular Weight Matters
- Functional Activity: A polysaccharide's bioactivity often correlates with its molecular weight and size distribution. For example, specific molecular weight ranges can enhance immunomodulatory effects or improve solubility in pharmaceutical formulations.
- Quality Control: Molecular weight distribution serves as a key quality parameter in product development and regulatory compliance, especially for therapeutic polysaccharides or functional food additives.
- Structural Characterisation: Molecular weight data supports further structural analyses, like methylation studies or NMR, to elucidate branching patterns or linkage types in complex polysaccharides.
How to Accurately Measure Polysaccharide Molecular Weight
Knowing the molecular weight of a polysaccharide isn't just a technical detail—it's central to unlocking its biological functions and commercial uses. Whether derived from natural sources or synthesized in a lab, polysaccharides play vital roles in drug development, bioprocessing, and medical applications.
Yet, determining their molecular weight is no easy task. Why? Because polysaccharides present a perfect storm of analytical challenges:
Diverse Size Profiles: Polysaccharides are polydisperse, meaning they're mixtures of molecules with different sizes and weights.
- Complex Shapes: Their three-dimensional structures in solution are hard to define, making it tricky to predict how they'll behave during analysis.
- High Interaction with Solvents: Many polysaccharides occupy large "exclusion volumes" due to strong solvent affinity or asymmetric shapes.
- Self-Association Tendencies: At higher concentrations, some polysaccharides tend to clump together, complicating measurements further.
Available Methods for Polysaccharide Molecular Weight Analysis
We provide several complementary techniques, each suited to specific sample types and analytical goals.
1. High-Performance Gel Permeation Chromatography (HPGPC)
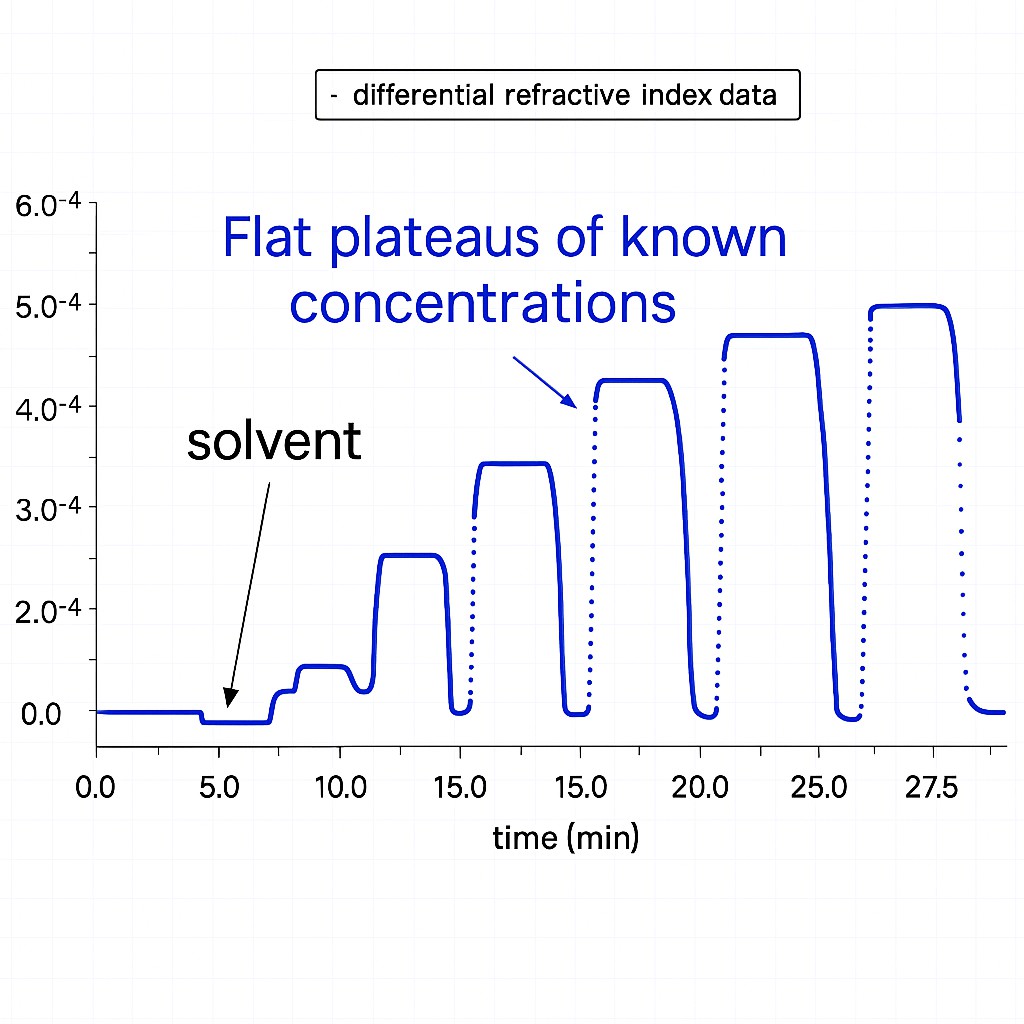
HPGPC is widely used for relative molecular weight determination due to its efficiency and high resolution. The technique involves:
- Passing polysaccharide solutions through a series of gel columns.
