Disulfide Bond Analysis – LC-MS/MS Mapping of Protein Disulfide Bridges
Disulfide bonds are covalent linkages between cysteine residues that stabilise protein folding and sustain biological function. In therapeutic proteins such as monoclonal antibodies, ADCs, and recombinant enzymes, accurate characterisation of disulfide bridges is recommended under ICH Q6B to confirm structural integrity.
Creative Proteomics provides disulfide bond analysis by mass spectrometry to confirm correct linkages, detect variants, and ensure product quality for research and development.
Problems We Solve
- Difficulty verifying native versus mispaired disulfide bonds
- Limited confidence in antibody disulfide mapping for regulatory filings
- Lack of high-resolution data for complex disulfide bond types
- Uncertainty in structural changes during stress, storage, or processing
Our Advantages
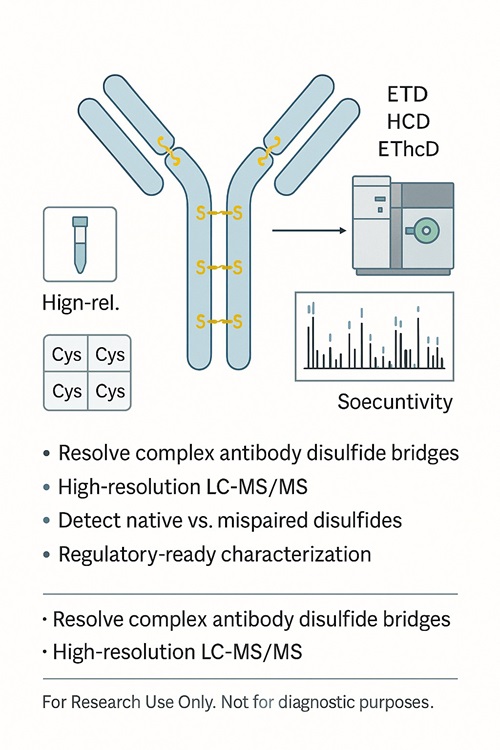
- Dual-workflow strategy (non-reducing + differential alkylation) for reliable disulfide bond mapping
- Advanced LC-MS/MS platforms with ETD, HCD, and EThcD fragmentation
- Proprietary and third-party software for accurate annotation of complex linkages
- Deliverables designed for regulatory compliance and publication readiness
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Introduction
- Challenges & Solutions
- Technical Approach
- Applications
- Practical Info
- FAQs
- Demo
- Case Study
What Are Disulfide Bonds?
A disulfide bond is a covalent bridge formed between two cysteine residues through oxidation of their thiol groups. These disulfide bridges are one of the most important Post-translational Modifications in proteins, acting as molecular stabilisers that ensure correct folding and maintain biological activity under stress conditions.
Examples of disulfide bonds in proteins:
- Antibodies: Two to three pairs in the hinge region, plus intrachain bonds in variable and constant domains, safeguard structural integrity and effector function.
- Insulin: Interchain disulfides link the A and B chains, while intrachain bonds stabilise each chain's fold.
- Growth factors and enzymes: Disulfides reinforce tertiary structures that are critical for signalling or catalytic activity.
Disulfide bond type: Bonds can form either intrachain (within the same polypeptide chain) or interchain (between different chains), both of which contribute to overall protein stability.
Salt bridge vs disulfide bond: While both act as stabilising forces, salt bridges are ionic interactions sensitive to pH, whereas disulfide bonds are covalent, more durable, and often essential for maintaining protein activity during purification, storage, or stress.
To explore the formation, biological functions, and analytical approaches for disulfide bridges in greater depth, see our resource Disulfide Bridges in Proteins: Formation, Function, and Analysis.
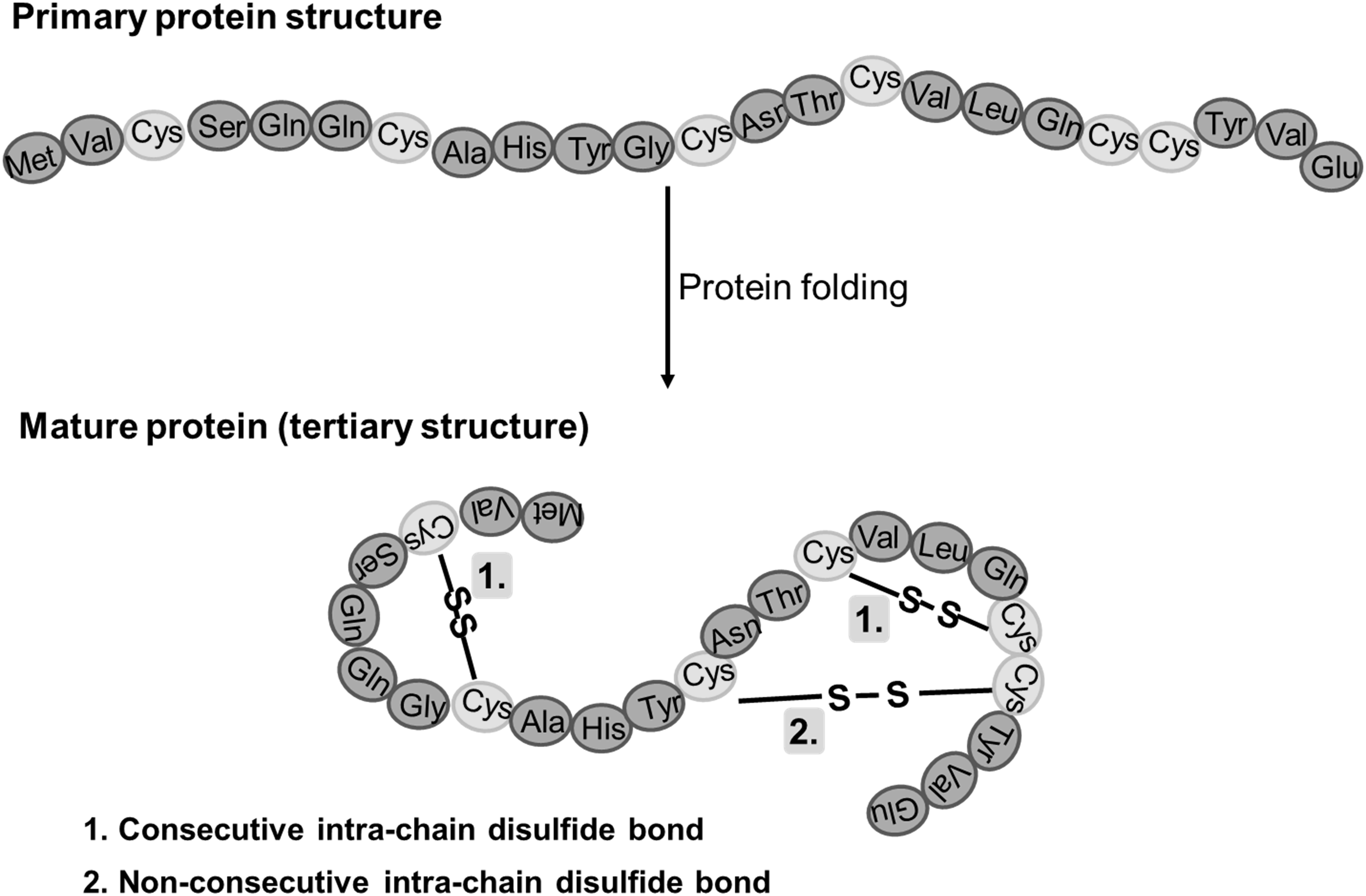 Figure 1. disulfide bonds in mature proteins
