High-Resolution PTMs Profiling Services
Creative Proteomics provides comprehensive, high-resolution PTM profiling services using cutting-edge mass spectrometry platforms. With extensive experience in protein research, we offer customized solutions for a wide spectrum of post-translational modifications—supporting studies in cell signaling, disease mechanisms, metabolic regulation, and more.
Submit Your Request Now
×- Background
- Service Overview
- Methods
- Advantage
- Workflow
- Platform
- Application
- Sample Requirement
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Publication
What Are Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)?
DNA provides the blueprint for building proteins, but the true complexity of the proteome goes far beyond the genetic code. Once a gene is transcribed into mRNA and translated into a protein, additional chemical changes—called post-translational modifications (PTMs)—step in to fine-tune that protein's function, structure, and stability.
In mammalian cells, the genome contains around 25,000 genes. This gives rise to over 100,000 mRNA transcripts. Translation expands this into more than 100,000 proteins. But here's where it gets even more intricate: with the help of alternative splicing and PTMs, the number of distinct functional protein species can exceed 1 million. That's a 40-fold increase from gene to functional protein—a testament to how essential PTMs are in expanding protein diversity.
Many proteins, even after translation, are not fully active. Some require enzymatic cleavage, while others depend on chemical tweaks—PTMs—to reach their functional form. These modifications can dramatically alter a protein's behavior, from where it's located in the cell to how it interacts with other molecules.
Types of PTMs
PTMs involve covalent changes to proteins and fall into several main categories:
- Chemical group additions: These include phosphorylation, glycosylation, acylation, and alkylation—modifications that can impact protein folding, signalling, and activity.
- Attachment of small proteins or peptides: Examples include ubiquitination and SUMOylation, which often regulate protein degradation or nuclear transport.
- Structural alterations: Such as the formation of disulfide bonds, which help stabilize protein structure.
Even a single modification at a specific amino acid site can generate a protein with a completely new function. To date, scientists have identified more than 200 different types of PTMs across nearly every class of protein—from nuclear transcription factors and enzymes to membrane receptors and structural proteins.
This extraordinary biochemical flexibility allows cells to respond to internal and external cues with remarkable precision—something that's critical in areas like drug development, where even small changes in protein activity can influence therapeutic outcomes.
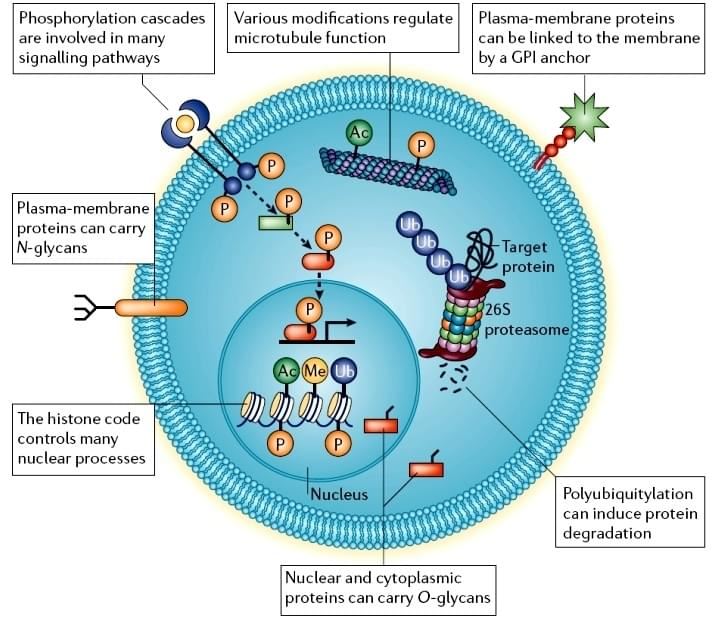 Figure 1. Cellular post-translational modifications[1].
Figure 1. Cellular post-translational modifications[1].
Comprehensive PTM Analysis Services by Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics offers end-to-end solutions for PTM proteomics analysis, leveraging years of expertise and state-of-the-art instrumentation. Whether you're studying protein regulation, signaling pathways, or disease mechanisms, our mass spectrometry-based PTM analysis services provide the precision and reliability you need.