- Detecting elution times with refractive index (RI) detectors.
- Comparing retention times against standard curves prepared from known molecular weight standards such as dextrans or pullulan polysaccharides.
Key parameters obtained from HPGPC include:
- Weight-average molecular weight (Mw)
- Number-average molecular weight (Mn)
- Polydispersity index (Mw/Mn), which indicates how uniform the molecular weight distribution is.
HPGPC is particularly useful for routine quality checks and can also serve as a baseline assessment before more advanced structural studies. However, it's a relative method—meaning the accuracy depends on how closely your polysaccharide resembles the calibration standards used.
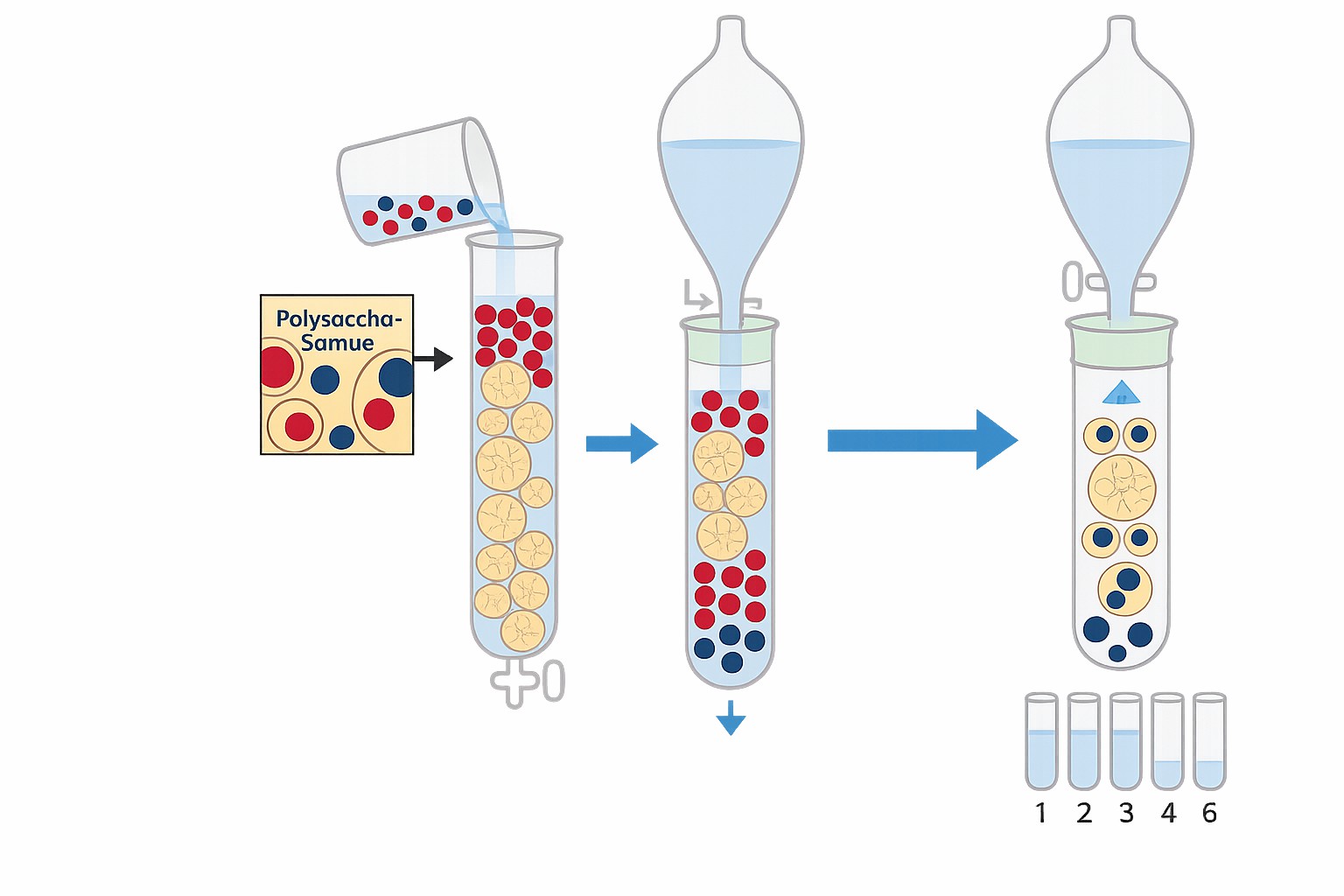 Figure 1. Principle of HPGPC Analysis.