Figure 1. disulfide bonds in mature proteins
Why Disulfide Bond Analysis Matters
Disulfide bonds are not only structural stabilisers; they are also recognised as important structural features in protein drug development. Regulatory guidance such as ICH Q6B recommends confirming the number and position of disulfide linkages and free thiols when cysteine residues are present in a therapeutic protein.
When disulfide bonds are mispaired, reduced, or shuffled, the consequences can be significant:
- Drug stability issues: mispaired bonds often drive aggregation and shorten shelf life.
- Reduced efficacy: incorrect disulfide bridges may alter protein conformation and reduce binding activity.
- Increased immunogenicity risk: structural variants can trigger unwanted immune responses.
- Comparability concerns: biosimilars must demonstrate identical disulfide bond mapping to originator products.
For biopharma teams, disulfide bond mapping by mass spectrometry is therefore essential to confirm structural integrity, evaluate stability under stress, and provide regulators with reliable analytical evidence.
Current Challenges in Disulfide Bond Mapping
Although LC-MS/MS disulfide bond analysis is widely used, several technical challenges remain:
- Ambiguous annotation: Commercial tools often provide partial or unclear interpretation of MS/MS spectra for disulfide-linked peptides.
- Candidate overload: Analysts may face dozens of possible linkages, with no reliable scoring system to prioritise results.
- Complex topologies: Simple interchain bonds are easy to assign, but nested disulfides, intrachain–interchain combinations, or multi-bonded peptides ("disulfide boxes") are far more difficult.
- Manual validation burden: Reviewing spectra one by one is time-consuming and inefficient.
How do we solve it
Creative Proteomics integrates advanced LC-MS/MS workflows with customised bioinformatics pipelines to address these issues. Our proprietary annotation tools, combined with expert review, allow confident mapping of even the most complex disulfide bond types. This approach saves clients time, reduces ambiguity, and ensures high-quality evidence suitable for regulatory and research needs.
What You Get
- Complete connectivity map: intrachain & interchain bonds, including nested topologies and multi-bond "disulfide boxes."
- Variant profiling: relative levels of native vs. mispaired linkages when design allows.
- Antibody-specific views: hinge and light/heavy-chain linkages with subclass patterns.
- Audit-ready package: raw data, search settings, PSM tables, annotated MS/MS spectra, QC metrics, and a concise interpretation memo.
Our Dual-Strategy Technical Approach
Creative Proteomics applies complementary mass spectrometry–based workflows to provide high-confidence disulfide bond characterization. Our approach balances experimental robustness with regulatory needs, ensuring reliable evidence of protein connectivity.
