Pull-Down Assay Service
Struggling with non-specific binding, low-abundance interactors, or inconclusive IP results? Our customizable pull-down assay service combines optimized enrichment strategies with high-resolution mass spectrometry to deliver the interaction evidence you actually need—quantified, annotated, and ready for publication.
Why Choose Our Pull-Down Assay Platform?
- Bait types supported: protein, RNA/DNA, small molecules, lipids
- Multiple quant options: label-free, TMT, PRM, MRM
- MS-based precision: FDR ≤ 1%, CV ≤ 10%, LOD in fmol range
- Controls built in: tag-only, beads-only, competition validation
- Deliverables ready for Methods sections, figures, and reviewers
Plan your pull-down with confidence—from sample to interactome.
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You Will Receive
- Raw Data Files: .raw, .wiff, plus converted .mzML
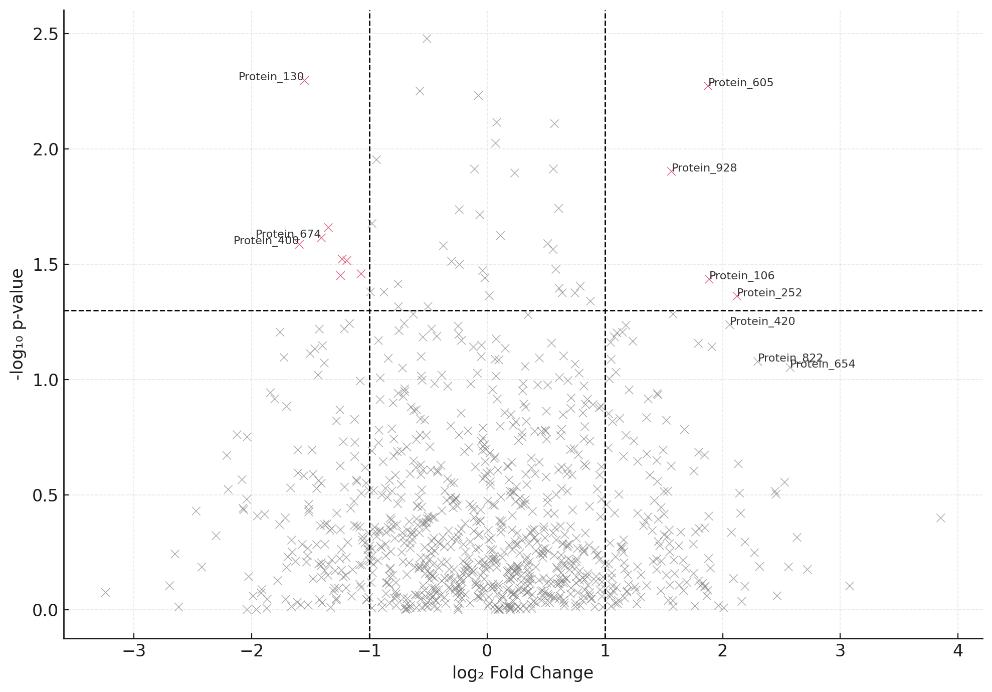
- Processed Tables: Interactor lists with fold change, p-values, FDR annotations
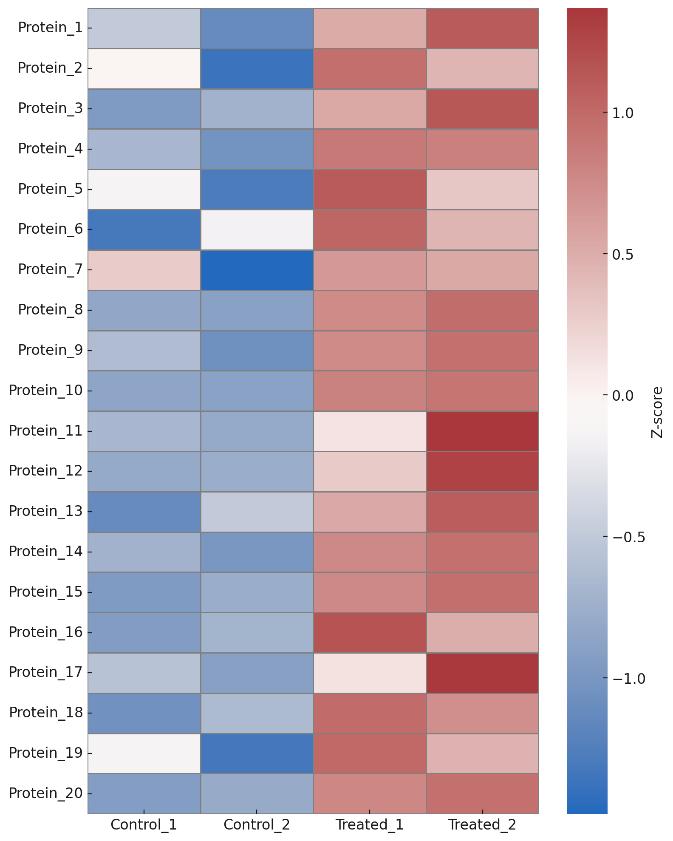
- Statistical Plots: Volcano plot, heatmap, enrichment charts
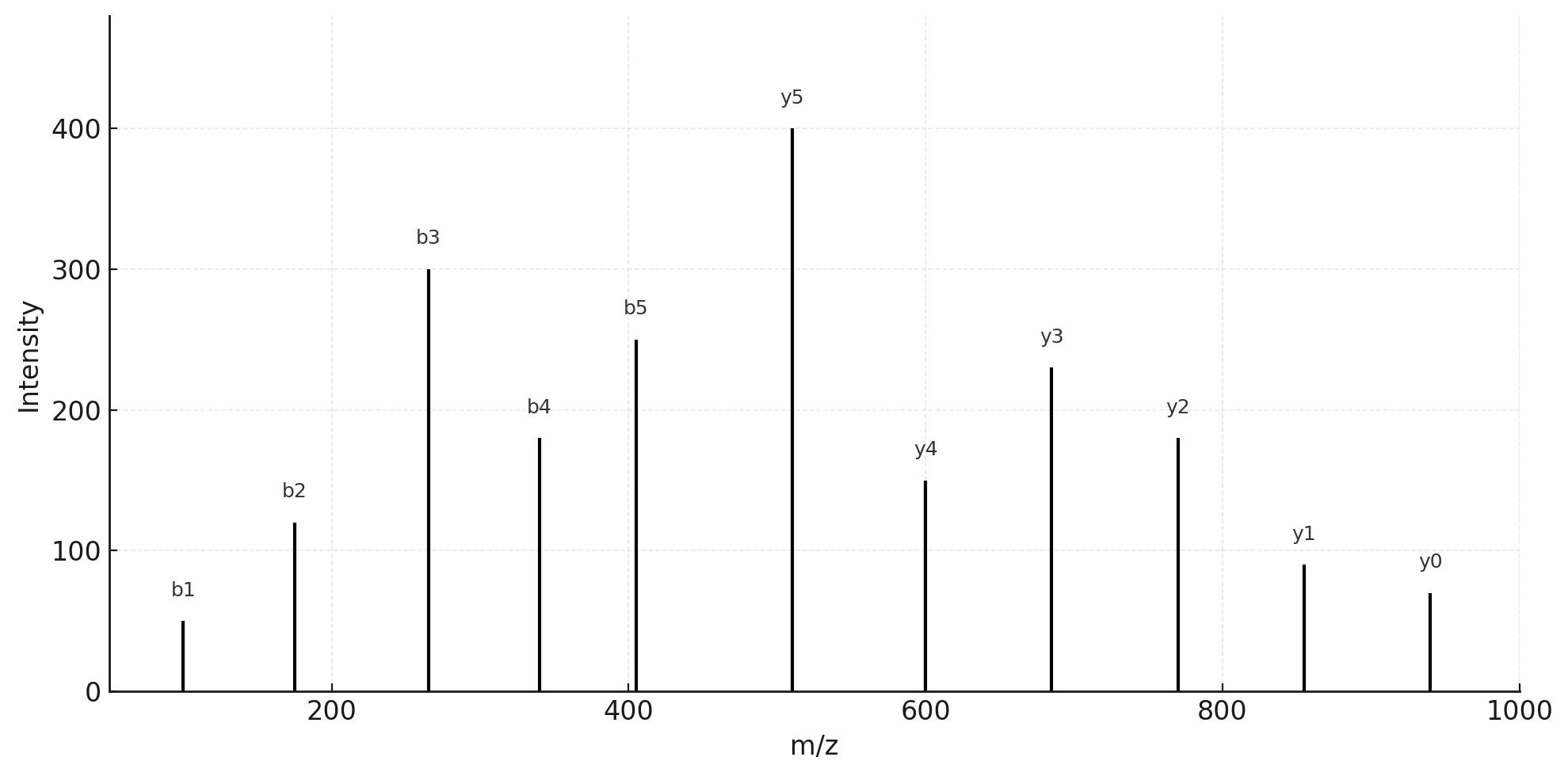
- MS/MS Spectra: Annotated fragment maps for top candidates
- Validation Options: PRM/MRM or Western blot (if requested)
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Workflow
- Methods
- Sample Requirement
- Data Analysis
- FAQs
What Is a Pull-Down Assay and Why It Matters?
