Citrullination Analysis Service
Citrullination transforms arginine residues and rewires immune signaling, inflammation, and disease pathways. At Creative Proteomics, we deliver high-resolution LC–MS/MS citrullination analysis combined with specific probe enrichment to accurately identify and quantify modified arginine sites—helping researchers reveal functional mechanisms in immunity, cancer, and neurodegeneration.
- Comprehensive detection: Identify and quantify citrullinated proteins and site-specific arginine modifications.
- Advanced technology: LC–MS/MS + citrulline-specific probe enrichment for precision and depth.
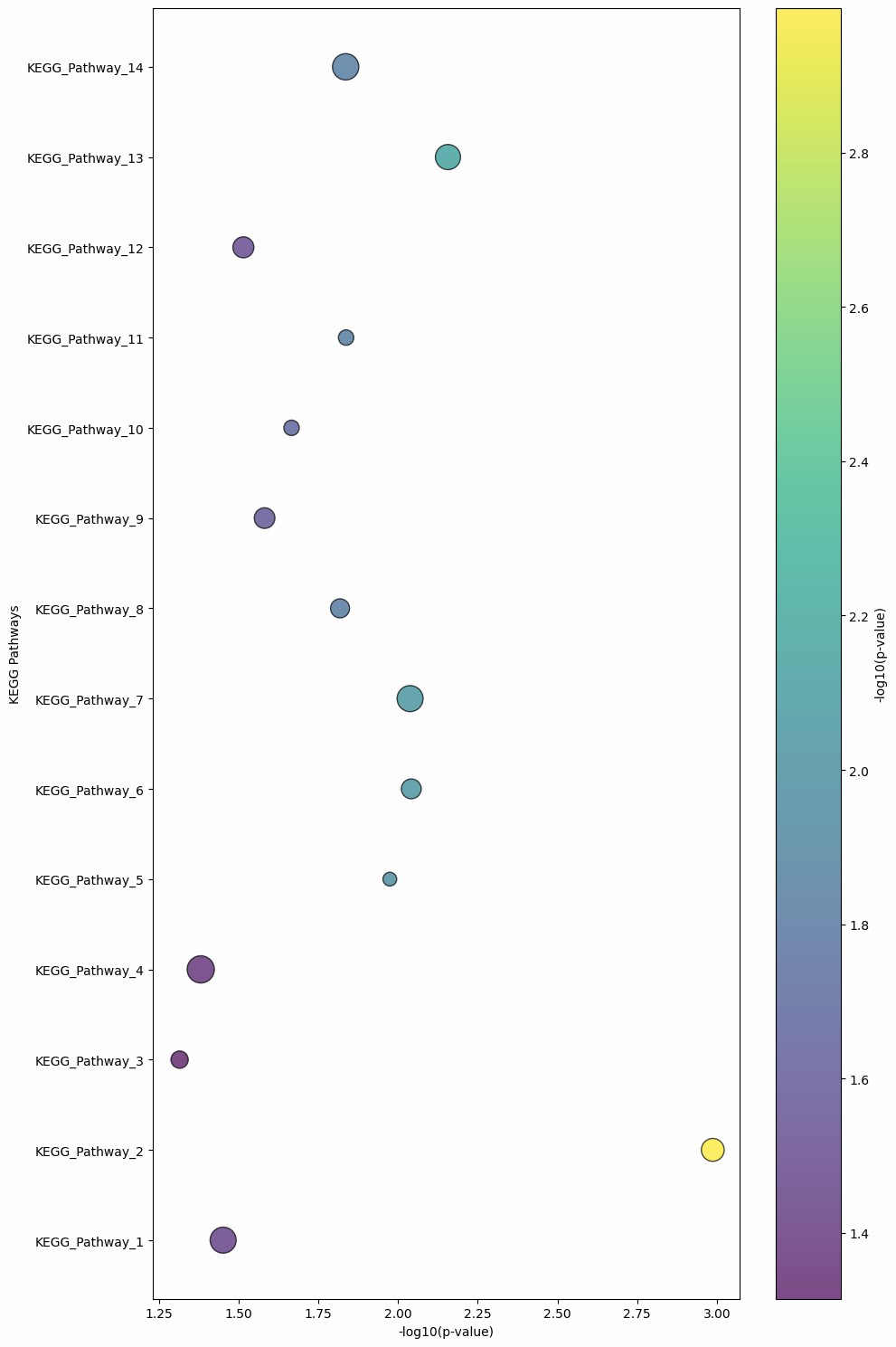
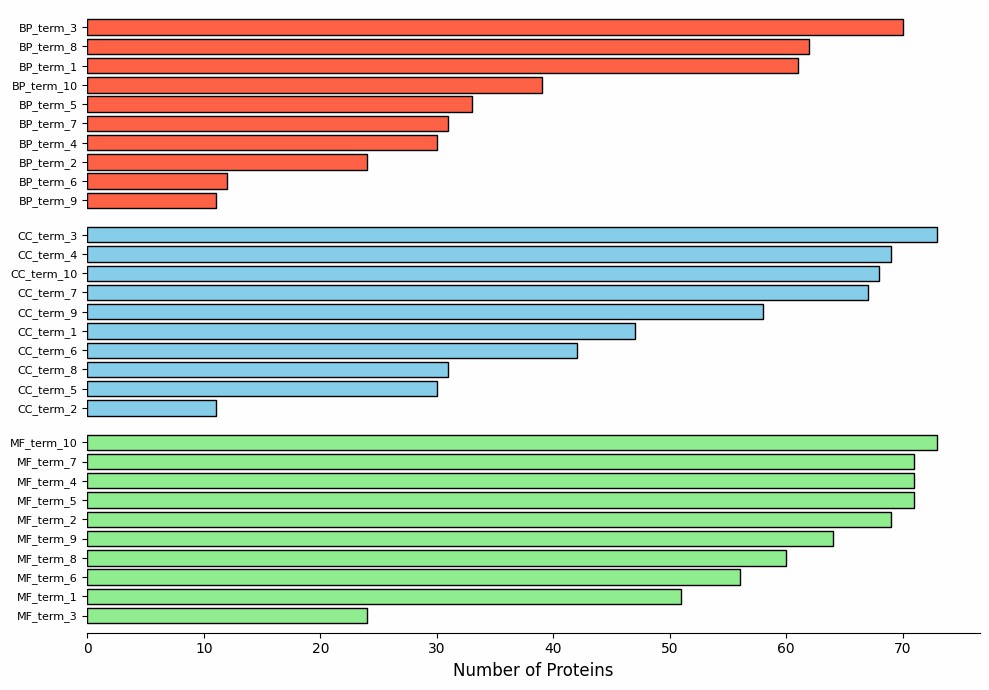
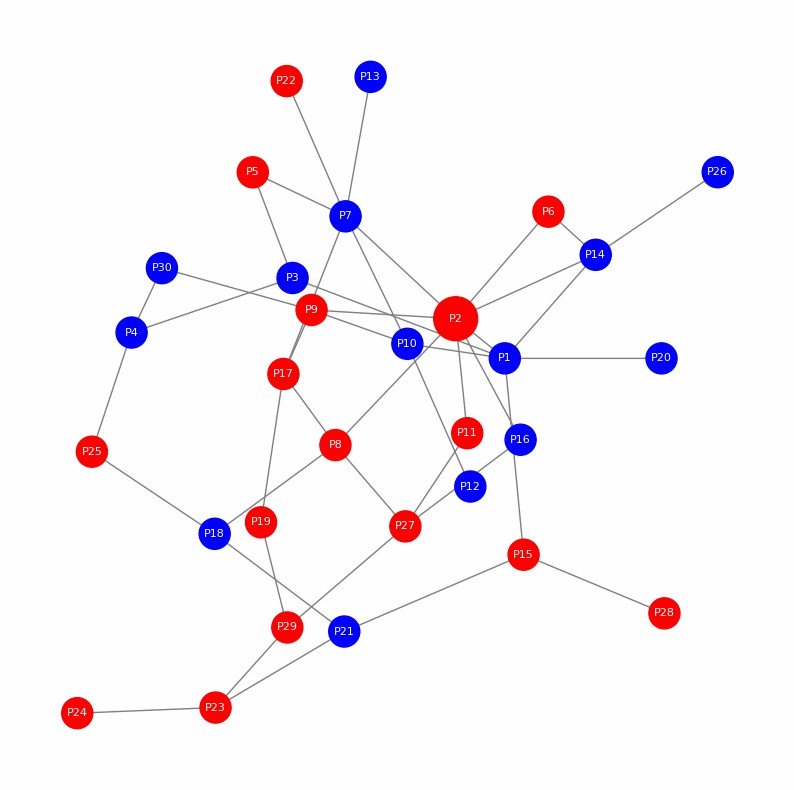
- Functional insights: Integrated bioinformatics for motif, pathway, and network interpretation.
