What Are Host Cell Proteins?
Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) are a heterogeneous and complex protein group produced by host cells, comprising both target proteins and proteins native to the host cell itself. HCPs differ significantly in molecular mass, isoelectric point, hydrophobic properties, and structures. Figure 1 shows a harvested product pool of bacterial and mammalian fermentation by two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis (2D-DIGE). Identification and quantification HCPs is important in the development of biopharmaceutical products to ensure product purity and patient safety. Protease of HCPs can influence the protein pattern in culture and influence the purification process. In addition, HCPs can undergo post-translational modifications that hindered the quantification and characterization. Moreover, high HCP variance results in different biochemical properties which might cause an immune response or allergic reactions even anaphylactic shock.
Although the host cells contain thousands of HCPs and that could potentially contaminate the final product and the host cells can be various organisms, such as, bacteria, yeast and cell lines derived from mammalian or insect species, there is no explicitly guideline that describes the selection of appropriate methods for characterization and quantification of HCPs and other impurities for biopharmaceuticals. Moreover, the regulatory agencies examine each protein drug on a case-by-case basis to determine appropriate maximum acceptable levels of HCPs and patient risk.
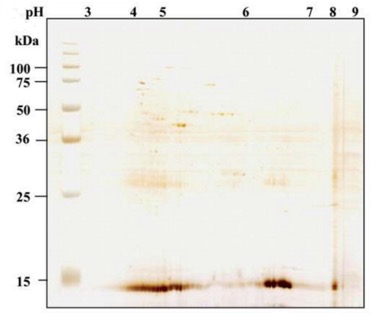 Figure 1 2D-DIGE silver stain of a harvested product
Figure 1 2D-DIGE silver stain of a harvested product
Regulatory Requirements for HCP Detection
Residual Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) serve as a crucial assessment parameter for process stability monitoring. They are essential quality control indicators for recombinant vaccines and monoclonal antibody drugs, with residual HCP content in bioproducts often regarded as a Critical Quality Attribute (CQA) of the product. National regulations, such as those by FDA and EMA, mandate the analysis and purification of biopharmaceuticals to reduce host cell protein (HCP) levels to acceptable thresholds. The extent of HCP acceptance will be evaluated based on specific circumstances, considering various factors including dosage, administration frequency, drug type, and disease severity. The recommended range by the US FDA is 1-100 ppm (ppm: parts per million).
Challenges in HCP Studies
Even minute quantities of Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) in the final drug can elicit immunogenic responses, necessitating their detection in both products and process intermediates.
The high heterogeneity of proteins presents significant challenges across all detection methods.
Low protein concentrations pose sensitivity challenges for detection methods.
Methods for HCP Detection, Identification, and Quantification
Various analytical techniques have been developed to comprehend the presence and abundance of Host Cell Proteins (HCPs) in biological processes.
The selection of appropriate test methods for identification and/or quantification of HCP have been a concern during process development and manufacturing. The methods used for HCP analysis can be classified as either immune-specific methods, such as, western blotting and ELISA, or non-specific methods, such as, electrophoresis and MS. In general, a qualitative or semi-quantitative method would be sufficient for sample purification and for lot release. However, during process of drug development and characterization, the ideal method not only should have the capability to recognize all HCPs species, but also should be quantitative, high-throughput, time-saving and labor-saving.
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)-Based HCP Analysis
This method is a routine approach utilized in multiple pharmacopeias for measuring total HCP concentrations. It boasts characteristics of high efficiency and convenience. ELISA is currently the most widely applied method for HCP detection. This technique is relatively simple, offers good accuracy, and allows for convenient establishment of control ranges and technical specifications.
However, in these methods, there may be instances of under-detection for non-immunoreactive or weakly immunoreactive proteins in animals. Additionally, these methods cannot be used to define the specific HCP components present.
2D-DIGE-Based HCP Analysis
This method involves the separation of HCP into individual components through gel electrophoresis, primarily enabling qualitative analysis of HCP composition.
Creative Proteomics offers the most comprehensive HCP antibody coverage analysis through the use of high-resolution large-area 2D fluorescence protein imprinting. The detection results include HCP, Western blot, and HCP/Western overlay images. The visualization of antibody coverage is achievable, a feature not attainable through other detection methods. Additionally, the calculation of HCP antibody coverage exhibits high consistency and accuracy. This method is employed for characterizing antibody coverage and detecting HCP contaminants produced during the production process of protein-based biopharmaceuticals and vaccines.