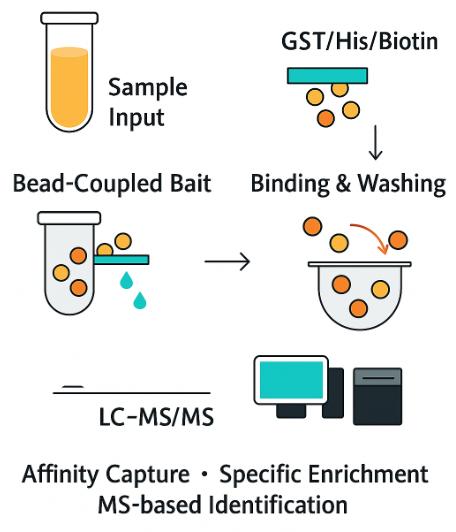
A pull-down assay is a biochemical technique used to isolate and identify interacting molecules, typically proteins, that bind to a specific "bait" molecule. The bait could be a tagged protein, biotinylated RNA, DNA, a small molecule, or lipid motif. Once the bait is immobilized on a solid support (e.g., beads or plates), any interacting molecules (referred to as "preys") are captured, washed, and then identified, often through mass spectrometry (MS).
When performed with appropriate controls and optimized protocols, pull-down assays deliver reliable, high-confidence interaction data, which is critical for understanding cellular mechanisms. This method is widely used in various research areas, including:
- Protein–Protein Interactions (PPIs): Mapping complex networks of proteins that cooperate within cellular processes.
- Ligand–Target Interactions: Investigating small molecules, drugs, or chemical probes and their binding partners.
- RNA/DNA–Protein Interactions: Studying how nucleic acids interact with proteins, especially in regulatory processes.
- Membrane-Binding Studies: Identifying lipid-binding proteins or enzymes involved in membrane trafficking.
The pull-down assay is indispensable in understanding complex biological systems, advancing research in areas such as drug discovery, biomarker identification, and cellular signaling. By isolating specific interactions, it enables a deeper understanding of how molecular networks function within the cell, facilitating targeted therapeutic approaches.
Pull-Down Assay Service Modules We Offer
Protein–Protein Interaction (Co-IP / AP–MS)
- Capture native or recombinant complexes using GST, His, FLAG, HA, or biotin tags
- Adjustable wash stringency tiers to balance specificity and yield
- End-to-end support from bait validation to MS-based interactor profiling
Small Molecule / PROTAC / Fragment-Based Pull-Down
- Covalently couple compounds to solid supports via amine/NHS or alkyne/click chemistries
- Include competitive elution to confirm binding specificity
- Ideal for chemoproteomics, target deconvolution, or hit validation
- Use biotinylated oligos, structure-stabilized aptamers, or motifs
- Optional RNase/DNase protection strategies
- Scrambled/mutant sequence controls to verify sequence specificity
Lipid or Membrane-Targeted Pull-Down
- Employ lipid-coated beads, liposomes, or nanodiscs
- Enrich lipid-binding proteins or membrane-associated complexes
- Compatible with detergents and membrane mimetics
Crosslinking-Assisted Capture
- Stabilize weak or transient interactions using MS-compatible crosslinkers (e.g., DSSO, BS3, DSP)
- Applicable to dynamic complexes or interaction time-course studies
- Combine with label-free or TMT quantification for comparative analyses
Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Readouts
- Label-Free Quantification (LFQ): For simple comparisons and pilot studies
- TMT/iTRAQ Multiplexing: For multi-condition, high-throughput workflows (up to 18-plex)
- Targeted Validation: Confirm top hits using PRM (Orbitrap) or MRM (Triple Quad)
- Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA): For robust, reproducible depth across samples
When to Choose Each Pull-Down Modality
- Tagged bait available, unknown partners: Protein–protein pull-down with tag-only and beads-only controls.
- Validating a chemical series: Small-molecule pull-down with competition elution and PRM/MRM confirmation.
- Mapping sequence-specific binders: RNA/DNA pull-down with scrambled or mutated controls to quantify specificity.