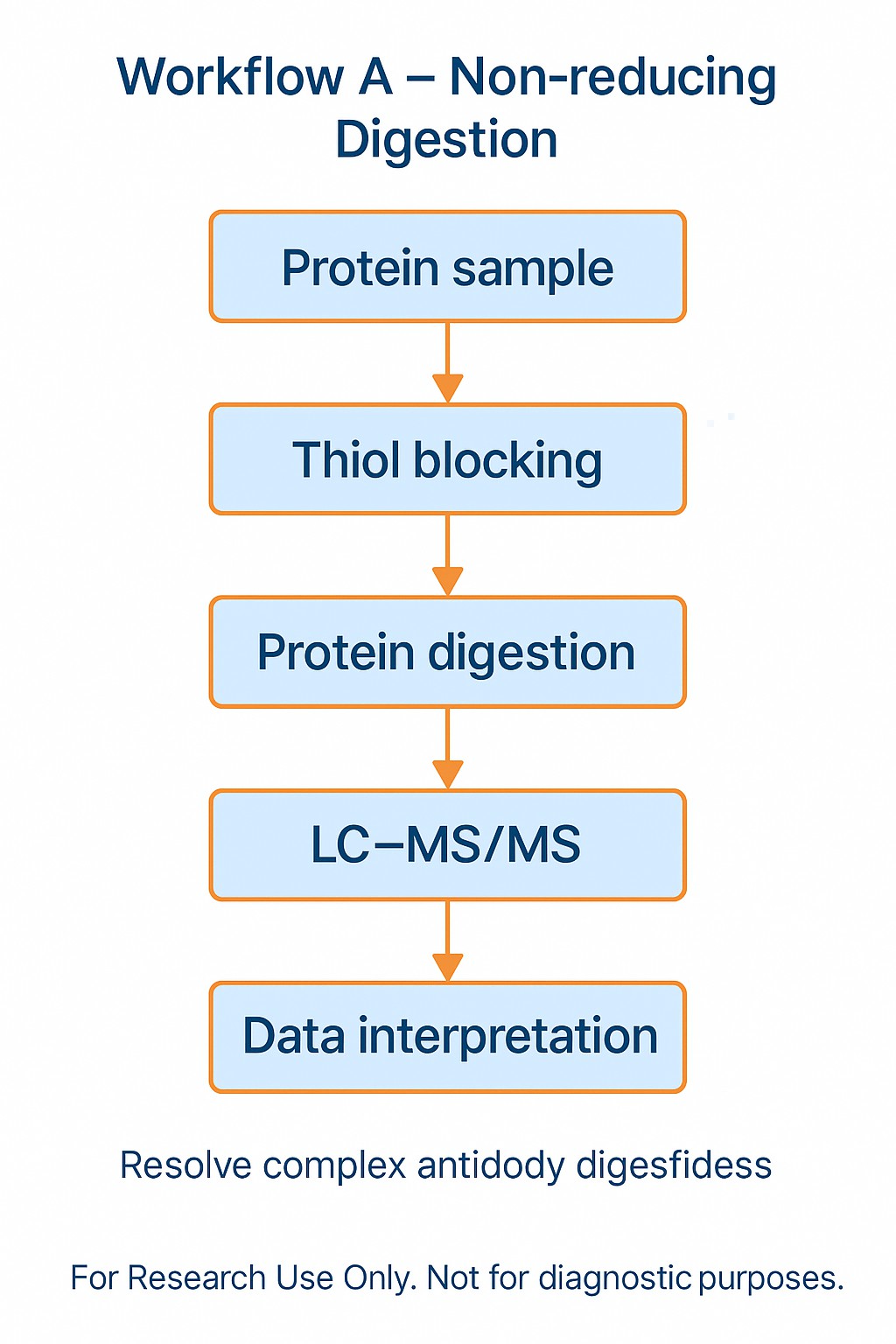
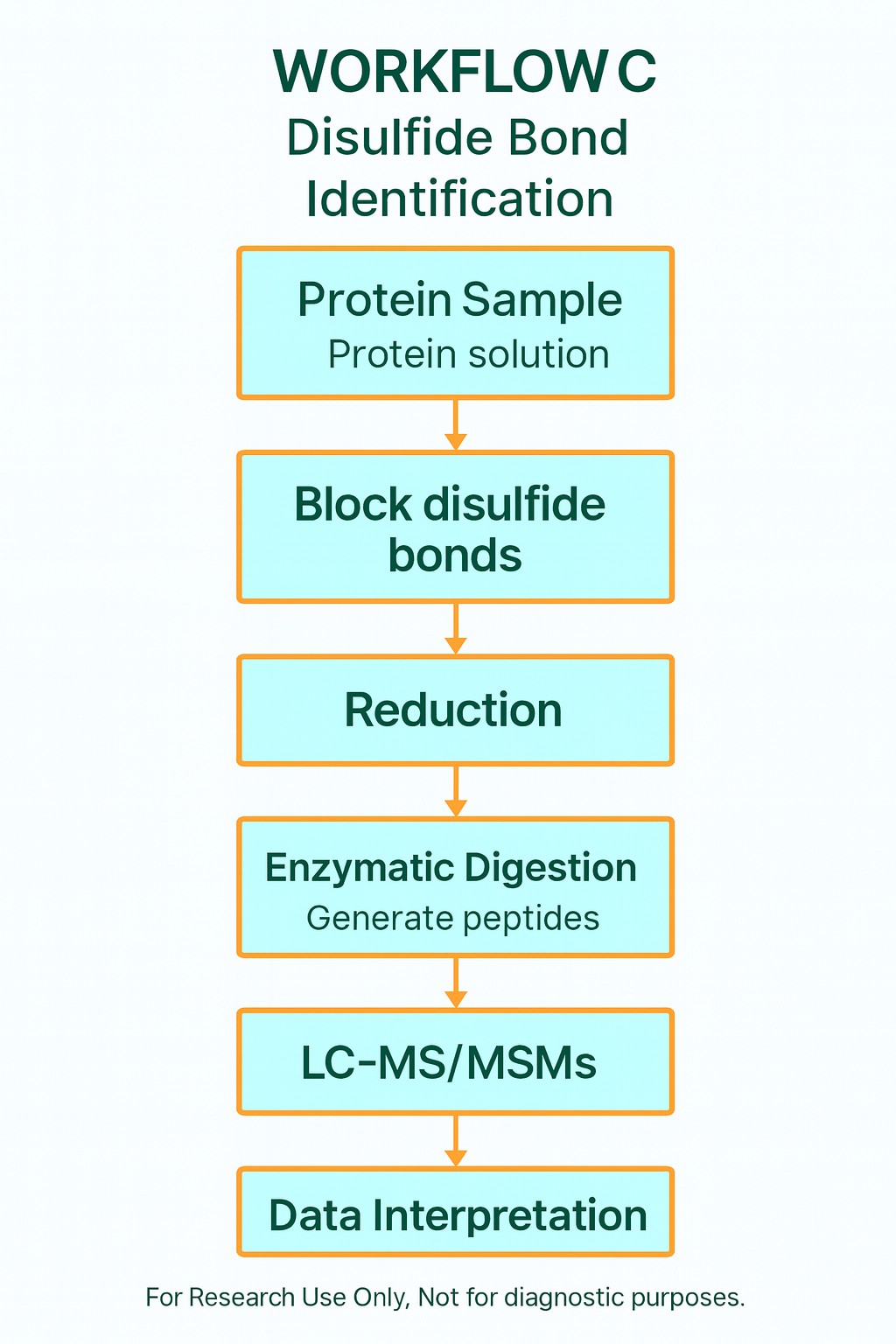
Strategy A – Non-reducing digestion
- Block free thiols immediately to prevent in-vitro scrambling.
- Perform controlled enzymatic digestion (e.g., trypsin, Lys-C, or pepsin) under non-reducing conditions.
- Map disulfide bond pairings directly by LC-MS/MS disulfide bond mapping.
- Strength: establishes exact cysteine pairings.
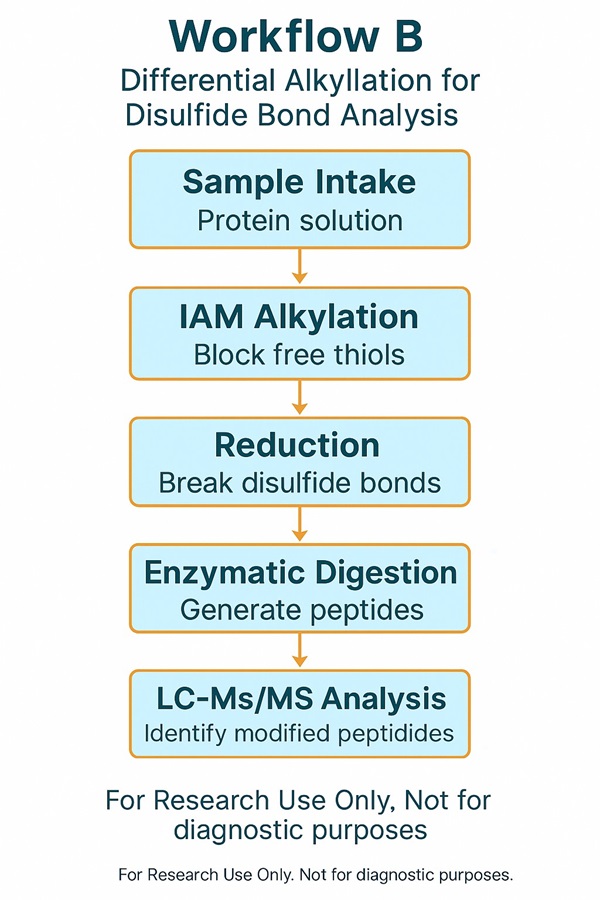
Strategy B – Differential alkylation (IAM → reduce → NEM)
- Label cysteines with iodoacetamide (IAM), reduce bonds, then re-label with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM).
- Distinguish free versus oxidised cysteines.
- Strength: clarifies which cysteine residues participate in disulfide bonds.