Explore Our Broad PTM Profiling Capabilities
Service Contents
- Common PTMs
- Redox Proteomics
- Emerging and Specialized PTMs
- Histone and Chromatin Modifications
- Other PTMs Services
Common PTMs
Identify and quantify phosphorylation sites to study signaling pathways.
Examine acetylation modifications affecting protein function and gene expression.
Detect methylation patterns influencing protein interactions and stability.
Analyze ubiquitin attachments that regulate protein degradation.
Characterize glycan structures impacting protein folding and cell signaling.
Investigate SUMO protein conjugation affecting nuclear transport and transcriptional regulation.
Our redox proteomics services encompass comprehensive analysis of reversible oxidative modifications, including:
- S-Nitrosylation Site Identification
- S-Glutathionylation Mapping
- Disulfide Bond Mapping (Intra- and Intermolecular)
- S-acylation
- Thiol Oxidation State Profiling
- Reversible Redox PTMs Enrichment & Quantification
- Comparative Redox Proteomics under Stress Conditions
Emerging and Specialized PTMs
Explore crotonylation's role in gene regulation and chromatin remodeling.
Assess nitric oxide-mediated modifications influencing protein function.
Study lipid attachments that target proteins to membranes.
Hydroxylation Site Identification
Identify hydroxyl groups added to amino acids, affecting protein stability.
Biotinylation Analysis
Detect biotin attachments used in protein purification and labeling.
Examine succinyl groups modifying lysine residues, impacting metabolism.
Analyze propionyl modifications influencing chromatin structure.
Investigate acyl group additions affecting protein localization and function.
Alkylation Analysis
Study alkyl group additions that can alter protein activity.
Glutathione Site Identification
Identify glutathione conjugation sites involved in oxidative stress responses.
Examine glutamyl groups added to proteins, affecting microtubule functions.
Analyze prenyl groups facilitating membrane attachment of proteins.
S-Myristoylation Analysis
Detect myristoyl groups influencing protein-membrane interactions.
Study palmitoyl modifications affecting protein trafficking.
Map disulfide bonds critical for protein structure and stability.
Assess non-enzymatic sugar additions linked to aging and diabetes.
Histone and Chromatin Modifications
Comprehensive profiling of histone modifications influencing gene expression.
Detailed analysis of methylation across the proteome.
In-depth study of acetylation patterns affecting chromatin dynamics.
Other PTMs Services
Customized analysis of additional or less common PTMs as per research requirements.
PTM Quantitative Proteomics Options
For researchers needing precise PTM quantification, we provide multiple labelling and label-free solutions:
- SILAC (Stable Isotope Labelling with Amino acids in Cell culture)
- iTRAQ/TMT (isobaric labelling for multiplexed quantification)
- label-free quantification, DIA (Data-Independent Acquisition), 4D-DIA label-free
- Targeted proteomics using SRM/PRM)
These technologies allow robust, reproducible measurements of PTM abundance across conditions or time points.
Download "Comparison of Three Label based Quantification Techniques iTRAQ TMT and SILAC"
MS-Based Strategies for Analysing PTMs
Protein function isn't determined by abundance alone. In fact, many key cellular activities depend on when, where, and how proteins are modified after translation. These PTMs—often reversible and highly dynamic—regulate protein activity, stability, localisation, and interactions.
To fully understand protein behaviour, it's essential to map PTMs across different biological contexts. That's where high-resolution mass spectrometry (MS) comes into play.
Why Mass Spectrometry Is Key to PTM Discovery
MS-based proteomics has transformed our ability to investigate PTMs with both breadth and precision. Here's why:
- Mass shift reveals modifications: When a protein undergoes a PTM, its molecular mass changes. MS instruments can detect these shifts with remarkable accuracy.
- High-throughput capability: Coupled with advanced search algorithms and bioinformatics platforms, MS enables large-scale identification of PTM sites across the proteome.
- Depth and versatility: Beyond PTMs, MS workflows also capture protein-protein interactions and subcellular localisation, offering a holistic view of cellular regulation.
