Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics
Exosome untargeted metabolomics is an untargeted metabolomics technique that uses Orbitrap ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry to accurately identify metabolites in exosome samples. Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive analysis of exosome metabolites using LC-MS/MS technology.
Submit Your Request Now
×- Services
- Advantages
- Workflow
- Sample Requirements
- Applications
- FAQs
- Demo
- Case
What is Exosome
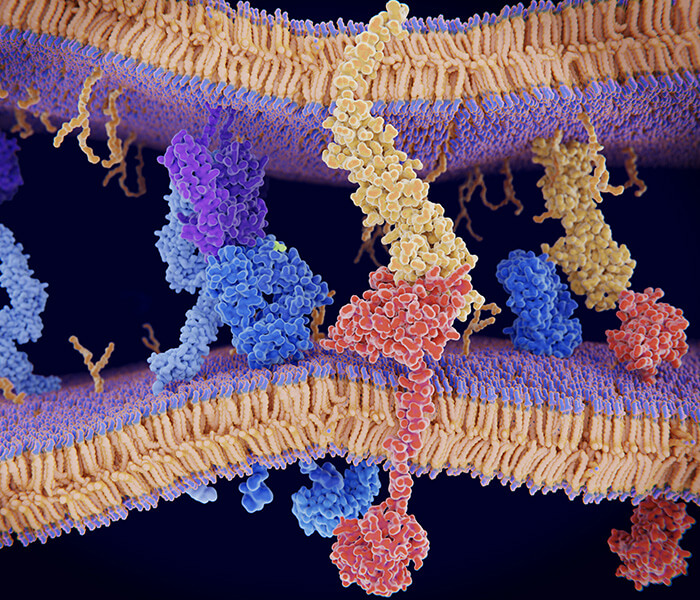
Exosomes (EX) are a heterogeneous group of extracellular vesicles (EVs) ranging in size from 40 to 160 nm. They are released by various cell types, including red blood cells, B cells, T cells, mast cells, platelets, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, adipocytes, epithelial cells, muscle cells, dendritic cells, and tumor cells. Exosomes originate from the inward budding of the endosomal membrane, forming multivesicular bodies that are released into the extracellular space through fusion with the plasma membrane. They are found in both the extracellular medium (in vitro) and body fluids (in vivo), such as blood, urine, saliva, breast milk, ascitic fluid, nasal secretions, tears, amniotic fluid, synovial fluid, lymph, cerebrospinal fluid, and semen. Exosomes play a crucial role in intercellular communication, influencing both normal and pathological conditions. They reach recipient cells in the local environment through paracrine signalling or travel to distant tissues via the circulatory system in an endocrine manner.
The metabolomics study of exosomes is relatively new, with knowledge of the metabolites in extracellular vesicles only emerging in recent years. Interest in the exosome metabolome has grown following the identification of lipids in exosomes. Subsequent studies of blood- and urine-derived exosomes have revealed a complex array of molecules.
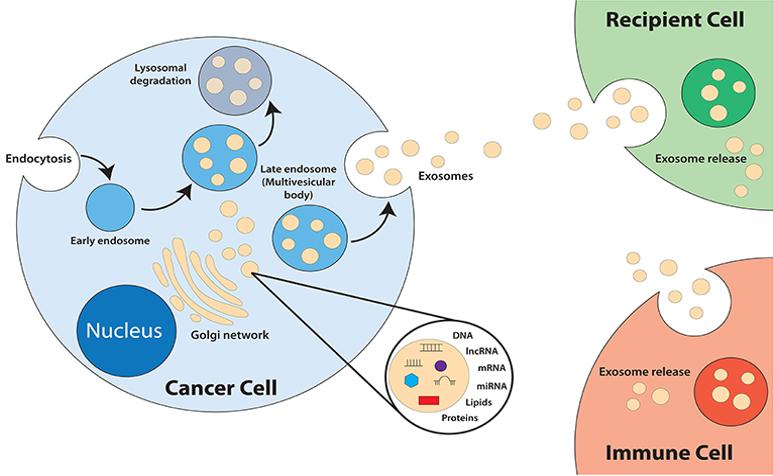 Figure 1. Cancer Exosomes. (Othman, N et al. 2019)
Figure 1. Cancer Exosomes. (Othman, N et al. 2019)
Why Need to do Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics
Although lipids are a major component of EVs, most studies on EV content focus primarily on proteins and nucleic acids. Exosome databases, such as ExoCarta, mainly catalogue proteins and RNA, leaving the study of exosome metabolomics relatively underexplored.