- Limitation: does not resolve which cysteines pair with each other.
Recommended: Combined A + B
- Apply both A and B on split aliquots.
- Provides site participation and precise pairing information.
- Recommended for regulatory filings, biosimilar comparability, and stability testing.
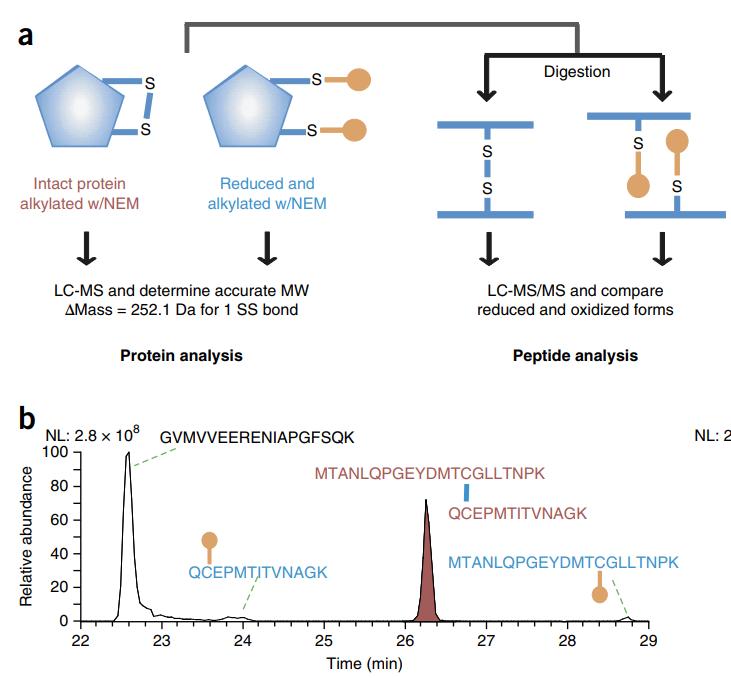
Principle of Disulfide Bond Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Our approach integrates non-reducing enzymatic digestion with high-resolution nanoLC-MS/MS detection to preserve native linkages and generate spectra that clarify both intrachain and interchain disulfide bond pairings. By combining primary and secondary MS data, we provide empirical evidence for confident assignment of disulfide connectivity.