In the past decade, this approach has revealed hundreds of thousands of PTM sites and uncovered previously unknown types of modifications in mammalian systems.
Enrichment Is Crucial for Low-Abundance PTMs
Despite MS sensitivity, many PTMs occur at low levels and fluctuate rapidly. This means that enrichment of modified peptides or proteins is often required before MS analysis. Without this step, rare or transient modifications may go undetected.
For example, using antibody-based enrichment or chemical tagging techniques significantly improves detection rates for modifications like phosphorylation or ubiquitination.
By combining sample enrichment with optimised MS workflows, researchers can now generate deep, quantitative insights into PTM landscapes—essential for uncovering regulatory mechanisms in cell biology, drug response, and disease progression.
Why Choose Creative Proteomics for MS-Based PTM Analysis?
1. High Accuracy with Low Variability
Our advanced MS systems and validated enrichment strategies yield precise, reproducible results with<5% coefficient of variation.
2. Versatile Sample Compatibility
We work with diverse sample types—from microbial cultures and cell lines to tissues and complex fluids—ensuring wide research applicability.
3. Expert Support at Every Step
With a seasoned PTM proteomics team and strict quality control, we deliver actionable, high-confidence data you can trust.
Step-by-Step Workflow for Identifying and Quantifying PTMs
Identifying post-translational modifications (PTMs) is key to understanding how proteins behave in different biological systems. Whether you're optimising a mass spectrometry-based PTM analysis or developing new monoclonal antibody production tips, a well-structured experimental workflow is critical for accurate results.
Here's how a typical PTM analysis pipeline unfolds:
- The experiment designed (clear intention);
- Choice of MS instrument and analysis method;
- Methods optimization;
- Sample preparation-protein extraction and determination of concentration;
- Proper protease(s) for full proteolytic digestion;
- PTM-peptides enrichment (optional);
- Peptides fractionations for in-depth identification by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (optional);
- LC-MS/MS analysis;
- Bioinformation analysis for full PTM proteins and sites annotation.
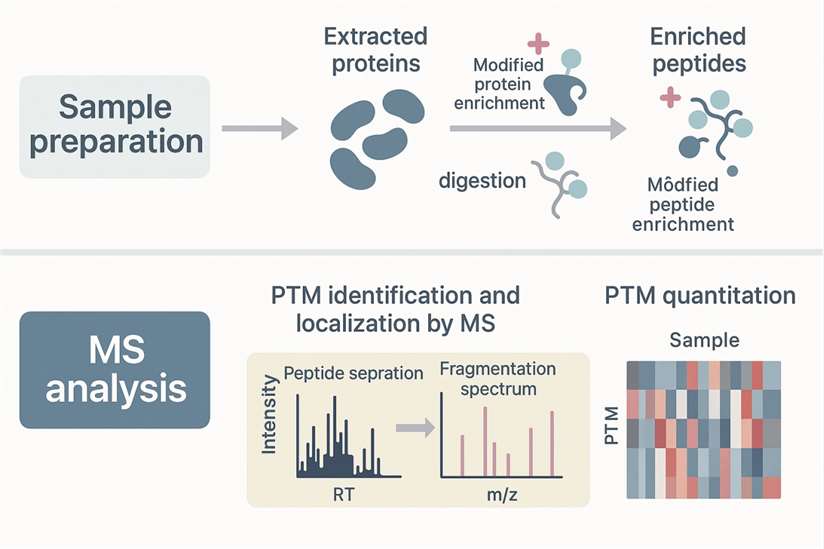
For a deeper dive into the science behind PTM workflows, don't miss our expert resource: [Overview of Post-Translational Modification Analysis].
Top-tier Platform
Equipped with top-tier platforms like Q-Exactive, Q-Exactive HF, and Orbitrap Fusion™ Tribrid™,timsTOF Pro mass spectrometer, we ensure fast, sensitive, and scalable results with reliable reproducibility across batches.

Thermo Q ExactiveTM series

AB Sciex 6500+

Thermo Orbitrap Fusion Lumos

Bruker timsTOF Pro
Application Scenarios
PTM analysis is essential in studies requiring precise regulation of protein function, including:
- Drug Target Validation: Identify functional PTM sites critical for target activation or inhibition.