- Research impact: Clarify PAD enzyme regulation in autoimmune, inflammatory, and oncogenic processes.
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Define
- What We Provide
- Technology Platform
- Workflow
- Advantages
- Applications
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case
- Publications
- Sample Requirement
What Is Citrullination?
Citrullination is a post-translational modification (PTM) of arginine, catalysed by a group of enzymes known as peptidyl arginine deaminases (PADIs). PAD enzymes require Ca²⁺ to catalyze citrullination, converting arginine (Arg) into citrulline with the release of ammonia. This reaction represents a calcium-dependent hydrolytic process in which the highly basic, positively charged arginine side chain is transformed into a neutral urea group. Despite the conversion only resulting in a small mass shift, the modification may impart a large functional impact on the protein, as citrullination of arginine causes a loss of positive charge and change electron acceptor properties. This change in physiochemical properties may alter protein structure, protein–protein interactions, and protein localization within the cell. However, the implications of citrullination at the cellular level remain not fully understood. Citrullination is known to play important physiological roles in maintaining stem cell potency, during the innate immune response, and in maintaining the skin barrier. Furthermore, dysregulation of citrullination is known to be a driving factor in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis, and cancer.
Citrullination Service at Creative Proteomics
To elucidate the functional implications of citrullination, it is crucial to be able to detect citrullination events in an unbiased manner. Furthermore, it is important to identify not only the citrullinated target proteins, but also the specific arginine residues that are targeted for citrullination.
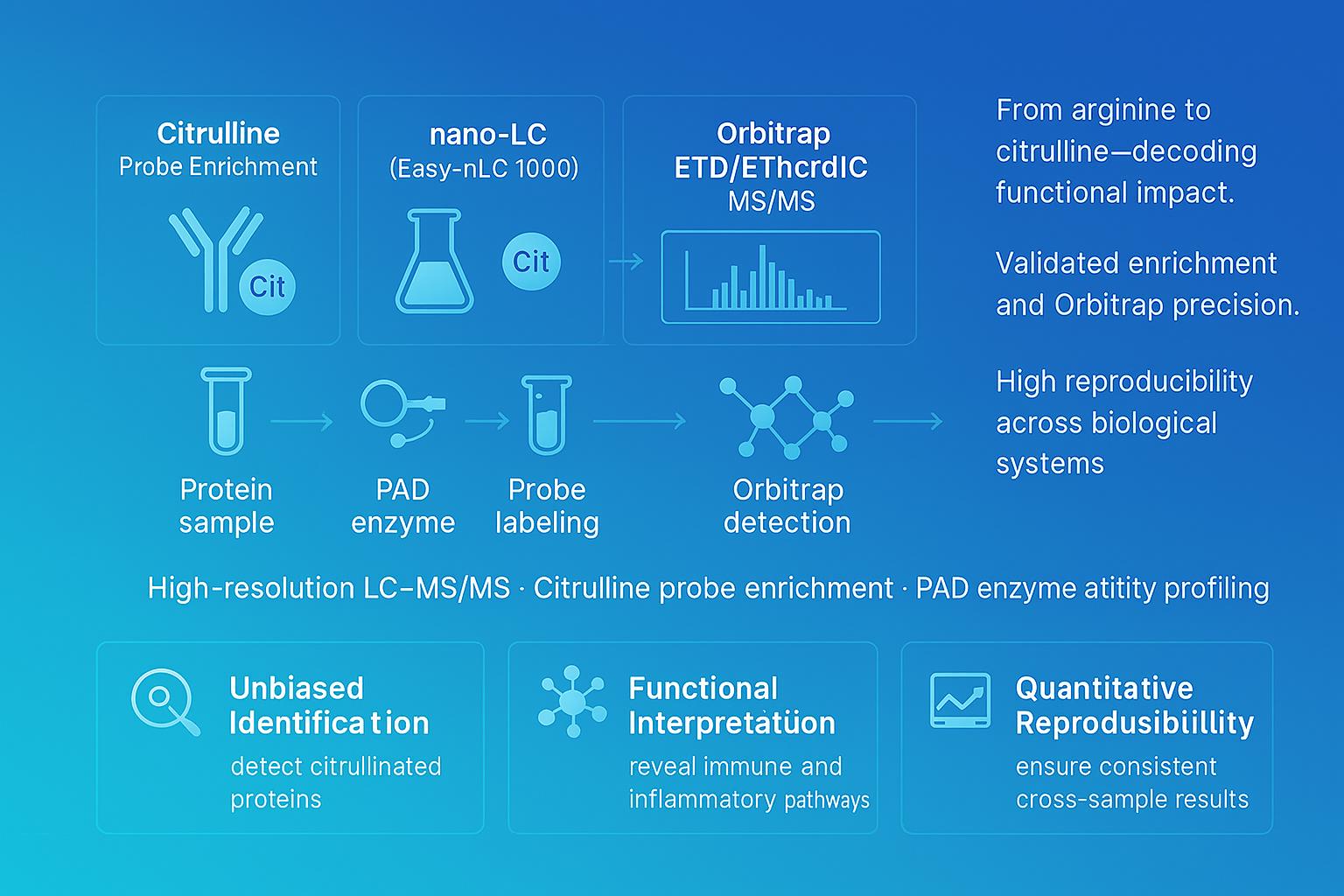
Creative Proteomics has established a highly sensitive LC-MS/MS pipeline that can analyze citrullination in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. Furthermore, we have optimized our protocol, to facilitate more rapid and sensitive site mapping service for citrullination. We rely on C18 column and Thermo Fisher Easy-nLC 1000 and Thermo Fisher LTQ Obitrap ETD to provide citrullination analysis service packages. We will take care of all aspects of the project, including protein extraction, probe labeling and enrichment, proteolysis, mass spectrometry analysis, raw mass spectrometry data analysis, and bioinformatics analysis.
Citrullination Research Platforms