Figure 1. Principle of HPGPC Analysis.
In high-performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC), a polysaccharide sample passes through a column packed with porous gel beads. Larger molecules elute first because they cannot enter the pores, while smaller molecules penetrate the gel matrix and elute later. The result is a separation based on molecular size, enabling molecular weight determination.
2. Size Exclusion Chromatography Coupled with Multi-Angle Laser Light Scattering (SEC-MALS)
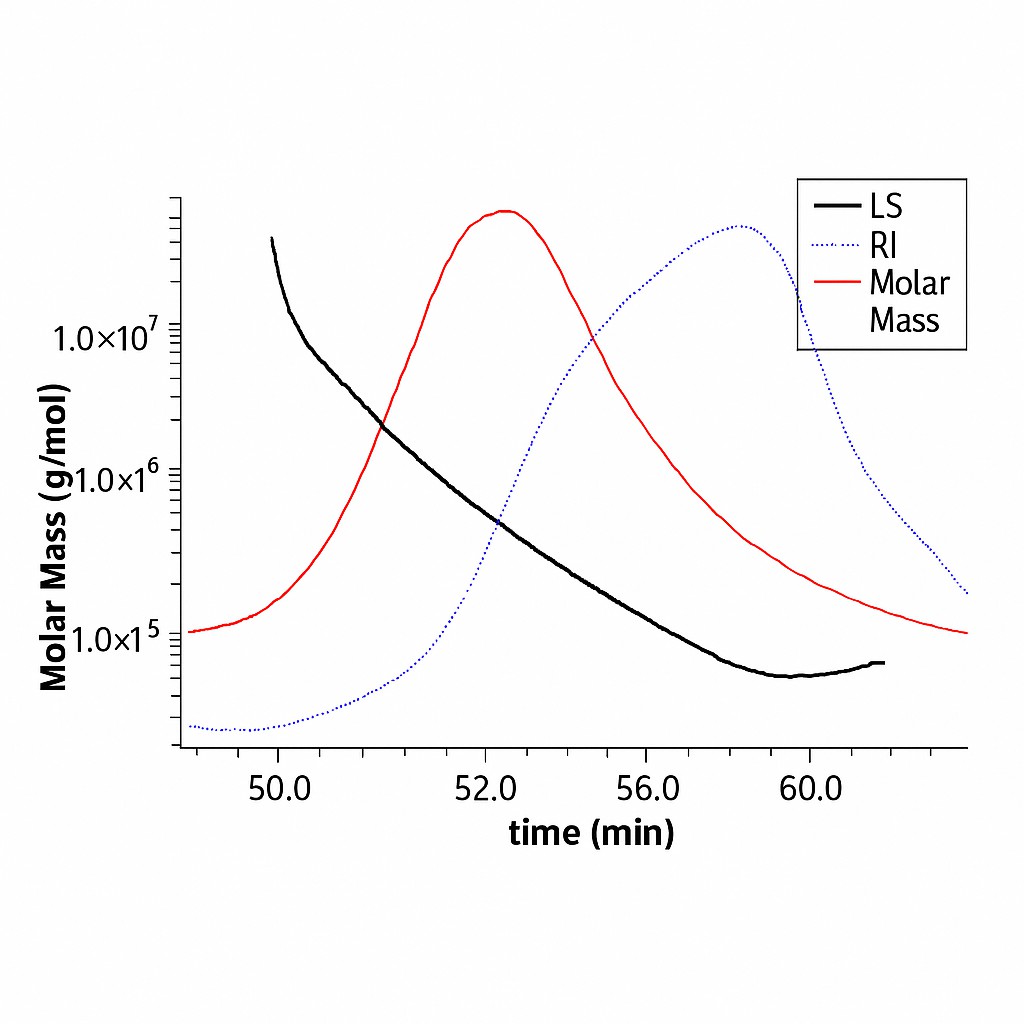
For absolute molecular weight measurement, SEC-MALS offers significant advantages. Here's how it works:
- A laser beam strikes the polysaccharide molecules as they elute from the chromatography column.