- Cancer Mechanism Research: Uncover dysregulated PTMs driving tumor progression or resistance.
- Signal Transduction Studies: Map dynamic phosphorylation or acetylation patterns in response to stimuli.
- Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Link acylation or succinylation changes to metabolic disorders.
- Neurodegeneration and Aging: Profile ubiquitination or SUMOylation events associated with protein turnover.
Whether for biomarker discovery or therapeutic development, our PTM profiling empowers high-confidence, actionable insights.
Sample Requirement
| Sample type | Recommended sample size | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal tissues | Hard tissues (bones, hair) | 300-500mg |
| Soft tissues (leaves, flowers of woody plants, herbaceous plants, algae, ferns) | 200mg | |
| Plant tissues | Hard tissues (roots, bark, branches, seeds, etc.) | 3-5g |
| Microbes | Common bacteria, fungal cells (cell pellets) | 100μL |
| cells | Suspension/adherent cultured cells (cell count/pellet) | >1*107 |
| Fluids | Plasma/serum/cerebrospinal fluid (without depletion of high abundance proteins) | 20μL |
| Plasma/serum/cerebrospinal fluid (with depletion of high abundance proteins) | 100μL | |
| Follicular fluid | 200μL | |
| Lymph, synovial fluid, puncture fluid, ascites | 5mL | |
| Others | Saliva/tears/milk | 3-5mL |
| Culture supernatant (serum-free medium cannot be used) | 20mL | |
| Pure protein (best buffer is 8MUrea) | 300μg | |
| FFPE | Each slice: 10µm thickness, 1.5×2cm area | 15-20 slices |
Deliverables
- A report that details:
- Types of post-translational modifications
- PTM locations and frequency
- Sample and method details
- A summary of quantitative PTM data
- An Excel file or HTML report with:
- Complete qualitative and quantitative PTM data
- Statistical analysis of modification changes across samples
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on PTM Proteomics
What Are the Most Common Post-Translational Modifications—and How Do They Differ?
Common Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) – Summary Table
| PTM Type | ΔMass (Da) | MS/MS Stability | Target Site(s) | Enrichment Method | Biological Roles & Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylation | +80 | +++ (Tyr), +/+ (Ser/Thr) | Ser, Thr, Tyr | TiO₂, IMAC-Fe, Phospho-specific antibodies | Signal transduction, stress response, cell cycle, cancer pathways |
| Acetylation | +42 | +++ | Lys | Acetyl-lysine antibodies | Histone modification, transcription regulation, apoptosis, protein stability |
| Methylation | +14 | +++ | Arg, Lys | Methylation-specific antibodies | Epigenetic regulation, protein trafficking, signal transduction |
| Ubiquitination | >1,000 | +/+ | Lys | Ubiquitin-specific antibodies | Protein degradation, cell cycle control, neurodegenerative research |
| Succinylation | +100–115 | ++ | Lys | Succinylation-specific antibodies | Metabolic regulation, inflammation, epigenetic remodeling |
| N-Glycosylation | >800 | +/+ | Asn | HILIC | Protein secretion, immune response, cell recognition |
| O-Glycosylation | 203–>800 | +/+ | Ser, Thr | HILIC | Signaling, disease biomarkers, stress adaptation |
| Fatty Acylation (Farnesyl, Myristoyl, Palmitoyl) | +204 to +238 | +++ to +/+ | Cys, Gly, Ser (varies) | Affinity purification, resin trapping | Membrane tethering, localization, protein-protein interactions |
| GPI Anchoring | >1,000 | ++ | C-terminal signal | Biotin-labeling, detergent phase separation | Anchoring proteins to outer plasma membrane |
| Hydroxylation | +16 | +++ | Pro, Lys | Standard peptide enrichment | Collagen stability, protein-ligand binding |
| Sulfation (sTyr) | +80 | + | Tyr | Anion exchange, antibodies | Receptor-ligand interactions, protein trafficking |
| Disulfide Bonds | -2 | ++ | Cys-Cys | Reduction-alkylation strategies | Protein folding, structural stability |
| Deamidation | +1 | +++ | Asn, Gln | Acidic hydrolysis artifacts | Regulatory effect, common modification artifact |
| Pyroglutamylation | -17 | +++ | N-terminal Gln/Glu | Enzyme-based cleavage detection | Blocks N-terminus, increases protein stability |
| Tyrosine Nitration | +45 | +/+ | Tyr | Nitrotyrosine antibodies | Oxidative stress marker, inflammation |
ΔMass (Da): Mass shift upon modification
MS/MS Stability: + (labile), ++ (moderately stable), +++ (stable)
Enrichment Method: Key to targeted MS analysis
Biological Roles: Summarized based on current research relevance in proteomics, drug development, and cell signaling
Why is PTM peptide enrichment important for mass spectrometry-based analysis?
