Animal Hormones Analysis Service
Protein and peptide hormones, such as those from the hypothalamus, pituitary, and pancreatic islets, are analyzed with ELISA Kits. Steroid and amino acid-derived hormones are detected via LC-MS/MS, allowing simultaneous analysis of multiple targets. These methods support research in animal physiology, disease, and nutrition.Creative Proteomics offers animal hormone analysis using advanced targeted metabolomics methods.
Submit Your Request Now
×- Services
- Workflow
- Technical Platforms
- Sample Requirements
- Applications
- Demo
- FAQs
Animal hormones are signaling molecules primarily secreted by animal secretory cells or endocrine glands. Most are proteins, while a smaller portion consists of RNA and steroids. Although present in small quantities, they play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
Classification of Animal Hormones
Higher animals have many endocrine glands that produce hormones, with the five major ones being the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads, and pituitary gland. These glands secrete various hormones, which can be classified based on their chemical structure into steroid hormones, amino acid-derived hormones, peptide and protein hormones, and aliphatic hormones, as detailed below:
Table 1. Classification of animal hormones.
| Nature | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Steroid Hormones | Corticosteroids | Promote the reabsorption and secretion of Na+ in renal tubules and collecting ducts, maintaining the balance of blood potassium and sodium levels (potassium retention and sodium excretion), acting on renal tubules and collecting ducts. |
| Androgens/Estrogens | Promote masculinization; testosterone is responsible for male reproductive organ development and secondary sexual characteristics; androgens also help maintain normal spermatogenesis. | |
| Progesterone | Promote the development of the uterus and mammary glands, preparing the endometrium for implantation and the breasts for lactation. | |
| Peptide and Protein Hormones | Growth Hormone | Promotes growth, mainly stimulating protein synthesis and bone development, affecting the entire body. |
| Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) | Stimulates thyroid growth and regulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones. | |
| Gonadotropins | Promote gonadal development and regulate the synthesis and secretion of sex hormones. | |
| Prolactin | Regulates maternal behaviors in certain animals and promotes the development and function of mammary glands for lactation. | |
| Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) | Promotes water reabsorption in renal tubules and collecting ducts, reducing urine output, maintaining body water balance, and affecting osmotic regulation in cells. | |
| Insulin | Regulates glucose metabolism, lowers blood glucose levels, promotes glycogen synthesis and storage, and inhibits gluconeogenesis. Acts on the liver. | |
| Amino Acid-Derived Hormones | Thyroid Hormones | Promote carbohydrate metabolism and growth, accelerate body metabolism and decomposition, especially enhancing nerve excitation and energy metabolism. Affect almost the entire body. |
| Adrenaline | Increases heart rate, dilates blood vessels, promotes glycogen breakdown, raises blood glucose levels, mainly acting on the heart and liver. | |
| Eicosanoid Hormones | Prostaglandins | Regulate the activity of certain hormones, causing inflammatory responses. |
Animal Hormones Analysis Services in Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive animal hormone analysis services, including the detection of antigens, metabolites, and degradation products. We deliver rigorous, compliant, and standardized third-party testing reports.
Targeted Hormones
Steroid Hormones: Includes testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, etc. These hormones are widely used to promote animal growth, and their residue levels must be monitored to ensure food safety.
Peptide Hormones: Such as growth hormone (GH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which regulate animal growth and reproduction.
Thyroid Hormones: Includes thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are essential for metabolism regulation. Measuring their levels helps assess animal health.
Synthetic Hormones: Such as dexamethasone and testosterone propionate, commonly used for growth enhancement or improving animal physique. Excessive residues may pose health risks.
Other Hormones: Includes adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which play key roles in various physiological processes.
Insect hormones: We offer insect hormone analysis services, capable of detecting over 20 different types of insect hormones. These hormones regulate key biological processes such as metabolism, growth, development, diapause, metamorphosis, and reproduction.
Our Advantages
- Wide Coverage: We can analyze a broad range of steroid hormones, offering comprehensive monitoring across various sample types (serum, plasma, urine).