However, the research on exosome metabolomics is imperative: on one hand, EVs are rich in certain lipids, such as cholesterol, phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylcholine (PC), and phosphatidylinositol (PI), suggesting that EVs may serve as lipid mediators for intercellular communication. On the other hand, from both a practical and clinical perspective, studying the metabolomics of EVs isolated from biological fluids is the most appropriate approach, as the metabolome of these EVs is a treasure trove containing disease biomarkers.
Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics in Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics' exosome untargeted metabolomics service ensures the smooth progression and reliability of results through carefully designed sample submission standards and strict quality control. By employing both particle count and BCA quantification methods to set concentration gradients, the sample submission system is optimized, ensuring data quality and laying a solid foundation for the efficient and high-quality execution of metabolomics projects.
We have launched two specialized products that utilize advanced metabolites profiling services to study the metabolic composition and functions of plant root and leaf exosomes, helping to gain deeper insights into the interactions between plants and their environment, as well as their adaptive mechanisms. If you require services for other species or tissues, please feel free to contact us.
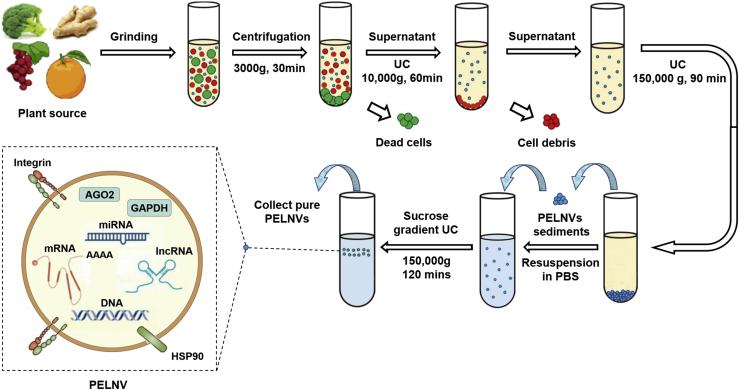 Figure 2. Isolation and preparation of plant exosom-like nanovesicles. (Dad, H. A et al. 2021)
Figure 2. Isolation and preparation of plant exosom-like nanovesicles. (Dad, H. A et al. 2021)
Exosome Isolation and Purification
We use advanced techniques like ultracentrifugation, PEG precipitation, and ultrafiltration to isolate and purify exosomes. Our customized methods ensure high purity for different types of samples.
Exosome Multi-Omics Solutions
We also offer combined multi-omics analysis, including exosome proteomics, lipidomics, and metabolomics, to give you a clearer and more complete view of exosome composition and function.
Our Advantages
- Platform Advantage: Utilizes an ultra-high resolution and ultra-high sensitivity LC-MS mass spectrometry platform, ensuring high data quality and precision.
- Technical Advantage: Capable of achieving over 700 level 1 identifications, ensuring high accuracy and reliability of the analysis results.
- Service Advantage: Equipped with a professional information analysis team, providing personalized analysis services to meet specific customer needs.
- Data Completeness: Provides detailed information on metabolites,enabling researchers to obtain comprehensive substance data and supporting in-depth analysis.
- Multi-Omics Integration: We offer a comprehensive multi-omics approach, integrating metabolomics, proteomics, and lipidomics, allowing for a more holistic understanding of biological processes and systems.
Workflow of Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics
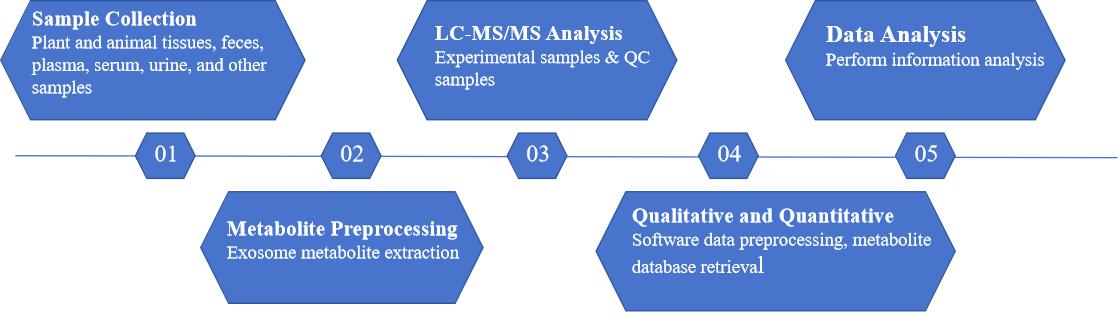 Figure 3. The workflow of exosome untargeted metabolomics.
Figure 3. The workflow of exosome untargeted metabolomics.