Enriching PTM peptides before mass spectrometry (MS) greatly improves sensitivity and accuracy. This is especially crucial for detecting low-abundance or dynamic modifications that may be missed in direct MS analysis.
How do I choose the right enrichment method for my PTM analysis?
The choice depends on:
- The type of post-translational modification (PTM)
- The specific amino acid residues modified
- The goal of your experiment (e.g., broad profiling vs. targeted analysis)
Matching your method to these factors ensures better identification and quantification results.
What are the best enrichment strategies for PTMs?
| Protein PTMs | Target amino acid residues | Affinity enrichment strategies | Chemical enrichment strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorylation | Ser, Thr, Tyr, His, Arg, Lys, Asp, Cys, Glu | IMAC, MOAC, SIMAC, SIMAC-HILIC, SCX, SAX, immunoenrichment, superbinder SH2 domains, ERLIC, hydroxyapatite AC, HILIC-IMAC | DBHA probe, HA-yne probe, isoDTB tag, photo-pTyr-scaffold probe, sulfonyl-triazole probe |
| Acetylation | Lys, Ser, Thr, N terminus | immunoenrichment, SCX, ZIC-HILIC, COFRADIC, antibody-IEF, antibody-SCX | alkyne-containing thioester probe, metabolic labelling by ethyl fluoroacetate |
| Methylation | Lys, Arg, His, Ala, Asn | immunoenrichment, IEF, SCX, HILIC, antibody-SCX, antibody-HpH RP, 3xMBT methyl-binding domains, antibody-propionylation | azide- and alkyne-analogues of SAM, chemoenzymatic labelling by ProSeAM |
| Glycosylation | Asn, Arg (N-linked) Ser, Thr, Tyr (O-linked) | lectins, modified glycosidases, immunoenrichment, IMAC, MOAC, HILIC | metabolic labelling by: Ac4ManNAz, Ac4GalNAz, Ac4FucAl, Ac4ManNAl, GalNAz, 1,3-Pr2GalNAz, GalNAzMe; chemoenzymatic labelling by UDP-GalNAz, Glyco-TQ |
| Ubiquitination | Lys, N terminus, Cys, Ser, Thr | protein degradation, trafficking, regulation of enzymes, translation, DNA repair | tagged-Ub, immunoenrichment, COFRADIC |
| Sumoylation | Lys | protein interactions, subcellular localization, enzymatic activities | tagged-SUMO, immunoenrichment, SUMO-interacting motifs |
IMAC: Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography
MOAC: Metal Oxide Affinity Chromatography
HILIC: Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography
SCX/SAX: Strong Cation/Anion Exchange
COFRADIC: Combined Fractional Diagonal Chromatography
ERLIC: Electrostatic Repulsion Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography
What are the Differences Between PTM Omics and Conventional Quantitative Proteomics
PTM proteomics adds a critical step beyond traditional quantitative proteomics: enriching the modified peptide segments after enzymatic digestion. This targeted enrichment allows researchers to identify and analyse specific modification sites during data processing. Unlike conventional proteomics, which focuses on whole-protein quantification, PTM proteomics centres on the peptide level—particularly the modified peptides.
