Untargeted Lipidomics Service with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Lipids play a crucial role in biological processes such as growth, development, and signal transduction. However, lipid metabolism disorders are also linked to various diseases, including cardiovascular conditions, metabolic disorders, and cancer.
To comprehensively analyze lipid alterations, the research team of Creative Proteomics, leveraging its cutting-edge UPLC-Orbitrap mass spectrometry (QE/HFX) platform for high-throughput lipidomic profiling. This approach integrated LipidSearch software (Thermo Scientific) for robust lipid identification and data processing.
Submit Your Request Now
×- Services Details
- Advantages
- Platform
- Workflow
- Application
- Delivery
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- Case Study
- Publication
- More Service
What Is the Lipidome?
Lipids are essential components of biological membranes, playing a crucial role in energy storage and cell signaling. The lipidome refers to the complete set of lipids within a biological system, including:
- 8 major lipid categories
- 80+ lipid classes
- 300 sub-classes
- Thousands of unique lipid species
Understanding the lipidome is key to studying cellular function, metabolism, and disease mechanisms.
What Is Untargeted Lipidomics?
Untargeted lipidomics is an advanced analytical approach that identifies and quantifies hundreds to thousands of lipid species in a single analysis. Unlike targeted methods, it provides a comprehensive snapshot of the lipid profile, making it a powerful tool for studying health and disease.
Why Is Untargeted Lipidomics Important?
Changes in lipid composition are linked to various diseases, including:
- Cancer – Altered lipid metabolism is a hallmark of tumor progression.
- Diabetes – Lipid imbalances play a role in insulin resistance.
- Alzheimer's Disease – Lipid dysregulation affects neurodegeneration.
- Cardiovascular Disease – Lipidomics helps assess heart disease risk.
By providing detailed lipid profiles, untargeted lipidomics supports precision medicine, allowing for:
Early disease detection
Personalized treatment monitoring
Biomarker discovery
Beyond human health, untargeted lipidomics is widely used in:
Drug discovery – Identifying lipid-based therapeutic targets
Systems biology – Understanding metabolic networks
Agricultural science – Enhancing crop lipid profiles for better nutrition
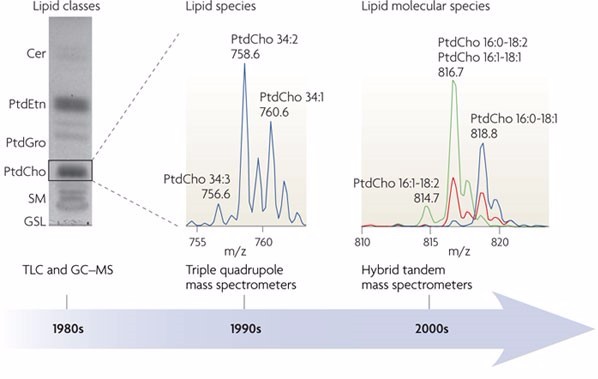 Figure 1. Analytical technologies for understanding the lipidome molecular complexity (Nature Review, Molecular Cell Biology)
Figure 1. Analytical technologies for understanding the lipidome molecular complexity (Nature Review, Molecular Cell Biology)
Comprehensive Untargeted Lipidomics Services
At Creative Proteomics, we provide high-sensitivity, high-reproducibility untargeted lipidomics services using UPLC-Q-TOF mass spectrometry. Our advanced analytical platforms ensure rapid, cost-effective, and reliable lipid profiling across diverse biological samples.
A detailed technical report is provided at the end of each project, including experimental procedures, MS/MS instrument parameters, and data analysis. Raw data processing and statistical analysis are available upon request.
Service Contents
- Comprehensive Plant Lipidomics
- Advanced Yeast Lipidomics
- Mammalian Lipidomics
Lipids are fundamental to plant cell structure, energy metabolism, and stress response. Our advanced plant lipidomics service provides full-spectrum analysis of glycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, and sterols using ultra-sensitive mass spectrometry. Covering leaves, seeds, and roots, this service delivers molecular-level insights into plant metabolic regulation.
Key Advantages of Our Plant Lipidomics Service
- Ultra-Sensitive Detection – Nanomolar-level threshold enables precise identification of low-abundance lipid biomarkers, decoding complex metabolic signatures.
- Broad Sample Compatibility – Supports cross-species analysis, including crops, medicinal plants, and model organisms like Arabidopsis thaliana, across various growth stages.
- Stress Response Mapping – Links lipid remodeling to drought tolerance, pathogen defense, and genetic modifications for resilience studies.
Applications
- Crop Stress Resistance – Tracks membrane lipid dynamics under stress conditions to identify key adaptive pathways.
- Metabolic Engineering – Monitors lipidomic shifts in genetically modified plants, guiding targeted metabolic interventions.
- Bioactive Compound Tracing – Investigates lipid networks in secondary metabolism to enhance the enrichment of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Yeasts, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae and various industrial strains, are vital to biotechnology, biofuel production, and metabolic engineering. Our specialized yeast lipidomics service delivers high-resolution characterization of sterols, glycerophospholipids, and sphingolipids—critical components influencing yeast metabolism and industrial performance.