- Suspected membrane/lipid interfaces: Lipid pull-down with nanodisc or liposome scaffolds and mild detergents.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics for Pull-Down Assays
- High Confidence Identification: Protein- and peptide-level FDR ≤ 1% with decoy validation.
- Quantitative Precision: Typical intra-run CV ≤ 10% and inter-run CV ≤ 15% for reporter or LFQ intensities (technical replicates).
- Sensitivity & Dynamic Range: LOD in single-digit fmol per injection; >5 orders of magnitude usable dynamic range.
- Specific Enrichment: Competitor or tag-only controls routinely achieve ≥10× median enrichment for true interactors versus background.
- Recovery: On-bead or in-gel workflows tuned for ≥80% peptide recovery on complex matrices (representative panels).
- Reproducible Prioritization: Effect-size ranking with adjusted p-values and shrinkage estimators to minimize false positives.
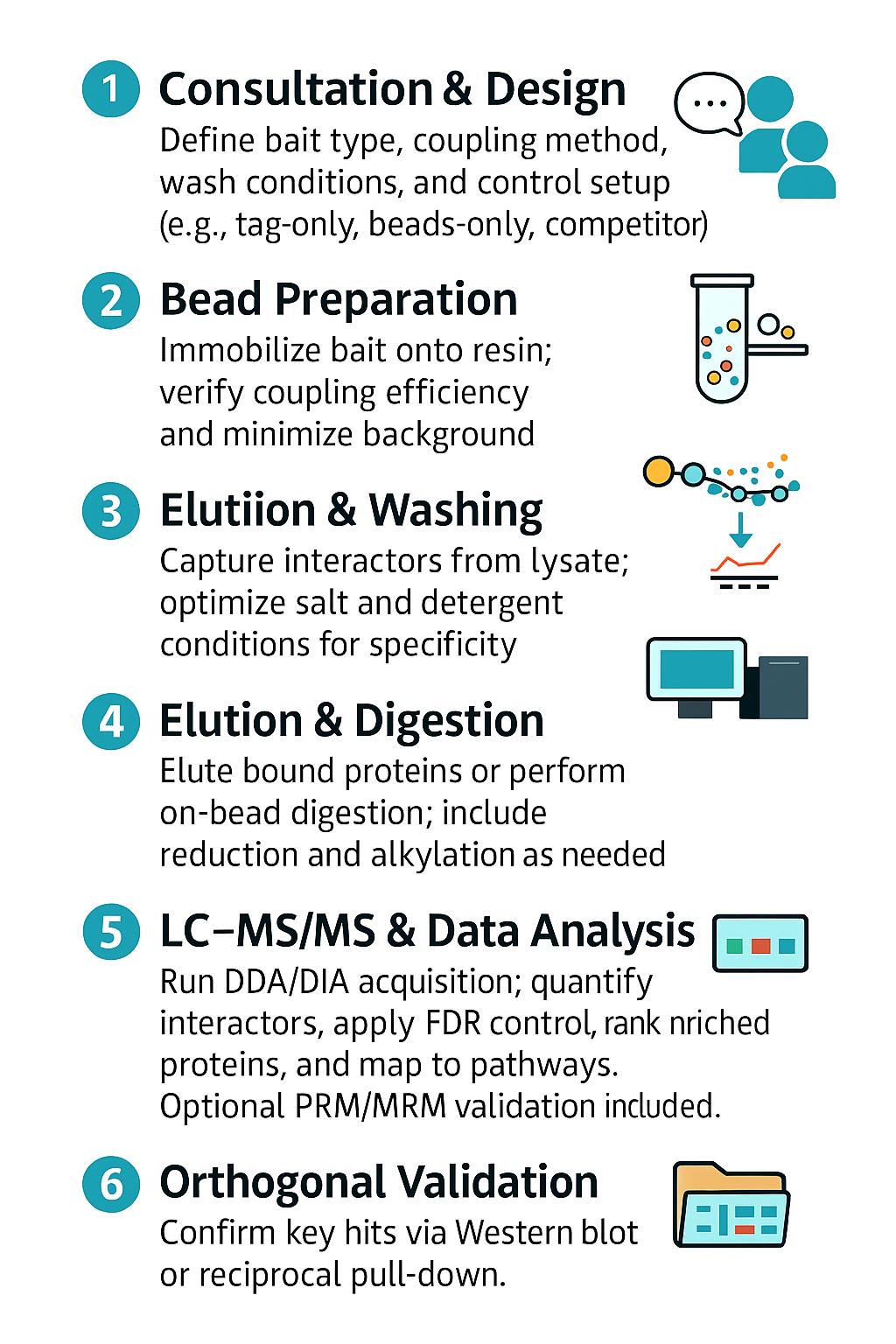
Workflow for Pull-Down Analysis
1. Consultation & Experimental Design – Define bait type, coupling strategy, wash stringency tiers, and control architecture (beads-only, tag-only, competition).