Why PTM Proteomics Focuses on Modification Sites Rather Than Whole Proteins
A key reason is that a single protein can have multiple modification sites. After enzymatic digestion, most peptides remain unmodified, with only a small proportion carrying modifications. Although modified peptides are enriched before mass spectrometry, this process rarely achieves full efficiency. For some modification types, enrichment efficiency can drop below 50%.
Non-modified peptides, still detected during analysis, contribute to overall protein quantification. However, the enrichment step often causes a significant loss of these unmodified peptides. As a result, protein quantification from PTM proteomics does not accurately reflect true protein abundance in the sample.
For label-free quantification approaches, protein level measurement becomes less relevant. Instead, the primary goal is to detect differences in the abundance of specific modification sites across samples. This explains why PTM proteomics prioritises the quantitative analysis of modifications at the site level rather than at the whole-protein level.
How to Identify N-Glycosylation Sites
Identifying N-glycosylation sites requires a series of precise steps:
- First, proteins are digested into peptides.
- Next, N-glycosylated peptides are enriched for targeted analysis.
- Glycosidases then cleave the glycan attached to asparagine (ASN) in the presence of ^18O-labelled water. This reaction increases the ASN mass by 2.9890 Da.
- High-resolution LC-MS detects these deglycosylated peptides, highlighting the specific modification.
- Finally, database matching confirms the molecular weight shift and peptide sequence, pinpointing the exact glycosylation site.
Can PRM be applied to the modified proteome?
Parallel Reaction Monitoring (PRM) can be applied to modified proteomes if internal standard peptides from prior omics studies are available. However, PRM faces higher complexity in this context, requiring careful experimental design and validation.
How are peptide segments with specific modifications enriched? Does the use of antibodies impact the results?
Enrichment strategies vary depending on the modification type. After capturing modified peptides using antibodies, an elution step separates these peptides from the antibodies. This step prevents antibody presence from skewing downstream results, ensuring data integrity.
How is the modified proteome analyzed?
Label-free quantification remains the standard approach for analyzing modified proteomes. In addition, 4D proteomics is gaining traction for its enhanced analytical power.
What advantages does 4D proteomics offer compared to conventional proteomics?
4D proteomics uses the timsTOF Pro mass spectrometer, leveraging Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry (TIMS). This adds a fourth dimension—ion mobility—to traditional retention time, mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), and ion intensity.
The benefits include:
- Increased scanning speed
- Improved detection sensitivity
- Enhanced depth of protein identification
- Higher throughput and quantitation accuracy
These advances enable more comprehensive and reliable proteomic profiling, especially for complex modified samples.
What are the applications of 4D proteomics?
| Product | Technology | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 4D-PTMs | 4D-label free | Suitable for all sample types, particularly advantageous for trace samples like paraffin sections and biopsy tissues. Recommended for sample sets of up to 30 cases. |
| 4D-DIA | Requires a minimum of 6 samples, library construction is needed. Applicable for large-scale protein profiling analyses, such as clinical cohorts and population studies. Recommended for sample sets of 30 cases or more. | |
| 4D-PTMs Proteomics | 4D-Phosphorylation | Widest range of applications, nearly applicable to all biological processes. Used in studies related to drug targets, tumor development, neurological diseases, and commonly employed in the investigation of signal transduction, cell cycle, regulatory mechanisms, stress response, growth and development, and cancer mechanisms, among others. |
| 4D-Acetylation | Metabolic regulation: Induces changes in metabolic enzyme activity and metabolic pathway alterations. Applicable in studies of energy metabolism regulation, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease development, etc. | |
| 4D-Ubiquitination | Protein expression degradation regulation: Mediates protein degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Used in studies of aging and degenerative diseases, immune inflammation, tumor progression, etc. |
Learn about other Q&A about other technologies.
Customer Case Study

Phosphorylation Site Mapping of TcPolβ Reveals Kinase-Specific Regulation inTrypanosoma cruzi
Published In: Microorganisms (2024)
Client: Universidad de Chile / Universidad de Valencia Research Collaboration
Service Provided by Creative Proteomics: Phospho-peptide enrichment & site-specific phosphorylation analysis by LC-MS/MS
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050907
- Project Background
- How Creative Proteomics Helped
- Key Results Enabled by Our Platform
DNA polymerase β (TcPolβ) in T. cruzi is essential for kinetoplast DNA repair and replication—processes vital for parasite survival. However, the molecular regulation of TcPolβ remained unclear. The research team sought to systematically characterize how different protein kinases modulate TcPolβ activity via phosphorylation and whether activation pathways (e.g., PKC-dependent signaling) enhance this modification in vitro and in vivo.