Technical Platforms

Thermo Q ExactiveTM series

AB Sciex 6500+

Thermo Orbitrap Fusion Lumos

Bruker timsTOF Pro
Sample Requirements
| Sample type | Recommended sample size | Pre-treatment and storage |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 100-200 mg | Snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Urine | 200-500 μL | 5000×g 4℃ Centrifuge for 30-60min, remove supernatant, store at -80℃. |
| Serum/plasma | >100 μL | Collected serum/plasma, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, bile and other body fluids | >200 μL | 4℃ Centrifuge for 10min, (or filter using 0.22μm membrane), remove supernatant and store at -80℃. |
| Suspension cells | >1*107 | Centrifuge and collect cells after liquid nitrogen snap freezing and store at -80℃. |
| Walled cells | >1*107 | Cultured walled cells are stored in 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80℃. |
| Cell supernatant | >2 mL | centrifuge at 4℃ for 3 minutes, take the supernatant and store at -80℃. |
Reports
- Experimental Procedure
- Relevant Mass Spectrometry Parameters
- Raw Data
- Metabolite Identification
- Metabolic Pathway Analysis
- Differential Metabolite Expression
- Statistical Analysis
Applications of Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics
Revealing Biological Mechanisms
Exosome metabolomics helps understand the biological processes behind things like the tumor environment, immune responses, and inflammation.
Identification of Biomarkers
Exosomal metabolites and proteins can help find biomarkers related to important biological processes, such as cell growth and immune reactions.
Investigating Therapeutic Targets
Exosome metabolomics helps find possible treatment targets and supports research on targeted drug delivery using exosomes.
Tools for Disease Risk Prediction
Exosome metabolomics helps study the risk of disease by spotting early changes in metabolism linked to chronic conditions.
Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics FAQs
Is it possible to request customized analyses or focus on specific metabolites?
Yes, customized analyses can be requested to focus on specific metabolites, pathways, or biological processes. Clients can specify their areas of interest, and the analysis will be tailored accordingly to meet those needs.
What biological processes can be explored using Exosome Untargeted Metabolomics?
This service can be used to explore a wide range of biological processes such as metabolic regulation, immune responses, tumor microenvironment interactions, inflammatory pathways, and disease progression mechanisms. It provides a comprehensive view of how exosome-derived metabolites contribute to these processes.
What support is provided after receiving the results?
After the results are delivered, a team of experts is available to assist with data interpretation, offer further analysis options, and discuss how the findings can be applied to specific research goals. Clients can receive consultations on follow-up studies or experimental design based on the results obtained.
Learn about other Q&A about other technologies.
Demo Results
Figures come from (Li, Y.et.al, Sci Rep,2023)
Case Study
Bioenergetic-active exosomes for cartilage regeneration and homeostasis maintenance
Journal: Science advances
Published: 2024
- Background
- Research Methods
- Results
- Conclusion
Cartilage is an avascular tissue with limited metabolic activity and regenerative capacity, making cartilage defects essentially irreversible. The commonly used clinical treatments for cartilage defects also have their limitations. Cartilage regeneration relies on a sufficient and sustained supply of bioenergy to promote cell differentiation and extracellular matrix synthesis. Under pathological conditions, chondrocytes often suffer from energy stress, characterized by metabolic disorders and reduced levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). However, progress in regulating the energy metabolism of cartilage regeneration remains limited to date.
Exosome Preparation and Characterization: Exosomes were extracted from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and characterized using techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and Western blotting.
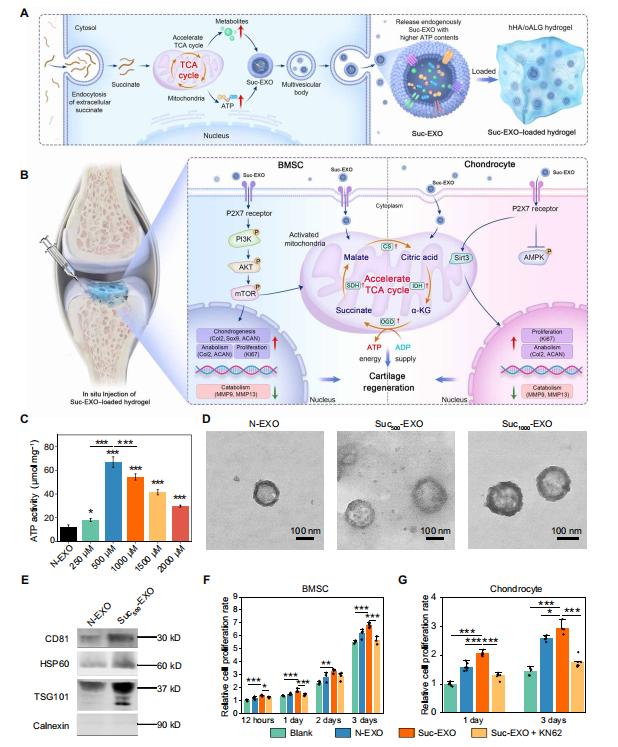 Figure 4. Preparation and characterization of bioenergetic-active exosomes. (Liu, X., et al. 2024)
Figure 4. Preparation and characterization of bioenergetic-active exosomes. (Liu, X., et al. 2024)
Metabolomics Analysis: The metabolome of the exosomes was analyzed using LC-MS to compare the metabolic differences between Suc-EXO and normal exosomes (N-EXO).