2. Bead Preparation & Coupling – Immobilize bait or prepare tag-specific resin; confirm coupling efficiency and leachate background.
3. Binding & Wash Optimization – Pilot capture from representative lysate; titrate salt/detergent to balance specificity and sensitivity.
4. Elution & Proteolysis – Competitive elution or denaturing elution; on-bead or in-solution digest with reduction/alkylation.
5. LC–MS/MS Acquisition – Discovery (DDA/DIA) plus optional targeted PRM/MRM for key interactors.
6. Bioinformatics & Prioritization – FDR-controlled IDs, differential enrichment, interactome ranking, and pathway network views.
7. Orthogonal Validation (Optional) – Western blot of sentinel interactors, reciprocal pull-down design, or peptide-level PRM/MRM panels.
8. Delivery – Raw files, processed tables, QC metrics, effect-size plots, and method details suitable for Methods sections.
Methods & Instrumentation Used for Pull-Down Analysis
Affinity Reagents & Coupling
Beads & Resins: Magnetic agarose beads (Ni-NTA, glutathione, streptavidin, anti-FLAG/HA)
Tag Types Supported: His, GST, FLAG, HA, biotin
Coupling Chemistries: NHS-ester, epoxy, amine-reactive for small molecule or synthetic bait immobilization
Controls: Beads-only, tag-only, scrambled bait, or competitor-ligand for specificity filtering
Binding & Washing
- Adjustable salt/detergent concentrations to optimize stringency
- On-bead blocking and competitor strategies to reduce background
LC–MS/MS Analysis
Thermo Orbitrap Eclipse / Exactive HF-X
- MS1 resolution: up to 120,000 (m/z 200)
- HCD fragmentation, mass accuracy ≤ 3 ppm
Label-Free Quantification (LFQ) or TMT (up to 18-plex) for relative quantitation
Targeted PRM (Orbitrap) or MRM (Triple Quad 6500+) for validation of selected hits
Data Processing & Interpretation
- FDR ≤ 1% at protein/peptide level (decoy-based)
- Differential enrichment analysis with effect size and p-value ranking
- Functional annotation via GO, KEGG, and PPI network visualization

Q Exactive HF-X MS (Figure from Thermo)

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)
Sample Requirements for Pull-Down Assay Analysis
| Material / Use Case | Minimum Amount | Preferred Format | Buffer Constraints (at binding) | Additives Tolerated | Required Controls | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purified protein bait (GST/His/FLAG/HA/biotin) | ≥ 50 µg | ≥ 0.2 mg/mL, neutral pH | Salt ≤ 300 mM; avoid > 0.1% SDS or > 0.5% deoxycholate | ≤ 0.1% NP-40/Triton; glycerol ≤ 10% | Tag-only and beads-only | Provide tag sequence and any fusion partners |
| Whole-cell or tissue lysate (for protein–protein) | 1–5 mg total protein | Clarified, DNase-reduced | Salt ≤ 300 mM; imidazole ≤ 10 mM for His workflows | Protease/phosphatase inhibitors allowed | Beads-only + mock bait | Indicate lysis detergents; we can adapt wash tiers |
| Biotinylated RNA (RNA pull-down) | ≥ 1 µg | RNase-free, folded if needed | Mg²⁺/K⁺ as required; avoid strong chaotropes | Mild heparin or tRNA block optional | Scrambled-sequence or unlabeled RNA | Provide secondary-structure info if available |
| Biotinylated DNA / motif probes | ≥ 0.5 µg | DNase-free | Monovalent salt ≤ 300 mM | Poly(dI•dC) optional block | Scrambled or mutated motif | State strand and biotin position |
| Small molecule (ligand immobilization) | 0.5–1 mg | DMSO or dry solid | Provide amine/azide/alkyne handle or linker map | DMSO usable during coupling | Competitor at equimolar excess | We can propose linker and coupling chemistry |
| Lipid motif / membranes | Consult | Lipid stock or vesicles | Detergent-compatible resins available | Mild zwitterionic detergents | Beads-only + non-binding lipid | Nanodisc or liposome formats supported |
General notes
- Please supply complete buffer recipes and any instability flags (e.g., metal sensitivity, redox reactivity).