To resolve kinase-specific phosphorylation patterns, the researchers entrusted Creative Proteomics with the downstream phosphoproteomics workflow:
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Sample Type | Recombinant TcPolβ phosphorylated in vitro by 4 kinases (TcCK1, TcCK2, TcAUK1, TcPKC1) |
| Sample Prep | In-gel digestion of TcPolβ bands from SDS-PAGE |
| Enrichment | Phosphopeptide recovery from trypsin-digested gel bands |
| Platform | NanoLC-MS/MS on high-resolution instruments |
| Bioinformatics | MaxQuant-based phosphosite localization and sequence alignment (using TcPolβ reference RNC61524.1) |
Advantage: Enabled detection of both serine/threonine and rare tyrosine phosphorylation events across specific kinase conditions.
Site-level Resolution:
MS analysis revealed 25 phosphorylation sites across all kinase treatments:
- TcCK1: 12 sites
- TcCK2 & TcAUK1: 3 sites each
TcPKC1: 7 sites
Table 1. Phosphorylated residues on TcPolβ by the indicated protein kinases as determined by MS analysis.
| Kinase | Phosphorylated Residues on TcPolβ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUK1 | S 69 | S 275 | T 366 | |
| CK2 | S 69 | S 275 | T 382 | |
| CK1 | S 13 | S 46 | T 49 | S 69 |
| S 185 | S 193 | S 275 | T 278 | |
| Y 307 | S 336 | T 338 | T 345 | |
| T 382 | ||||
| PKC1 | S 13 | S 46 | T 49 | S 69 |
| S 185 | S 275 | T 382 | Y 302 | |
Unexpected Dual-Specificity:
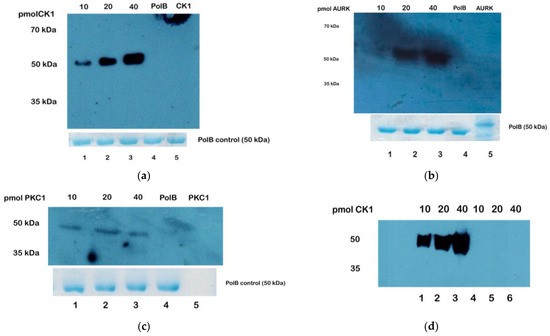 Western blot analysis of TcPolβ phosphorylation by different T. cruzi protein kinases and detected by anti-phosphor antibodies.
Western blot analysis of TcPolβ phosphorylation by different T. cruzi protein kinases and detected by anti-phosphor antibodies.
Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Title: In Vitro Identification of Phosphorylation Sites on TcPolβ by Protein Kinases TcCK1, TcCK2, TcAUK1, and TcPKC1…
Journal: Microorganisms (2024)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050907 - Title: Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Regulate the Fate and Function of T-Lymphocyte Via Reprogramming Lipid Metabolism
Institution: Saint Louis University (Dissertation, 2023)
Link: https://search.proquest.com/openview/8ee9ca786d08344a371a238fa15f7375 - Title: Exploratory phosphoproteomics profiling of Aedes aegypti Malpighian tubules during blood meal processing…
Journal: PLOS ONE (2022)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0271248 - Title: The Interplay between GSK3β and Tau Ser262 Phosphorylation during the Progression of Tau Pathology
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2022)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911610
References
- Jensen ON. Interpreting the protein language using proteomics. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2006 Jun;7(6):391-403. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1939
- Mann M, Jensen ON. Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nature Biotechnology. 2003 Mar;21(3):255-61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0303-255
- Brandi J, Noberini R, Bonaldi T, et al. Advances in enrichment methods for mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis of post-translational modifications. Journal of Chromatography A. 2022 Aug 16;1678:463352. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463352