Cellular Experiments: The effects of Suc-EXO on the proliferation, migration, anti-inflammatory response, cell metabolism, and chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs and chondrocytes were evaluated.
Animal Experiments: Suc-EXO was encapsulated in injectable hydrogels and injected into a full-thickness cartilage defect model in New Zealand white rabbits. Cartilage regeneration and homeostasis maintenance were assessed through macroscopic evaluation, histological analysis, and immunohistochemical staining.
Exosome Characterization
Compared to N-EXO, Suc-EXO showed a significant increase in ATP content, with average diameters of 121.5 nm and 126.1 nm, respectively. Both exosome types expressed exosome markers CD81, HSP60, and TSG101, while the exosome-negative protein Calnexin was not detected.
Metabolomics Analysis
A total of 730 exosomal metabolites were detected, with 167 metabolites showing significant changes in Suc-EXO. These changes primarily involved the TCA cycle and amino acid metabolism pathways, indicating a significant upregulation of metabolites in the exosome energy metabolism pathways.
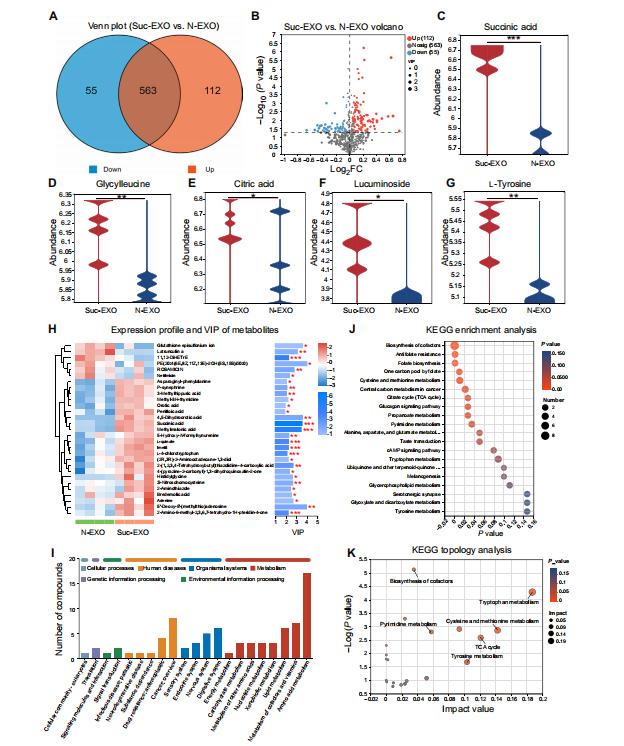 Figure 5. Exosomes metabolomic profiling of Suc-EXO versus N-EXO. (Liu, X., et al. 2024)
Figure 5. Exosomes metabolomic profiling of Suc-EXO versus N-EXO. (Liu, X., et al. 2024)
This study successfully developed a bioenergetically active exosome (Suc-EXO) that promotes cartilage regeneration and maintains cartilage homeostasis by modulating cellular energy metabolism.
Publications
Here are some publications from our clients:

- Untargeted metabolomics reveal sex-specific and non-specific redox-modulating metabolites in kidneys following binge drinking. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1530/REM-23-0005
- Comparative metabolite profiling of salt sensitive Oryza sativa and the halophytic wild rice Oryza coarctata under salt stress. 2024 https://doi.org/10.1002/pei3.10155
- Thermotolerance capabilities, blood metabolomics, and mammary gland hemodynamics and transcriptomic profiles of slick-haired Holstein cattle during mid lactation in Puerto Rico. 2024 https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2023-23878
References
- Othman, N., Jamal, R., & Abu, N. (2019). Cancer-Derived Exosomes as Effectors of Key Inflammation-Related Players. Frontiers in immunology, 10, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02103
- Dad, H. A et al. (2021). Plant Exosome-like Nanovesicles: Emerging Therapeutics and Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Molecular therapy, 29(1), 13–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.030
- Liu, X., Jiang, S., Jiang, T., Lan, Z.,et al. (2024). Bioenergetic-active exosomes for cartilage regeneration and homeostasis maintenance. Science advances, 10(42), eadp7872. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adp7872