Easy-nLC 1000 (Figure from Thermo Scientific)

Thermo Fisher LTQ Obitrap ETD (Figure from Thermo Scientific)
Workflow of Citrullination Analysis
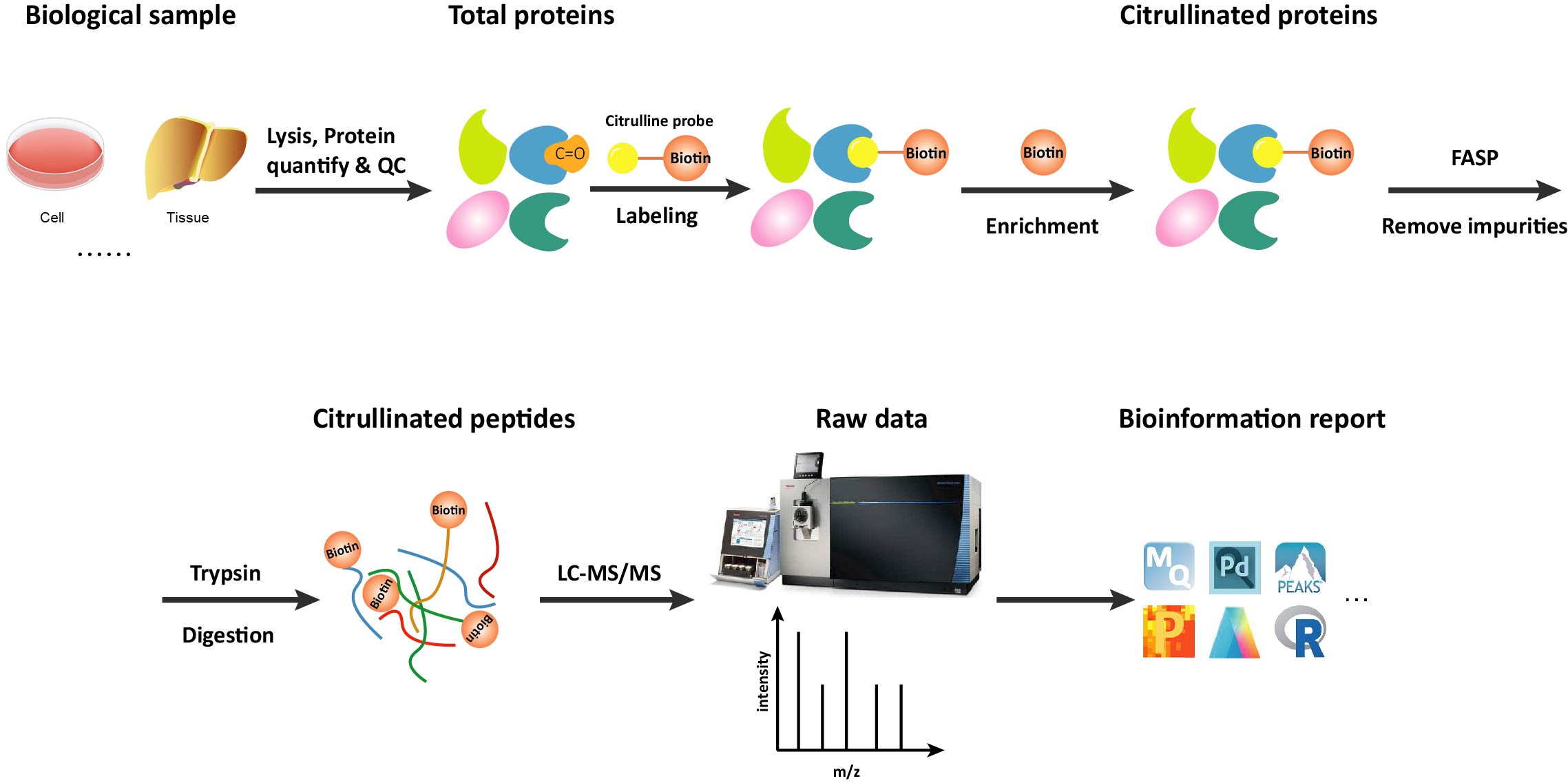
Advantages Our Citrullination Service
- Professional detection and analysis capability: Experienced research team, strict and matured techniques.
- Breadth: we could skillfully deal with protein samples derived from a wide range of sources, encompassing cell, animal and plant tissues, etc.
- High specificity and accuracy: Skillful quantification proteomics techniques, and PTMs enrichment methods.
- High stability and reproducible: Obtain consistent and reproducible inter- and intra- assay results for data analysis.
- Advanced Analytical Platforms: Use of high-sensitivity mass spectrometry and state-of-the-art tools, ensuring precise, repeatable results.
- End-to-End Support: Offer full-spectrum services from design to data interpretation, with continuous technical support throughout the research process.
Applications of Citrullination





Biomarkers and Drug development[1]
Citrullinated proteins can be used as potential biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis evaluation.
Small molecule inhibitors that target PADI enzymes, such as Cl-amidine, are being developed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Autoimmune disease research
