Histone Propionylation Analysis Service
At Creative Proteomics, we offer a comprehensive Lysine Propionylation Analysis Service designed to support research in epigenetics, metabolism, and stress biology. By combining advanced high-resolution LC-MS/MS with proprietary enrichment workflows, we help clients:
- Identify propionylated proteins with high sensitivity
- Pinpoint specific modification sites
- Reveal functional impacts in biological pathways
Whether you're exploring novel regulatory mechanisms or validating protein function in response to metabolic cues, our service equips you with the data you need—fast and with confidence.
Submit Your Request Now
×
- List of Propionylated Proteins & Modification Sites
- Quantitative Comparison Tables
- Functional Enrichment Analysis
- PTM Motif & Subcellular Localization Prediction
- Protein Interaction Network Maps (optional)
- Publication-Ready Graphs & Full Data Reports
- What is
- Service Details
- FAQ
- Demo
- Publication
- Case Study
Function of Protein Propionylation
Gene expression in eukaryotic cells is carefully controlled—not just by transcription factors, but also through epigenetic mechanisms. One critical layer of this control involves histone modifications, which influence how DNA is packaged and expressed. Thanks to advances in high-resolution mass spectrometry, researchers are now uncovering a wider range of these modifications than ever before.
Among the most intriguing is lysine propionylation, a newly characterized, reversible post-translational modification. Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, propionylation attaches a propionyl group to lysine residues on proteins, subtly altering their structure and function. Unlike more commonly studied modifications like acetylation, propionylation is emerging as a key player in:
- Metabolic enzyme regulation
- Cellular stress responses in both bacteria and mammals
- Photosynthesis control
- Epigenetic modulation across domains of life
In bacteria, for example, propionylation has been linked to global metabolic control and enzyme activity shifts, while in eukaryotes, it contributes to chromatin remodelling and gene regulation.
What Is Lysine Propionylation?
Protein propionylation is a type of lysine acylation where a propionyl group—derived from metabolic intermediates like propionyl-CoA—is covalently attached to the ε-amino group of a lysine residue. This modification is typically catalyzed by acyltransferase enzymes, many of which also mediate acetylation. Like other post-translational modifications, propionylation is reversible and can be dynamically regulated by deacylase enzymes such as sirtuins.
Mechanistically, propionylation is similar to acetylation, but the longer carbon chain of the propionyl group introduces distinct steric and chemical properties that can alter protein structure and function in unique ways. These differences may affect how proteins interact with DNA, other proteins, or regulatory complexes.
In the context of histones, histone propionylation modifies the chromatin landscape by neutralizing lysine's positive charge, thereby reducing its interaction with negatively charged DNA. This leads to chromatin relaxation, potentially enhancing gene transcription. While histone acetylation has been well-characterized in this regard, emerging evidence suggests that propionylation may respond more directly to fluctuations in cellular metabolism, linking nutrient status to epigenetic regulation.
Beyond histones, propionylation has been detected in various non-histone proteins involved in metabolism, transcriptional control, and stress response—highlighting its broader biological relevance.
Our Propionylation Proteomics Service
At Creative Proteomics, our Propionylation Analysis Service provides comprehensive solutions to identify and quantify this emerging PTM. Using advanced mass spectrometry workflows, we help research teams decode the functional implications of propionylation in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.
Key Advantages of Our Propionylation Analysis Service
Our propionylation profiling platform is designed for researchers who demand high sensitivity, scalability, and actionable results. Here's what sets it apart:
- Exceptional Specificity and Enrichment Performance
Our workflow achieves strong signal clarity by isolating only propionylated peptides, significantly reducing background interference and improving site-level confidence. - High-Throughput, High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Leveraging advanced LC-MS/MS systems, we enable large-scale identification of propionylated peptides with excellent resolution and reproducibility—ideal for both discovery and validation studies. - Quantitative Comparison Across Conditions
By integrating well-established quantification methods (e.g., label-free, TMT/iTRAQ), our service supports precise comparison of protein propionylation levels between biological groups, treatments, or time points.
Whether you're studying histone protein modification, metabolic enzymes, or regulatory networks, our Propionylation Analysis Service provides the depth and reliability needed for impactful discoveries.