Key strengths of this principle:
- Precision and accuracy: Accurately identifies the exact cysteine pairings while reducing false positives.
- Versatility: Suitable for diverse disulfide bond configurations, including simple, nested, and multi-bonded peptides.
- Efficiency: Streamlined pre-processing workflow minimises extra steps and improves turnaround.
Service Workflow
Project design
Define molecule class, IgG subclass (if mAb), anticipated linkages, stress/comparability goals, glycan considerations, and desired quant level.
Sample prep under controlled conditions
- Immediate free-thiol blocking to avoid in-vitro shuffling.
- pH and temperature set to minimize unintended reactivity.
- Optional deglycosylation if glycans hinder detection of S–S-linked peptides.
Orthogonal digests
- Start with a primary enzyme (e.g., trypsin) to generate tractable interchain peptides.
- Add a secondary protease if needed to expose challenging linkages without over-shortening peptides.
LC-MS/MS acquisition
EThcD-centric method with ETD/HCD support; ion mobility where beneficial.
Data analysis & curation
Disulfide-aware search; candidate ranking; spectrum-level verification; quantitative summaries of variants.
Reporting & review
Comprehensive report, raw data, annotated spectra, method details, and concise biologically-framed conclusions.
Instrumentation and fragmentation
- High-resolution LC-MS/MS platforms supporting ETD, HCD, and EThcD.
- EThcD advantage: detects both S–S cleavage and backbone ions (b/y and c/z), improving spectrum interpretability and linkage confirmation—often outperforming ETD-only for counts and per-linkage evidence density.
- Ion mobility–enabled runs optional for low-abundance disulfide peptides.
Advanced Bioinformatics (Fewer Ambiguities, Faster Decisions)
- Search with established engines for disulfide-linked peptides, plus an expert curation layer.
- Optional proprietary MS/MS annotation logic for complex, intertwined linkages (nested/intramolecular + multiple interchain bonds).
- Outputs include ranked candidates with spectrum-level evidence, targeted manual validation for critical linkages, and clear accept/reject calls.
Applications
Disulfide bond analysis supports a wide range of research and development needs in the life sciences. By combining LC-MS/MS disulfide bond mapping with tailored workflows, Creative Proteomics provides actionable insights for therapeutic development and protein characterization.
Antibody Disulfide Mapping
- Confirm correct hinge and interchain disulfide bridges in IgG subclasses (IgG1–4).
- Assess mispaired or scrambled linkages introduced during purification or low-pH viral inactivation.
- Support biosimilar comparability studies by validating identical disulfide bond patterns against originators.
Recombinant and Peptide Therapeutics
- Verify interchain and intrachain bonds in hormones such as insulin.
- Characterize cysteine-rich peptides and enzymes with complex disulfide topologies.
- Detect disulfide bond type changes introduced during refolding or formulation.
Stress and Stability Studies
- Monitor disulfide bond shuffling under thermal stress, oxidative conditions, or long-term storage.
- Differentiate true in-sample disulfide changes from artefacts introduced during sample preparation.
- Generate quantitative profiles of variant disulfide bridges for stability documentation.
Disease-Related Protein Research
- Study protein misfolding events in neurodegenerative disorders where disulfide disruptions occur.
- Investigate the role of disulfide bridges in cell-surface receptors and growth factors.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics?
Dual-workflow design: Combines non-reducing digestion and differential alkylation for the most reliable disulfide bond characterization.
Advanced mass spectrometry: Orbitrap Lumos, Orbitrap Eclipse, and Bruker timsTOF Pro with ion mobility ensure high sensitivity and resolution.
Comprehensive fragmentation strategies: ETD, HCD, and EThcD fragmentation maximize identification of complex disulfide bond types.
Expert bioinformatics pipelines: Proprietary and third-party tools (PEAKS, UNIFI, pLink-SS, SlinkS) deliver confident annotation of simple and nested disulfide bridges.
Antibody expertise: Proven ability to map hinge, variable, and constant region disulfides across IgG subclasses.
Non-antibody flexibility: Tailored solutions for insulin, cysteine-rich peptides, recombinant proteins, and enzymes.
Stress and comparability studies: Support for biosimilar development and research comparability by detecting shuffling or mispaired bonds under stress conditions.
Regulatory alignment: Data packages structured to meet ICH Q6B requirements for disulfide bond evaluation.
Publication-ready outputs: Annotated spectra, peptide-level evidence, and interpretation memos suitable for manuscripts and regulatory submissions.
Integrated PTM insights: Cross-service expertise in phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, acetylation, and redox modifications.