- High Throughput: Efficient sample preparation and quick analysis enhance throughput.
- High Sensitivity: Accurate hormone level assessment within clinical reference ranges for different populations.
- Strict Quality Control: High standards in linearity, accuracy, precision, and recovery rates ensure reliable and reproducible results.
Workflow of Animal Hormones Analysis
The technical workflow for animal hormone analysis involves grinding and homogenizing the sample, followed by precise weighing to ensure accurate quantities. The target compounds (hormones or metabolites) are then extracted using suitable methods. These compounds are analyzed using advanced techniques such as LC-MS/MS to quantify hormone levels and identify metabolites. The resulting data is processed to assess concentrations and any anomalies, and a detailed report is generated with findings, interpretations, and recommendations for further actions or research.
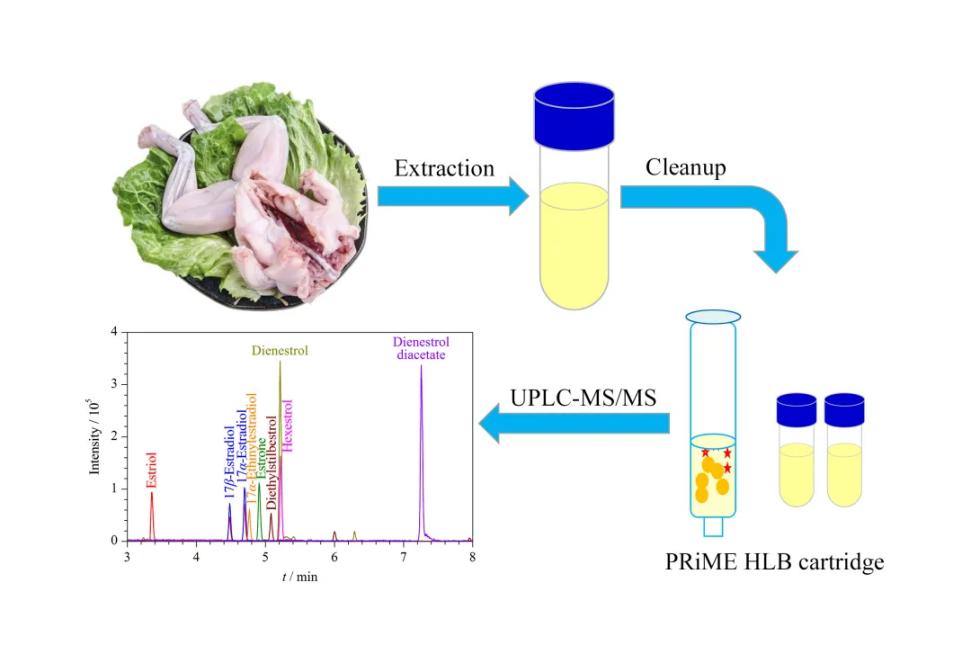 Figure 1. The workflow of animal hormones analysis.
Figure 1. The workflow of animal hormones analysis.
Technical Platforms
See more Creative Proteomics Mass Spectrometry
The targeted metabolomics service provided by Creative Proteomics is based on our cutting edge separation and analytical platforms. Our experienced technicians have optimized protocols, in order to provide best service to meet customers' requirement.
Sample Requirements
| Sample type | Recommended sample size | Pre-treatment and storage |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | 100-200 mg | Snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Urine | 200-500 μL | 5000×g 4℃ Centrifuge for 30-60min, remove supernatant, store at -80℃. |
| Serum/plasma | >100 μL | Collected serum/plasma, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen, stored at -80℃. |
| Cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, bile and other body fluids | >200 μL | 4℃ Centrifuge for 10min, (or filter using 0.22μm membrane), remove supernatant and store at -80℃. |
| Suspension cells | >1*107 | Centrifuge and collect cells after liquid nitrogen snap freezing and store at -80℃. |
| Walled cells | >1*107 | Cultured walled cells are stored in 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, snap freezing in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80℃. |
| Cell supernatant | >2 mL | centrifuge at 4℃ for 3 minutes, take the supernatant and store at -80℃. |
Reports
- Sample Information: Provides detailed information on sample type, collection and storage conditions, and preparation process.