- The intensity of scattered light at multiple angles relates directly to the molecular weight and the concentration of the polymer in solution.
- Unlike HPGPC, SEC-MALS does not require calibration with standards, making it highly accurate for diverse polysaccharide structures.
Additional insights from SEC-MALS:
- Root-mean-square radius (Rg): Provides information about molecular size and shape in solution.
- Aggregation states: Helps determine whether polysaccharides exist as single chains, compact spheres, or extended rods in solution.
However, accurate results depend on knowing the specific refractive index increment (dn/dc), a parameter describing how the polymer's refractive index changes with concentration. This value can vary significantly based on the polysaccharide's composition, molecular weight, solvent system, and even the laser wavelength used.
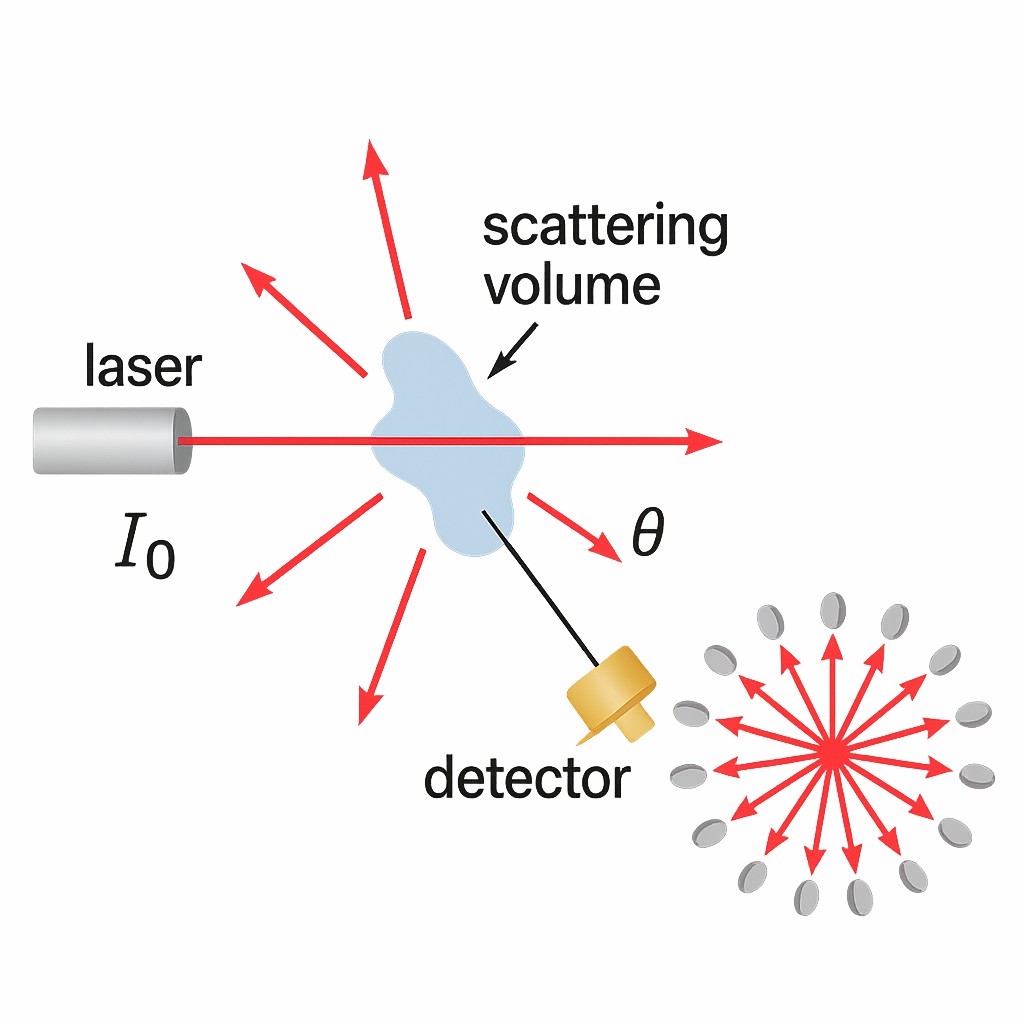 Figure 2: The principle of SEC-MALLS method
Figure 2: The principle of SEC-MALLS method
Schematic representation of the SEC-MALS technique, showing how a laser beam interacts with a sample to generate scattered light measured at multiple angles, enabling absolute molecular weight and size determination without calibration standards.