Citrullinated proteins play a key role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and are prime targets for anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA), which can be used for early diagnosis and disease surveillance[2].
Tumor
Citrullination can regulate the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes by altering chromatin structure, and it may be a potential target for tumor therapy[3].
Neurodegenerative disease
In Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), citrullinated modification is closely associated with neuroinflammation, protein aggregation, and may affect the function of tau and α-synuclein.
Citrullinated modification may become a novel biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases for early detection and intervention.
Cardiometabolic health
There is evidence that L-citrulline has atheroes-endothelial protective effects and is beneficial for muscle and metabolic health (via vascular and non-vascular pathways) in susceptible/elderly populations[4].
Citrullination Service Sample Requirements
| Sample | Sample Quantity | |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | animal tissue | 200-500mg |
| fresh plant | 200-500mg | |
| Cell | suspension cell | > 3x107 |
| adherent cell | > 3x107 | |
| Protein | Total protein > 5mg and concentration >1 μg/μL | |
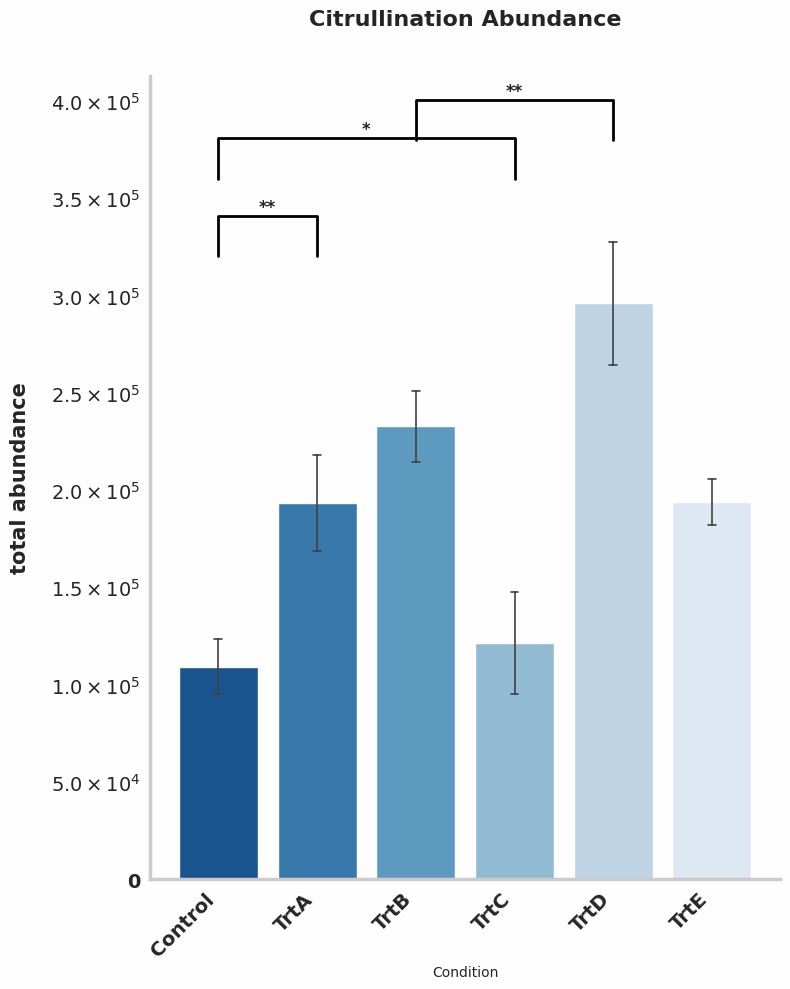
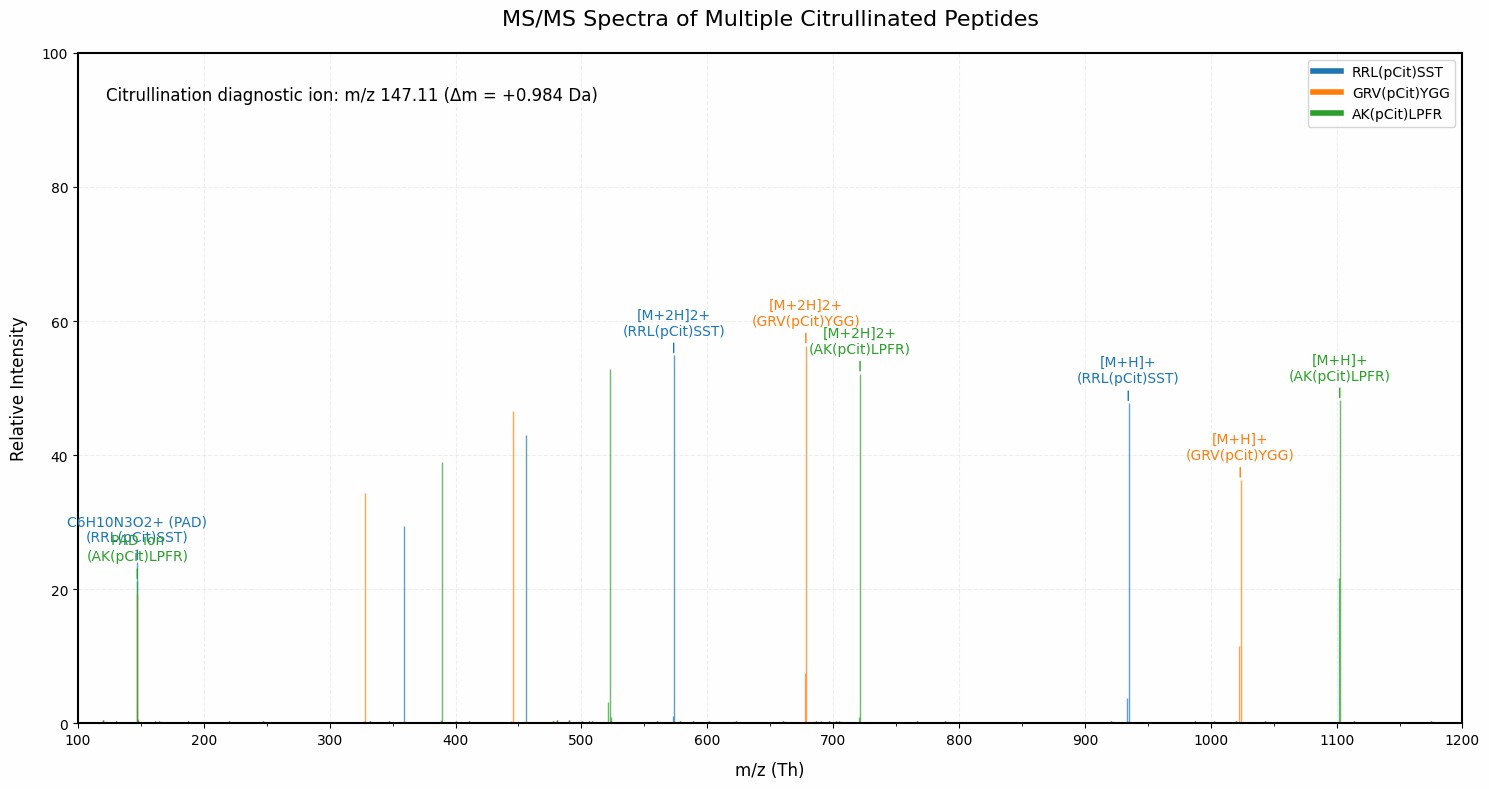
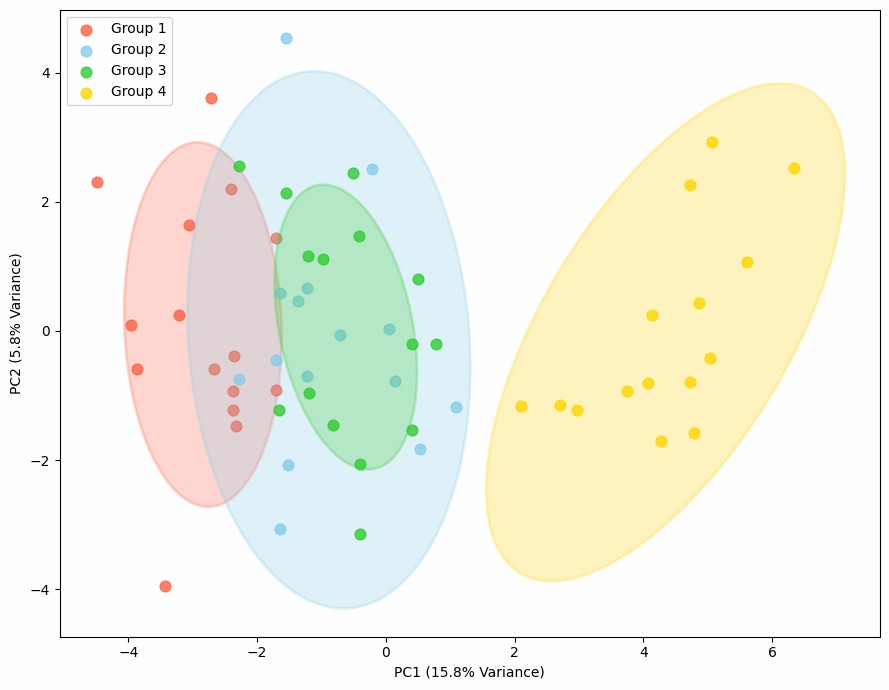
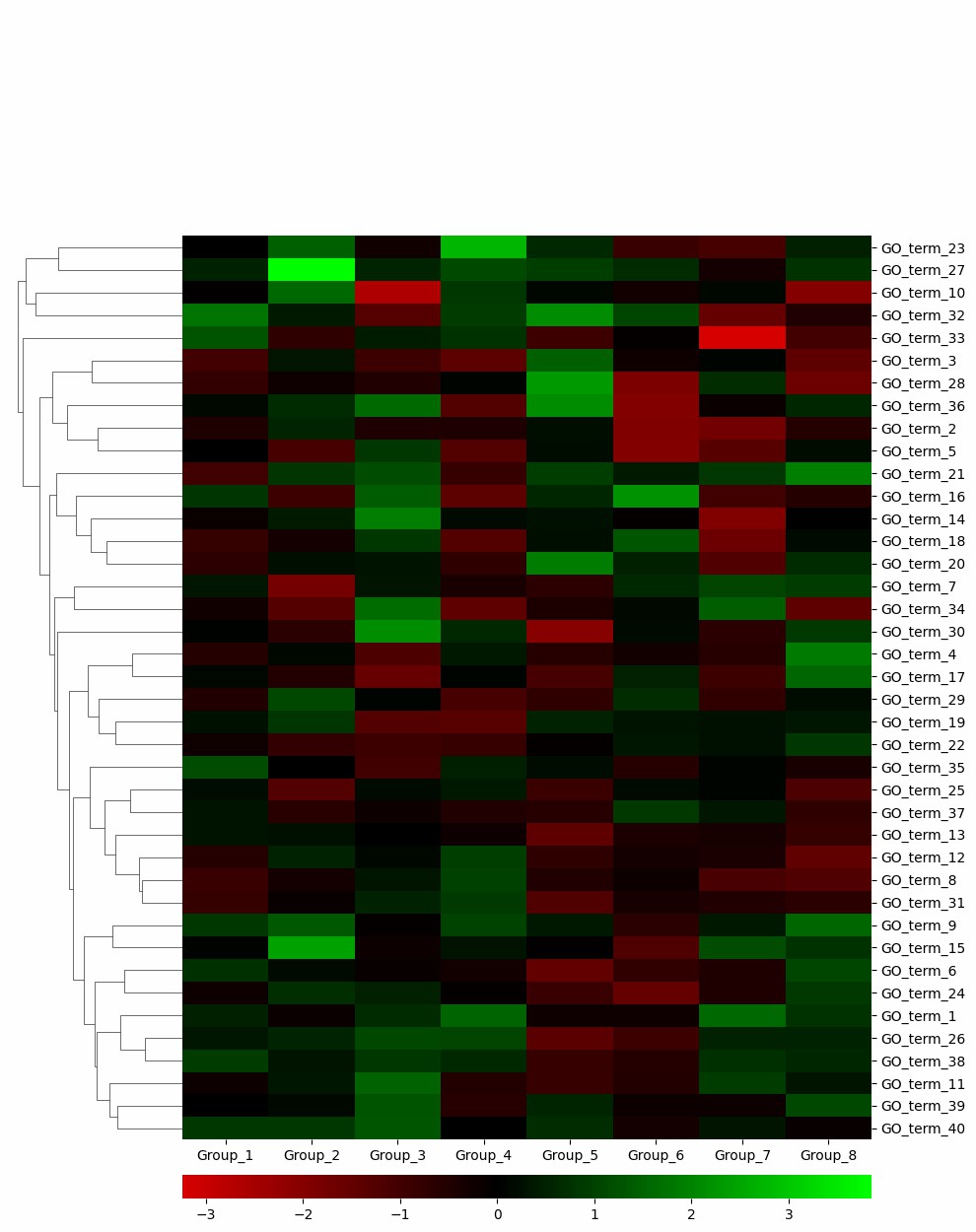
Demo Result of Citrullination Service
FAQs of Citrullination Service
Which sample types are accepted by the service?
We accept a variety of sample types including cells, tissues, plant tissue and more. If you have other special sample types, please consult in advance.
Whether the sample needs pretreatment?
We recommend that customers provide fresh or frozen samples, which should avoid repeated freezing and thawing, and we will be responsible for subsequent protein extraction and pretreatment. If you have already extracted the protein, please communicate with us in advance about the sample handling method.
Learn about other Q&A.
Case Study

Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Hyperactivation of the proteasome core particle in Caenorhabditis elegans protects against proteotoxic stress and extends lifespan. 2021. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-960676/v1
- Immunoproteomics characterization of Leishmania panamensis proteins for potential clinical diagnosis of mucosal Leishmaniasis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12824
- Confirmation of translatability and functionality certifies the dual endothelin1/VEGFsp receptor (DEspR) protein. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12867-016-0066-8
- 3-D physiomimetic extracellular matrix hydrogels provide a supportive microenvironment for rodent and human islet culture. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.057
- Protein interactors of Spindle Pole Body (SPB) components and septal proteins in fungus Neurospora crassa: A mass spectrometry-based dataset. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2023.109980
References
- Zhu, D., Zhang, Y., & Wang, S. (2021). Histone citrullination: a new target for tumors. Molecular cancer, 20(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01373-z
- Ciesielski, O., Biesiekierska, M., Panthu, B., Soszyński, M., Pirola, L., & Balcerczyk, A. (2022). Citrullination in the pathology of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders: recent advances and future perspectives. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS, 79(2), 94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04126-3
- Allerton, T. D., Proctor, D. N., Stephens, J. M., Dugas, T. R., Spielmann, G., & Irving, B. A. (2018). l-Citrulline Supplementation: Impact on Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients, 10(7), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070921