Sample Requirements
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Purified Protein | ≥100 µg (≥1 µg/µL, ≥80% purity) | Avoid detergents, salts, glycerol, or reducing agents (DTT, β-ME). |
| Monoclonal Antibody / ADC | ≥100 µg | Provide formulation details (buffers, stabilisers). |
| Cells | 5×10⁶ – 1×10⁷ cells | Suspension or adherent; wash to remove serum before submission. |
| Animal Tissue | 200–500 mg (soft tissue) 2–5 g (hard tissue) | Flash-freeze immediately; ship on dry ice. |
| Plant Tissue | 200 mg (leaves/flowers) 2–5 g (roots/bark/seeds) | Avoid degradation by rapid freezing. |
| Biofluids | 20–100 µL plasma/serum/CSF 3–5 mL synovial/ascitic fluid | Store at –80 °C; avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles. |
| Microbes | 50–100 µL packed cell pellet | Provide strain details and growth conditions if relevant. |
Storage & Shipping: All samples should be stored at –80 °C and shipped on dry ice. Repeated freeze–thaw cycles should be avoided to prevent artefactual disulfide scrambling.
Deliverables
- Disulfide connectivity table (cysteine pairings, peptide IDs, ppm error)
- Annotated MS/MS spectra for each disulfide bond linkage
- Variant summary (native vs. mispaired disulfide bridges)
- Method details and QC data (instrument settings, thresholds, controls)
- Interpretation memo with key findings and recommendations
FAQs
What is disulfide bond mapping by mass spectrometry and how does it work?
Disulfide bond mapping by mass spectrometry refers to the process of identifying which cysteine residues are covalently linked (disulfide bridges) using LC-MS/MS data. In this approach, proteins are digested under non-reducing conditions, preserving native disulfide bonds in crosslinked peptides. Fragmentation spectra (MS/MS) are then interpreted to match observed fragments against theoretical peptide pairs, enabling assignment of intrachain and interchain disulfide bond types.
Why is annotation of MS/MS spectra for disulfide-linked peptides so challenging?
The major difficulty lies in interpreting MS/MS data for crosslinked peptides: commercial tools often yield ambiguous annotations, especially when multiple candidate linkages are possible. Common tools struggle with complex topologies such as nested disulfides or multi-bond "disulfide boxes." Moreover, many candidate peptides must be manually vetted because scoring systems lack discrimination, making high-confidence identification laborious. (See supporting discussion in mass-spec literature.)
How do you distinguish native disulfide bonds from artefacts or scrambling during sample prep?
We minimise artefacts by immediately blocking free thiols following sample receipt, controlling pH and temperature during digestion, and employing dual-workflow strategies (non-reducing plus differential alkylation). This approach limits in vitro scrambling and helps confirm which disulfide linkages reflect the original protein's state.
Can your service detect mispaired or shuffled disulfide bonds under stress or processing conditions?
Yes. Using sensitive LC-MS/MS acquisition and our annotation pipeline, we detect both native and variant disulfide bonds. By comparing stressed vs control samples, we quantify shifts in disulfide bond prevalence and identify mispairing events.
Do glycans near cysteines interfere with disulfide bond mapping?
They can. Glycosylation adds mass heterogeneity and can reduce peptide ionization or fragmentation quality. In cases where glycans are close to disulfide-linked cysteines, we may recommend deglycosylation or tailored digestion to reduce interference—while preserving disulfide integrity.
What sample quality and amount do you require?
We typically require ≥ 100 µg of purified protein at ≥ 1 µg/µL concentration and ≥ 80% purity to ensure sufficient signal and clean spectra for disulfide bond mapping. Lower amounts may still be feasible with customised protocols.
Why choose Creative Proteomics for disulfide bond characterization?
Because we combine advanced instrumentation (ETD, HCD, EThcD fragmentation), dual-workflow design, and expert curation with custom software tools. We excel in resolving complex disulfide topologies, flagging ambiguities, and delivering audit-grade results suitable for publication and regulatory use.
Learn about other Q&A.
Demo
The specimens under investigation comprise either protein or peptide samples, with emphasis on gauging the molecular weight of the peptide molecule encompassing disulfide bonds. The determination entails discerning both the amino acid sequence and the specific disulfide bond pairing arrangement within said peptide entity.
Case Study: Streamlining the Characterization of Disulfide Bond Shuffling and Protein Degradation in IgG1 Biopharmaceuticals Under Native and Stressed Conditions

Journal : Front Bioeng Biotechnol
Published: 2022
- Background
- Experimental Protocol
- Results
- Conclusion and Discussion
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) have been shown to negatively impact the efficacy and safety of proteins by altering their native conformation, stability, target binding, and pharmacokinetics. The formation of disulfide bonds aids in proper protein folding and contributes significantly to normal protein function. Disulfide bond mispairing, however, can reduce drug stability, decrease efficacy, and increase immunogenicity. Therefore, regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH designate disulfide bonds as critical quality attributes (CQAs) in biopharmaceuticals, with ICH also noting disulfide bond mispairing as a common mechanism of protein degradation.
This study investigates changes in disulfide bond mispairing ratios of monoclonal antibodies during stress stability using LC-MS/MS. The research combines results from comparative size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and SDS-PAGE to characterize the degradation trend of biopharmaceuticals. This research offers a standardized workflow for biopharmaceutical companies and regulatory agencies, providing direction for the identification and quantification of disulfide bonds and mispairing in biopharmaceuticals.