- Analytical Methods: Describes the analytical techniques used, including sensitivity, detection limits, and quality control measures.
- Hormone Quantification Results: Reports the concentration, reference range, and residual levels of each target hormone.
- Metabolite & Degradation Product Analysis: Identifies hormone metabolites and degradation products, and analyzes their biological significance.
Appliacations of Animal Hormones Analysis
Environmental Factors Research
The influence of environmental pollutants or stressors on hormone levels aids in studying the potential health risks of environmental factors.
Animal Reproduction Research
Hormones have a critical impact on animal reproduction. Monitoring hormone levels helps optimize animal breeding management and breed improvement.
Pathological Mechanism Research
By analyzing changes in hormone levels, the intrinsic mechanisms of disease onset and progression are revealed, providing deeper insights into the pathophysiological processes.
Disease Biomarker Research
Changes in hormone levels can serve as biomarkers for various diseases, aiding in early diagnosis and disease monitoring.
Demo Results
Figures come from (Li, Y.et.al, Sci Rep,2023)
Animal Hormones Analysis FAQs
What are the main considerations in steroid hormone analysis using mass spectrometry?
Steroid hormones, including estrogens, androgens, progestogens, and corticosteroids, regulate key physiological processes and have similar structures, making them challenging to analyze. Traditional methods like Radioimmunoassay (RIA) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) are sensitive but limited to measuring one hormone at a time and can suffer from cross-reactivity and poor reproducibility.
LC-MS/MS is now the preferred method for directly measuring steroid hormones. However, due to similar fragmentation patterns and the need to monitor precursor ions that lose 18Da (water), separating and accurately identifying these hormones can be difficult. Estrogen, for example, is challenging to analyze because of its low concentration and polarity. Derivatization methods, such as using Dansyl chloride, can help improve the sensitivity and specificity of estrogen detection, making LC-MS/MS a more reliable tool for comprehensive steroid hormone analysis.
What sample types are required for animal hormone analysis?
Common sample types include blood, serum, plasma, saliva, urine, and even feces. The choice of sample depends on the hormones being measured and the specific requirements of the analysis. Samples are usually collected in a non-invasive or minimally invasive manner to ensure animal welfare.
Are the hormone analysis services available for all animal species?
Hormone analysis services are available for a variety of animal species, including mammals (e.g., rodents, livestock, pets), birds, and even aquatic animals. However, the specific services may vary depending on the species and available testing protocols.
Learn about other Q&A about other technologies.
Publications
Here are some publications in Metabolomics research from our clients:

- Living in extreme environments: a photosynthetic and desiccation stress tolerance trade-off story, but not for everyone. 2023. https://doi.org/10.22541/au.168311184.42382633/v2
- NUDT22 promotes cancer growth through pyrimidine salvage and the TCA cycle. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1491465/v1
- Physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic insights of three extremophyte woody species living in the multi-stress environment of the Atacama Desert. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04484-1
- The Vibrio cholerae type six secretion system is dispensable for colonization but affects pathogenesis and the structure of zebrafish intestinal microbiome. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.00151-21
- The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475
References
- Mourad M et al. Brain Biomarkers of Long-Term Outcome of Neonatal Onset Urea Cycle Disorder. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2016; 2(4):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns2040010
- Ma, Y., et al. (2023). Adipocyte Thyroid Hormone β Receptor-Mediated Hormone Action Fine-tunes Intracellular Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Systemic Homeostasis. Diabetes, 72(5), 562–574. https://doi.org/10.2337/db22-0656
- Ramírez, S., et al. (2022). Hypothalamic pregnenolone mediates recognition memory in the context of metabolic disorders. Cell metabolism, 34(2), 269–284.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.023