Technical Advantages
2D-DIGE HCP analysis holds significant advantages over ELISA and standard 2D protein imprinting:
High Sensitivity: The sample volume used in 2D-DIGE is much smaller than that in conventional 2D staining, making it suitable for samples with limited quantities.
Wide Dynamic Range: The high sensitivity and broad dynamic range of 2D-DIGE facilitate the detection of both high- and very low-abundance proteins, surpassing the detection range of conventional 2D methods and yielding more accurate results.
Simple Operation, High Reproducibility: Traditional 2D detection involves running two separate gels, one for staining total HCP proteins and the other for staining antibody-immune proteins, followed by a comparison of the results from the two gels. In contrast, 2D-DIGE streamlines the process onto a single gel, reducing errors arising from multiple gel runs and comparisons.
Sample Requirements
HCP Protein: Customers can provide bacterial precipitates or cells for us to extract total protein, or they can provide pre-extracted total protein. Bacterial precipitate should be no less than 1g; cell precipitate should be no less than 1x10^7 cells; protein solution or freeze-dried powder are both acceptable, with a total amount greater than 1mg and a solution concentration greater than 1ug/ul.
Antibodies: The total amount of antibodies should be greater than 50ug.
Mass Spectrometry-Based HCP Analysis
Mass spectrometry enables the detection of the presence of many proteins within the same sample. This approach provides a certain level of quantification and allows for the comparison of protein content across different samples.
LC-MS/MS, including GeLC-MS/MS proteomic analysis, can identify all proteins in a mixture, ranging from one-dimensional gel bands and immunoprecipitation (IP) samples to whole-cell lysates or tissue, making it suitable for HCP analysis. The general workflow of mass spectrometry-based HCP analysis includes: protein fractionation of protein mixtures (1D gel bands or liquid samples) based on pI or Mw (optional); reduction/alkylation and trypsin digestion of samples followed by separation via HPLC and mass spectrometry detection; database searching and identification of the obtained protein information.
Creative Proteomics employs state-of-the-art high-resolution nano liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization (nanoLC-ESI) Orbitrap mass spectrometry, enabling us to detect and characterize these low-abundance impurities with the highest accuracy.
Sample Types: Liquid samples, gel-encased samples, or IP beads can all be submitted.
Protein Amount: We recommend 5-200 µg of total protein per sample.
Protein Concentration: Sample concentration of 5-20 mg/ml is recommended.
While no single method above can accurately and efficiently determine HCP, they can be combined in various ways. For instance, combining ELISA with 2D-PAGE and utilizing immunoblotting can verify the antibody coverage in ELISA, thereby enhancing the accuracy of the ELISA method. 2D-PAGE can also be coupled with LC-MS/MS to identify specific HCP components, aiding in the identification of high-risk factors.
Comparison of Various HCP Detection, Identification, and Quantification Methods
| Analytical technologies used for monitoring and measuring HCPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aim | Analytical technique | Application | Limitations |
| Visualisation of HCPs | 2D-PAGE and 2D-DIGE | Study dynamics of HCP profile | Only most abundant proteins observed Masking effect of product Labour intensive Concerns of multiproduct assays |
| Westerm blotting | Observe HCP profile using anti-HCP sera | Labour intensive. Concems as to what is usod as the mmunogen to generate antibodies (e.g. Nul cel line host, fractionated pools?) | |
| SELDI-TOF | Rapidly monitor changes in HCP profile | No information on HCP identity | |
| Quantitation of HCP amounts | ELISA | Measure total HCP levels | No intormation on HCP dentty |
| Wostern blotting | Specific HCP levels relative to other samples | Limited comparabilty across samples | |
| FT-MIR | Quantitative determhation of HCPs Can use in situ | Limit of quantitation unknown | |
| LC-MRM | High-throughput quantification | ||
| Identification of spocific HCPs | LC-MS/MS | Can be coupled with 2D-PAGE to identify specific HCPs | Labour intensive if coupled to 2D-PAGE |
| 2D-LC/MS | Good coverago and identification possibie | Time consuming | |
| Western blotting | Confirm presence of specific HCPs | Not high throughput | |
| Expensive multiple antibodles required | |||
| Requires target to be immunogenic and antibodies present in sera to identify a specific HCP | |||
Report
A detailed technical report will be provided at the end of the whole project, including the sample preparation, experimental procedure and instrument parameters.
The stain results, protein list (FDR<1%)/and concentration/amount will be reported in the report.