The batches of samples, including Rituximab Originator (Rit OR), Rituximab Biosimilar (Rit BS), Bevacizumab Originator (Bev OR), and Bevacizumab Biosimilar (Bev BS), were divided into three portions each. One portion served as a control, while the other two portions were separately incubated at 37°C and 240rpm for 2 weeks and 4 weeks. After denaturation and NEM blocking at all time points, enzymatic digestion was performed using Trypsin Platinum and rLys-C under pH=5.4 conditions. LC-MS analysis, utilizing the Byos Disulfide Bond workflow, was conducted to assess and quantify disulfide bond mispairing. Verification was accomplished through complementary SEC and SDS-PAGE analyses.
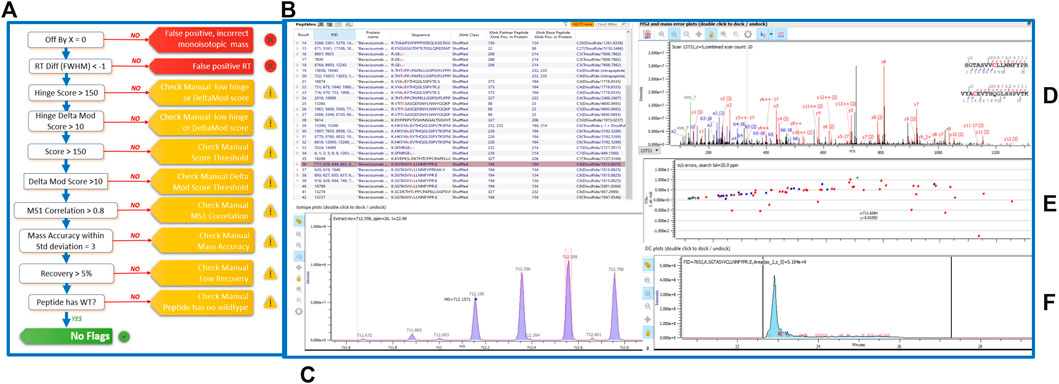 Figure 2: Disulfide bond analysis conducted using the Byos Disulfide Bond workflow.
Figure 2: Disulfide bond analysis conducted using the Byos Disulfide Bond workflow.
LC-MS Findings: Initially, all four sample batches exhibited low levels of disulfide bond mispairing. Generally, both the originator and biosimilar forms of the two monoclonal antibodies displayed a gradual increase in disulfide bond mispairing under the aforementioned stress conditions over time. The specific observations are as follows:
Rituximab Originator: Disulfide bond mispairing increased from 0.24±0.21% (baseline) to 0.51±0.11% (4 weeks).
Rituximab Biosimilar: Disulfide bond mispairing increased from 0.27±0.07% (baseline) to 0.36±0.08% (4 weeks).
Bevacizumab Originator: Disulfide bond mispairing increased from 0.58±0.08% (baseline) to 1.46±1.10% (4 weeks).
Bevacizumab Biosimilar: Disulfide bond mispairing decreased from 1.62±0.78% (baseline) to 1.10±0.50% (2 weeks), then increased to 1.25±0.20% (4 weeks). The abnormal intermediate increase could possibly be attributed to factors such as small sample size, which may not align with the SEC and SDS-PAGE test results.
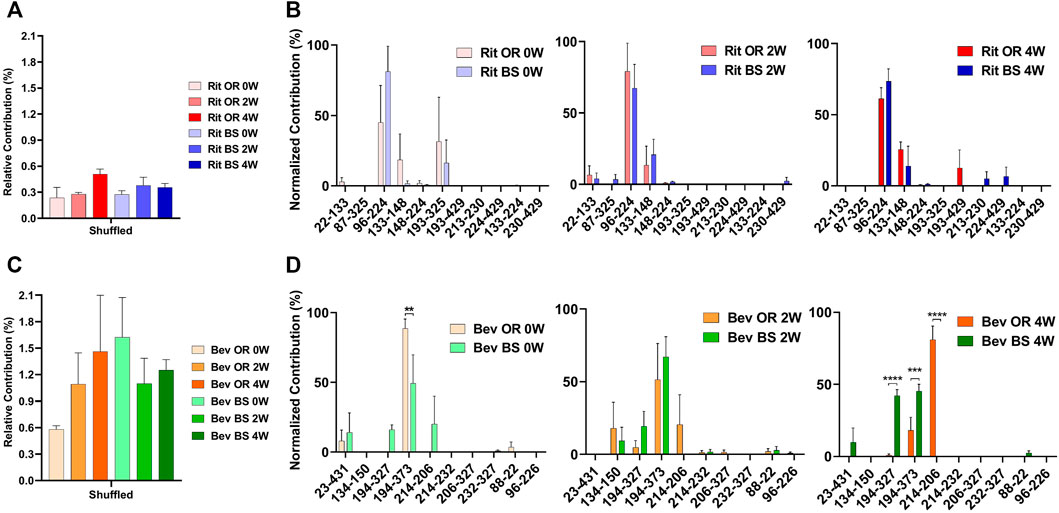 Figure 3: Disulfide Bond Mispairing Results Compilation
Figure 3: Disulfide Bond Mispairing Results Compilation
SEC and SDS-PAGE Results: Under the aforementioned stress conditions, SEC analysis revealed a degradation trend over time in all four sample batches. However, the distinction lies in the observed formations – Rituximab resulted in fragmentation, whereas Bevacizumab formed aggregates. This trend was further substantiated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis patterns.