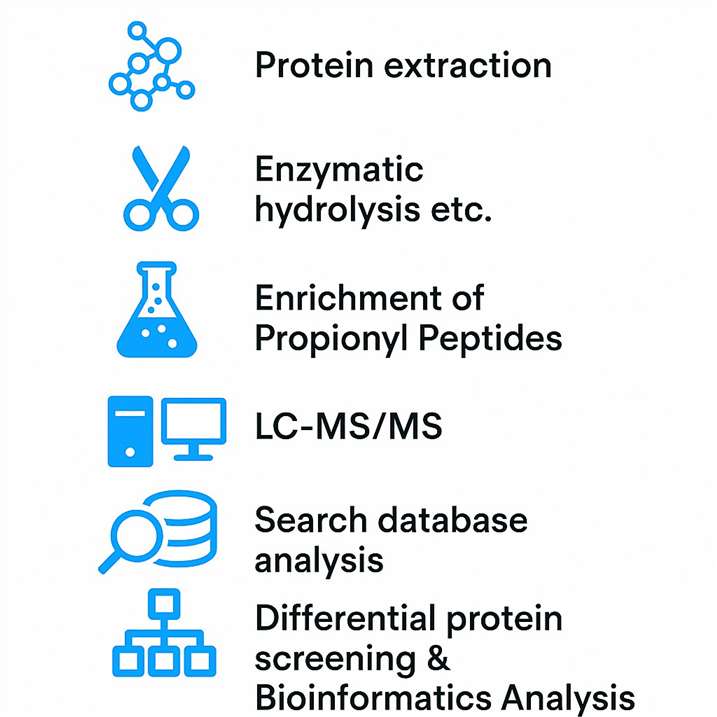
Step-by-Step Workflow
Sample Preparation
- Accepts tissues, cells, serum, plasma, or protein solutions
- Protein extraction and digestion using standard proteomics protocols
Enrichment of Propionylated Peptides
- Affinity-based enrichment to isolate lysine-propionylated peptides
- Improves detection sensitivity by reducing background signal
High-Resolution LC-MS/MS
- Run on Orbitrap or Q Exactive platforms for accurate mass detection
- MS/MS fragmentation ensures precise identification of modification sites
Data Acquisition & Interpretation
- Peptide-spectrum matching and database search
- False discovery rate (FDR) control and PTM site localization
- Optional quantitative analysis (label-free or TMT/iTRAQ-based)
Bioinformatics & Functional Insight
Customized Bioinformatics Services Overview
| Service Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Modified Protein & Site Identification | Detect modified proteins and pinpoint specific propionylation or PTM sites. |
| Result Characterization | Analyze peptide length, protein coverage, and unique peptide distribution. |
| Motif Prediction | Predict conserved sequence motifs around modification sites. |
| GO Functional Classification | Classify proteins by biological process, molecular function, and cellular role. |
| COG Annotation | Annotate protein functions based on evolutionary orthologous groupings. |
| Pathway Annotation | Map proteins to biological pathways via KEGG or Reactome. |
| Protein Interaction Network (Advanced) | Predict and visualize interaction networks for modified proteins. |
| Protein Domain Prediction (Advanced) | Identify functional or structural domains in modified proteins. |
| Subcellular Localization (Advanced) | Predict likely cellular compartments where proteins are active. |
Applications of Propionylation Analysis Service
Epigenetic Research
- Identify and quantify histone propionylation sites to study chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation.
- Reveal how metabolic states influence epigenetic marks via acyl-CoA dynamics.
Metabolism and Enzyme Regulation
- Detect propionylation on key metabolic enzymes to assess post-translational control under stress or nutrient shifts.
- Understand how acylation affects enzyme activity, stability, and pathway flux.
Microbial and Photosynthetic System Studies
- Investigate propionylation in cyanobacteria, algae, and bacteria to uncover adaptive strategies.
- Analyze photosynthetic regulation and microbial energy balance via lysine acylation patterns.
Drug Discovery and Biomarker Development (Research-Use Only)
- Profile propionylation events to identify novel regulatory proteins or pathway targets.