3. Other Methods Available
Depending on your project goals, we also offer alternative techniques:
- Viscometry: Simple, cost-effective for approximate molecular weight estimation but less precise for complex polysaccharides.
- Osmotic Pressure Measurements: Suitable for determining number-average molecular weights, particularly for low-to-moderate molecular weight polysaccharides.
- Analytical Ultracentrifugation: Separates molecules based on size and shape using centrifugal forces.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Useful for smaller polysaccharides or comparing molecular weight profiles across batches.
- Mass Spectrometry: Increasingly used for lower molecular weight polysaccharides or oligosaccharides but less practical for high molecular weight polymers.
Each method has unique strengths, and our experts help clients select the best analytical strategy based on sample properties and research objectives.
Our Technical Advantages
Choosing Creative Proteomics means accessing:
- Advanced Instruments: Our platform includes the Waters 2414 Refractive Index Detector and the DAWN multi-angle laser light scattering system from Wyatt Technology, enabling both relative and absolute molecular weight determination.
- Low Sample Requirements: Typically, only 5–10 mg of polysaccharide powder is needed.
- Broad Solvent Compatibility: We handle analyses in aqueous solutions, DMSO, DMF, THF, chloroform, and other GPC solvents.
- High Accuracy and Repeatability: Our systems ensure reliable, reproducible results, essential for regulatory submissions and product development.
- Fast Turnaround: We deliver clear reports, including detailed data interpretations and graphical outputs, to support your decision-making.
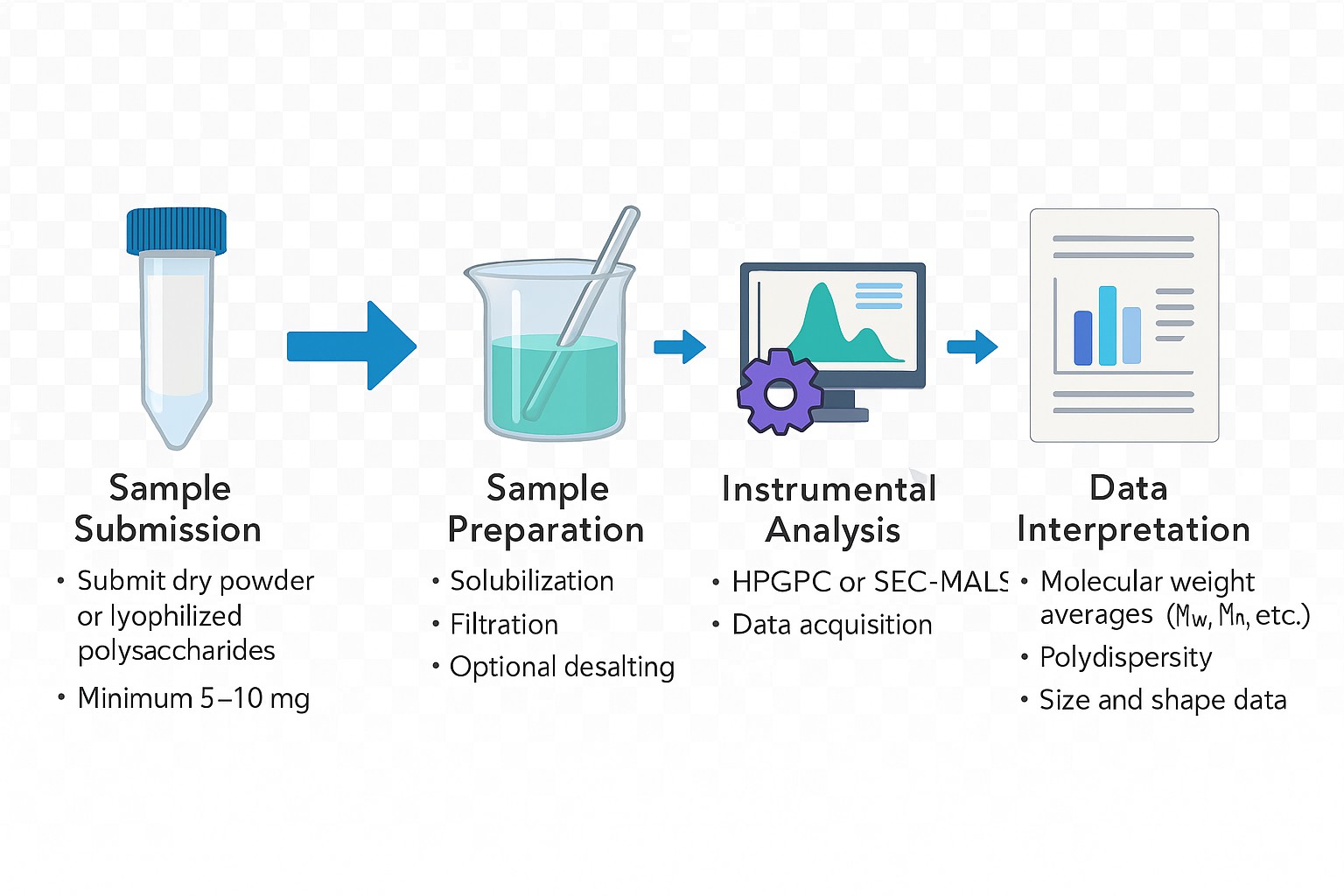
Workflow
Applications Across Industries
Our polysaccharide molecular weight services support projects in diverse fields, including:
- Functional food and nutritional ingredient development
- Herbal medicine research (activity, pharmacology, toxicity studies)
- Glycoprotein characterisation in biopharma pipelines
- Bio-colloid research
- Food science and nutritional biochemistry