- Avoid cross-linking agents in the final binding step unless coordinated; residual crosslinker can bias enrichment.
- Ship on cooling media appropriate for biomolecule stability; include SDS-PAGE snapshot or A280/fluorometric quant when possible.
Demo Results
Use Cases for Pull-Down Assays
Validate Predicted Interactions
Confirm physical binding between candidate molecules (e.g., domain–ligand, mutant vs. wild-type). Use as biochemical proof for model hypotheses.
Detect Condition-Specific Binding
Compare interactors under different stimuli, timepoints, or treatments. Quantify changes with LFQ or TMT labeling.
Study Non-Protein Targets
Capture protein partners of RNA, DNA motifs, or lipids using biotinylated or immobilized baits. Map regulation beyond protein–protein networks.
Filter Non-Specific Background
Use tag-only, beads-only, or competitor controls to distinguish true interactors from matrix noise or sticky proteins.
Build Interaction Networks
Define high-confidence interactomes for pathway reconstruction, functional annotation, or systems modeling.
FAQ of Pull Down Assay
What problems can pull-down assays solve that co-IP or yeast two-hybrid can't?
Pull-down assays offer tag- or chemistry-defined capture under tunable buffer conditions, making them better suited for identifying direct or near-direct interactors, detecting weak/transient bindings, and avoiding antibody dependence. Unlike co-IP, they allow precise control over background subtraction and bait immobilization.
How should I choose between label-free, TMT, PRM/MRM, or DIA quantification for my experiment?
Use label-free for flexible discovery workflows and cost efficiency, TMT for high-throughput multi-group comparisons, PRM/MRM for targeted validation of specific candidates, and DIA when cross-run reproducibility and deep proteome coverage are priorities.
What types of controls are necessary to confidently interpret enrichment results?
A minimum control set should include tag-only, beads-only, and a competition or mutant control. These help distinguish specific interactors from non-specific matrix binders and resin stickiness. Mock lysate controls are also recommended for background profiling.
How can I reduce non-specific binding without losing true weak interactors?
Optimize salt and detergent concentration to maintain specificity while preserving labile interactions. Blocking strategies using BSA, tRNA, or non-specific IgG can reduce noise. Avoid over-washing and favor competitive elution when possible.
What are the most common reasons pull-down assays fail or yield low confidence data?
Inadequate bait coupling, low sample concentration, incompatible buffer additives (e.g., high SDS or urea), or omission of proper controls can compromise data quality. Suboptimal wash conditions may either suppress weak interactors or inflate background noise.
Should I perform elution under native or denaturing conditions? On-bead or in-solution digestion?
Native (competitive) elution preserves interaction profiles and is ideal for quantitative analysis. Denaturing elution increases recovery but may introduce background. On-bead digestion reduces losses from cleanup steps, while in-solution digestion improves peptide purity.
How are "significant interactors" defined in pull-down data?
Typically based on fold-change thresholds combined with adjusted p-values (e.g., FDR ≤ 1%). Additional filtering may include replicate consistency and biological relevance (e.g., known complex membership or pathway annotation).
What orthogonal validation methods are recommended for top hits?
Reciprocal pull-down, tag swap experiments, targeted PRM/MRM, and Western blotting of sentinel interactors. These approaches help distinguish biologically relevant interactions from statistical outliers.
Can I use pull-down assays to study RNA-binding, DNA-binding, or lipid-binding proteins?
Yes. Biotinylated nucleic acids or lipids can be immobilized for capture. When combined with proper controls (e.g., scrambled/mutant sequences, non-binding lipids), this approach enables identification of nucleic acid- or membrane-interacting proteins.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Regulation of toxic shock syndrome toxin‐1 by the accessory gene regulator in Staphylococcus aureus is mediated by the repressor of toxins. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14353
- Mechanistic and biomarker studies to demonstrate immune tolerance in multiple sclerosis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.787498
- Trypanosoma cruzi DNA Polymerase β Is Phosphorylated In Vivo and In Vitro by Protein Kinase C (PKC) and Casein Kinase 2 (CK2). 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223693
- In vitro assays reveal inherently insecticide-tolerant termite symbionts. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1134936
- Parkinson’s disease-associated LRRK2-G2019S mutant acts through regulation of SERCA activity to control ER stress in astrocytes. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.03.738