- Complement broader PTM screening workflows (acetylation, succinylation, etc.) in functional proteomics.
Sample Requirements for Propionylation Proteomics Analysis
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount Required |
|---|---|
| Fresh animal tissue | ≥ 600 mg |
| Fresh plant tissue | ≥ 6 g |
| Cell culture | ≥ 1 × 10⁷ cells per tube × 3 tubes |
| Fungi and bacteria | ≥ 600 mg |
| Serum / Plasma | 450 μL × 4 tubes |
| Protein solution | Total protein of 5–10 mg |
| Body fluids (e.g., urine) | 15 mL × 4 tubes (centrifuge at 1000 × g for 5 min; discard sediment) |
| Other fluids (e.g., saliva, amniotic fluid, cell culture supernatant) | > 15 mL |
FAQ
How will the propionylation analysis results be delivered, and what will the data report include?
We provide a comprehensive report that makes it easy to understand your propionylation analysis results. The report includes clear tables of identified propionylated peptides/proteins along with their modification sites and confidence scores. If your project involves quantitative comparisons (e.g. treated vs control samples), the report will highlight statistically significant changes in propionylation levels between conditions. We also include thorough bioinformatic analyses of the modified proteins – for example, differential protein analysis, clustering, and functional annotations such as Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment or pathway analysis to put the findings in biological context. All results are organized with expert commentary in an easy-to-understand data package, with key findings (like significantly altered propionylation sites) clearly highlighted so you can interpret the data at a glance.
Can propionylation analysis be combined with other post-translational modification (PTM) studies (such as acetylation or methylation)?
Yes. Proteins often carry multiple post-translational modifications simultaneously, so integrating propionylation analysis with other PTM studies can provide a more holistic view of protein regulation. We offer flexibility to either focus on propionylation alone or perform multi-PTM profiling. In a combined PTM workflow, we can design parallel analyses (or sequential enrichment steps) for propionylation and other modifications (like acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, etc.). The data from these analyses can then be integrated to investigate cross-talk between modifications and to understand how propionylation correlates or interferes with other PTMs on the same proteins. This integrative "meta-PTM" approach allows researchers to see the broader regulatory networks and co-modification patterns, which is especially useful in complex signaling or epigenetic studies. Our team can advise on the experimental design to efficiently combine propionylation profiling with other PTM analyses.
What are the technical limitations or common pitfalls in propionylation mass spectrometry workflows?
While propionylation analysis is a powerful technique, there are some important technical considerations and potential pitfalls to be aware of:
Low-Abundance Modifications: Propionylation on proteins is often a low-abundance modification. Without enrichment steps, propionylated peptides might be overwhelmed by unmodified peptides in the sample. We mitigate this by using specific enrichment strategies for propionylated peptides, which is crucial since propionylated proteins/peptides can be present at much lower levels than their unmodified counterparts.
Sample Complexity and Data Analysis: A typical proteomic sample contains thousands of peptides, making modified site identification challenging. Analyzing mass spectra to confidently identify propionylation sites requires specialized software and expert knowledge. Our bioinformatics team uses dedicated PTM search algorithms and validation steps to distinguish true propionylation sites from background signals. Nonetheless, the complexity of the data means that thorough analysis (and often longer processing times) is needed to avoid misidentifications.
Detection Sensitivity (False Negatives): Even with advanced instruments, very low-abundance modified peptides may go undetected if their signal falls below the instrument's detection threshold. It's not uncommon that a protein detectable by a highly sensitive antibody (e.g. Western blot) is not detected by mass spectrometry if its abundance is extremely low. We address this by using high-sensitivity settings and replicate analyses when necessary, but researchers should be aware that absence of a propionylation site in the MS results could mean it was below detection limits rather than truly absent.
Need for Validation: As a best practice, key findings from the discovery workflow may be validated with orthogonal methods. Mass spectrometry results for propionylation (especially novel sites or critical regulatory sites) are often confirmed using targeted approaches like PRM (Parallel Reaction Monitoring) or immunological assays when available. This step helps ensure the modifications identified are real and reproducible, since confirming important low-level PTMs can be challenging. We can provide guidance for follow-up validation strategies if needed.