From small research batches to large-scale manufacturing validation, our team is ready to support your polysaccharide characterisation needs.
Sample Requirements and Submission Guidelines
To ensure accurate analysis, please follow these guidelines when preparing samples:
- Sample Type: Dry polysaccharide powders or lyophilised material.
- Quantity: 5–10 mg per sample.
- Biological Replicates: Minimum of three replicates is recommended.
- Sample Uniformity: Ensure samples are well-mixed to avoid inconsistencies.
- Desalting: If your polysaccharide is in solution and contains salts, desalting is recommended before submission.
- Labelling: Use clear, unique sample IDs rather than generic labels like "A/B/C."
- Documentation: Always include a completed technical request form with your shipment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What's the difference between HPGPC and SEC-MALS for my polysaccharide project?
HPGPC estimates molecular weight by comparing your sample's retention time to known standards—ideal for routine checks. SEC-MALS, in contrast, directly measures absolute molecular weight and reveals details like molecular shape and aggregation, making it the best choice for complex or novel polysaccharides.
How much sample do I need to provide?
Typically, only 5–10 mg of dry polysaccharide powder is sufficient for analysis. Our team will advise if your project requires special handling.
Can you handle polysaccharides that are difficult to dissolve?
Yes. We're experienced in working with polysaccharides in various solvents, including aqueous solutions, DMSO, DMF, and others. We'll guide you on optimal sample preparation to ensure accurate results.
Will the data be suitable for regulatory submissions?
Absolutely. Our analytical platforms generate robust, reproducible data suitable for regulatory filings, product development, and publication.
How do I choose between relative and absolute molecular weight analysis?
It depends on your goals. For quality control of known polysaccharides, relative methods like HPGPC may be sufficient. For research on novel polysaccharides or precise characterization, we recommend SEC-MALS for its ability to measure absolute molecular weight and structural features.