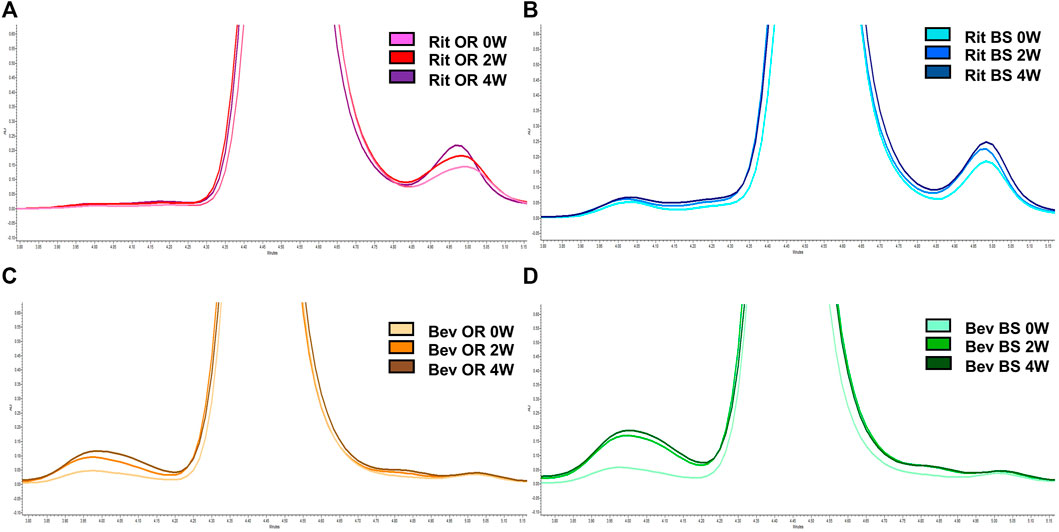 Figure 4: Representative SEC chromatograms
Figure 4: Representative SEC chromatograms
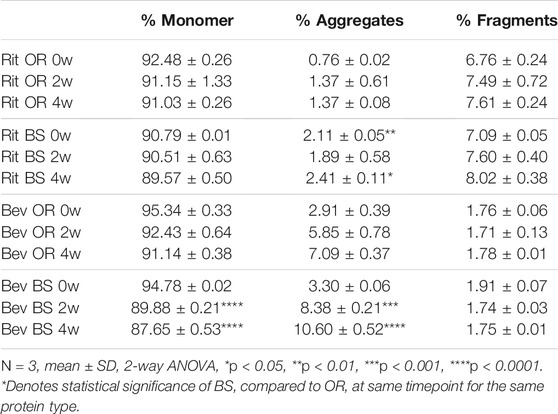 Table 1: SEC data
Table 1: SEC data
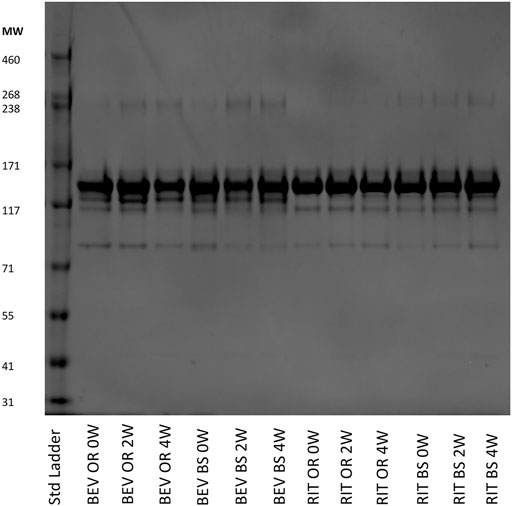 Figure 5: SDS-PAGE results
Figure 5: SDS-PAGE results
Through the implementation of stress conditions at 37°C and 240rpm, the authors comprehensively assessed the alterations in two IgG1 monoclonal antibodies, both originator and biosimilar versions, using a tri-dimensional approach encompassing LC-MS/MS, SEC, and SDS-PAGE. The observed congruence between the trends in disulfide bond mispairing and degradation suggests a potential correlation, thereby offering insights into the identification, characterization, and quantification of protein disulfide bonds.
Our PTMs Review
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Title: In Vitro Identification of Phosphorylation Sites on TcPolβ by Protein Kinases TcCK1, TcCK2, TcAUK1, and TcPKC1…
Journal: Microorganisms (2024)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050907 - Title: Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Regulate the Fate and Function of T-Lymphocyte Via Reprogramming Lipid Metabolism
Institution: Saint Louis University (Dissertation, 2023)
Link: https://search.proquest.com/openview/8ee9ca786d08344a371a238fa15f7375 - Title: Exploratory phosphoproteomics profiling of Aedes aegypti Malpighian tubules during blood meal processing…
Journal: PLOS ONE (2022)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0271248 - Title: The Interplay between GSK3β and Tau Ser262 Phosphorylation during the Progression of Tau Pathology
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2022)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911610
References
- Bošnjak I, Bojović V, Šegvić-Bubić T, et al. Occurrence of protein disulfide bonds in different domains of life: a comparison of proteins from the Protein Data Bank. Protein engineering, design & selection, 2014, 27(3): 65-72.
- Coghlan J, Benet A, Kumaran P, Ford M, Veale L, Skilton SJ, Saveliev S, Schwendeman AA. Streamlining the Characterization of Disulfide Bond Shuffling and Protein Degradation in IgG1 Biopharmaceuticals Under Native and Stressed Conditions. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 14;10:862456. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.862456. PMID: 35360407; PMCID: PMC8963993.