By anticipating these challenges – using enrichment, advanced analysis tools, careful interpretation, and validation – our service is designed to deliver reliable propionylation data while minimizing common pitfalls.
What instrumentation is used for propionylation analysis, and how do you ensure data quality?
We perform propionylation analysis using state-of-the-art high-resolution LC–MS/MS instrumentation. In particular, we employ modern mass spectrometers (such as Thermo Fisher Orbitrap platforms) known for their high mass accuracy and sensitivity. These instruments allow us to detect propionylated peptides with great confidence, even amid complex protein digests. High-resolution MS is crucial for distinguishing modified peptides and pinpointing propionylation sites with precision.
Quality assurance is a top priority throughout the workflow. We start with rigorous sample preparation and often run an SDS-PAGE or similar check on protein extracts to ensure good sample quality and digestion efficiency before MS analysis. The mass spectrometer itself is calibrated and tuned for optimal performance, and we include appropriate controls or reference standards in runs when possible to monitor consistency. During data processing, we apply strict filters (such as a 1% false discovery rate for peptide identifications) so that only high-confidence propionylation site identifications are reported. We also track key quality metrics in each experiment – for example, the number of peptides and proteins identified, the sequence coverage obtained, and the reproducibility of quantification across replicates. If any of these metrics fall below accepted thresholds, our team will investigate and, if necessary, re-optimize the run or repeat the analysis. Finally, every report is reviewed by experienced scientists to ensure the data quality meets our standards. These measures collectively ensure that the propionylation data you receive are both reliable and accurate.
Is this propionylation analysis service intended for clinical diagnosis or only for research purposes?
Our propionylation analysis service is for research use only. It is not a clinical diagnostic test, and the data we provide should not be used to inform patient care or medical decisions. We emphasize that all results and reports are intended to advance scientific research or drug discovery efforts, not for use in any diagnostic procedures.
Learn about other Q&A.
Demo

Publication

- MS-CETSA functional proteomics uncovers new DNA-repair programs leading to Gemcitabine resistance. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4820265/v1 A proteome-wide profiling study exploring PTM-driven chemoresistance mechanisms in oncology.
- Pan-lysyl oxidase inhibition disrupts fibroinflammatory tumor stroma, rendering cholangiocarcinoma susceptible to chemotherapy. https://doi.org/10.1097/HC9.0000000000000502 Used mass spectrometry-based PTM profiling to characterize tumor microenvironment remodeling.
- Impaired phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments by RPE in CLN3 disease is a consequence of altered sphingolipid metabolism. https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2796715 Demonstrated altered acylation patterns linked to lipid metabolic dysfunction in retinal degeneration.
Case Study: Synechocystis Propionylation Profiling

Yang et al., Lysine Propionylation is a Widespread Post Translational Modification Involved in Regulation of Photosynthesis and Metabolism in Cyanobacteria (Int J Mol Sci, 2019) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194792
- Background
- Technical Approach
- Results
- Conclusion & Implications
- Lysine propionylation is a reversible post-translational modification (PTM), adding a propionyl group to lysine residues via propionyl-CoA. It is known to regulate protein function in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
- Despite its relevance, propionylation had not been systematically explored in photosynthetic organisms.
- Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, a model cyanobacterium, was chosen to study the extent and function of this PTM in photosynthesis and carbon metabolism.
Sample Conditions
Cyanobacteria cultures were exposed to diverse environmental stresses (e.g., high light, nitrogen deficiency, glucose supplementation) to capture condition-dependent propionylation changes.
Enrichment Strategy & MS Workflow
- High-affinity pan-anti-propionyl-lysine antibodies enriched modified peptides.
- Peptides were analysed using high-resolution LC–MS/MS (Orbitrap-class instrumentation).
Data Processing & Bioinformatics
- Propionylation sites were manually validated and mapped onto proteins.
- Functional annotation and pathway enrichment were performed to contextualise the modifications.