Can your analysis detect polysaccharide branching or conformational details?
Yes. Techniques like SEC-MALS provide insights into molecular size, radius of gyration, and aggregation states, helping you assess structural details like branching or molecular shapes.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
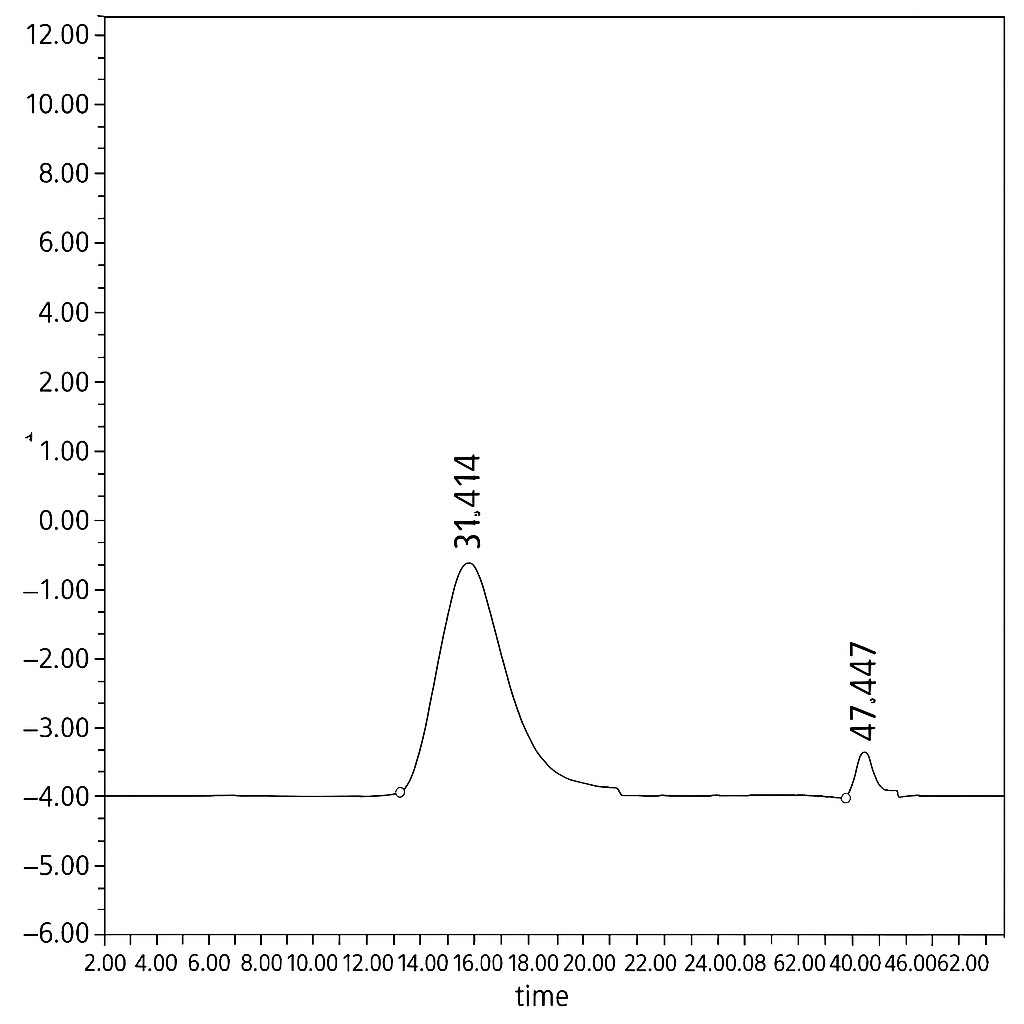
Data Example
Publications
Here are some publications in Glycomics research from our clients:

- Modulation of the Endomembrane System by the Anticancer Natural Product Superstolide/ZJ-101. International journal of molecular sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119575
- Identification of the O-Glycan Epitope Targeted by the Anti-Human Carcinoma Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) NEO-201. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14204999
- Alternative glycosylation controls endoplasmic reticulum dynamics and tubular extension in mammalian cells. Science advances. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe8349
- Conformational differences between functional human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein trimers and stabilized soluble trimers. Journal of Virology. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01709-18