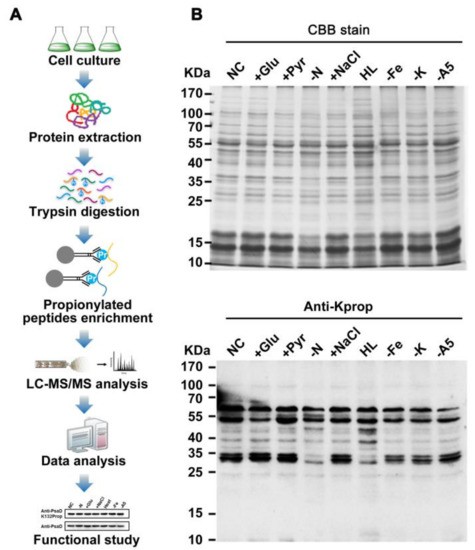 Illustration of this workflow
Illustration of this workflow
Proteome-wide Identification
- A total of 111 propionylation sites were mapped on 69 proteins across photosynthesis and metabolism pathways.
Functional Enrichment
- Bioinformatic analysis showed strong enrichment in photosynthetic protein families and carbon fixation pathways (e.g., Calvin cycle enzymes) .
These results directly parallel our own service outputs that connect PTM mapping with pathway context.
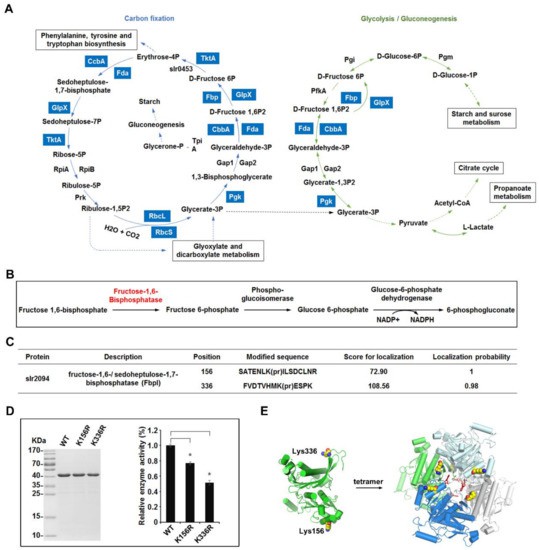 Overview of the lysine propionylation events involved in cellular metabolism in Synechocystis.
Overview of the lysine propionylation events involved in cellular metabolism in Synechocystis.
Targeted Functional Validation
- Fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase (FbpI): Mutagenesis at propionylated lysines resulted in reduced enzyme activity, confirming functional relevance.
- Photosystem I subunit D (PsaD): High-light exposure caused increased propionylation on Lys84, Lys107, and Lys132. This was confirmed via MS/MS and immunoblotting.
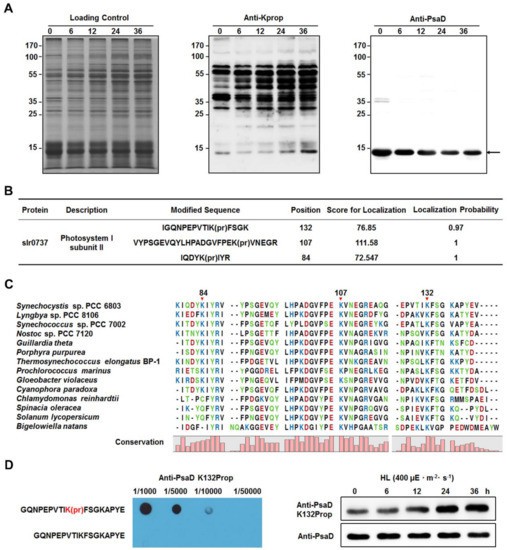 Identification of lysine propionylation in subunit II of photosystem I (PsaD).
Identification of lysine propionylation in subunit II of photosystem I (PsaD).
This study confirmed that propionylation is a functionally significant PTM in cyanobacteria, influencing key metabolic and photosynthetic processes.
- It established that propionylation is environmentally responsive, with modifications correlating to stress conditions.
- It demonstrated the power of integrated workflows combining enrichment, quantitative MS, and bioinformatics for actionable PTM interpretation.
Reference
- Adam F Kebede, et al. Histone propionylation is a mark of active chromatin. Nature structural & molecular biology.(2017). DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3490