Key Advantages of Our Yeast Lipidomics Service
Optimized Lipid Extraction – Overcomes yeast's rigid cell walls to maximize lipid recovery.
Metabolic Engineering Support – Provides insights for strain optimization in biofuels, enzyme production, and pharmaceutical applications.
Comparative Lipid Profiling – Enables side-by-side analysis of wild-type and genetically modified strains to assess functional lipid variations.
Comprehensive Service Workflow
- Tailored Sample Preparation – Custom protocols designed for complex matrices, including fermentation broth and solid-state cultures.
- High-Resolution UPLC-QTOF Analysis – Achieves >95% lipid molecular coverage for precise profiling.
- Robust Lipid Annotation – Cross-referenced with the LipidMaps database for accurate compound identification.
- Metabolic Flux and Lipid Remodeling Models – Provides in-depth insights into lipid dynamics for pathway optimization.
Lipid imbalances play a hidden yet critical role in metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory conditions. Our comprehensive mammalian lipidomics platform offers customized profiling for plasma, tissue samples, cerebrospinal fluid, and cell cultures. Through precision biomarker identification, we accelerate breakthroughs in medical research.
Core Service Advantages
- Clinical-Grade Biomarker Discovery – AI-assisted lipid profiling pinpoints disease-specific signatures in cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions, expediting drug target validation.
- Ultra-High-Resolution Lipid Mapping – UPLC-Q-TOF MS delivers ppm-level quantification, overcoming biological matrix complexity to capture low-abundance lipid variations.
- Intelligent Data-Driven Diagnostics – Integrates KEGG pathway enrichment, machine learning modeling, and multi-omics validation to generate clinically actionable lipid-based strategies.
By bridging lipidomics with precision medicine, we empower researchers to identify novel therapeutic targets and enhance disease research.
Why Choose Our Lipidomics Services?
- Extensive Lipid Database – LipidSearch database with 1.7 million lipid molecules, covering 8 major categories and 300 subcategories
- High Identification Capability – Average projects detect 3,000+ lipid species, with some exceeding 5,000
- Cutting-Edge Technology – QE-series high-resolution mass spectrometry combined with high-efficiency chromatography for high-throughput lipid analysis
- Stringent Quality Control – Industry-leading QC workflows ensure highly accurate qualitative and quantitative lipidomics data
- Broad Sample Compatibility – Supports cells, tissues, blood, urine, feces, bacteria, nematodes, and more
- Multi-Omics Integration – Combine lipidomics with transcriptomics and proteomics to uncover complex metabolic pathways
Key features of the lipidomic analysis included:
Lipidomics Core Facility
Our lipidomics core facility is equipped with state-of-the-art separation and analytical platforms, including the Thermo Orbitrap Exploris 480. Our expert team has developed optimized protocols to ensure the highest data accuracy, reproducibility, and quality.
 Thermo Orbitrap Explories480 (thermofisher.com)
Thermo Orbitrap Explories480 (thermofisher.com)
Our Lipidomics Workflow
Our untargeted lipidomics analysis is powered by LC-MS/MS technology, following a standardized workflow:
Sample Collection & Lipid Extraction
Experiment Design & Data Acquisition (LC-MS/MS)
Data Preprocessing (Peak extraction, PQN correction, data filtration)
Differential Lipid Analysis (PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA, t-tests)
Lipid Identification & Functional Annotation (KEGG pathway, metabolic network analysis)
Comprehensive Data Interpretation

Our expert team ensures optimized protocols, stringent quality control, and in-depth statistical analysis to deliver highly accurate lipidomics insights.
Untargeted Lipidomics Data Analysis Workflow
Untargeted lipidomics leverages mass spectrometry (MS) and advanced bioinformatics to identify and analyze lipid metabolites. Our workflow ensures high-quality data processing, statistical validation, and biological interpretation.
Three Key Stages of Lipidomics Data Analysis
Quality Control & Basic Data Analysis
Differential Lipid Analysis
Functional Annotation & Pathway Analysis
This structured approach enables researchers to identify lipid biomarkers, track metabolic changes, and uncover disease-related lipid dysfunctions.
 Data analysis process
Data analysis process
Data Analysis Content
| Type of analysis | Analysis content | Problem to be solved |
|---|---|---|
| Quality control | TIC, OC, etc. | Obtain high quality data |
| Profile | Superclass | Obtain classification information |
| Difference analysis | Univariate statistical analysis (volcano plot, etc.) | Reflects between-group differences for each variable |
| Multidimensional statistical analysis (PCA, PLSDA, OPLSDA, etc.) | Assess the difference between groups and find the influencing variables that lead to the difference between groups | |
| Functional analysis | hierarchical cluster analysis | Obtaining expression pattern information for metabolites |
| Correlation analysis | Measures the degree of correlation between two variables | |
| KEGG analysis | Learn more about relevant metabolic pathways and functions | |
| Advanced analysis | Regression analysis | Establish associations between important metabolites and other indicators |
| Trend clustering analysis | Exploring the trend pattern of metabolite levels | |
| Machine learning | Screening for biomarkers with good diagnostic performance |
Applications of Lipidomics Profiling
Untargeted lipidomics enables a comprehensive analysis of lipid profiles, helping researchers uncover key metabolic changes linked to health and disease. By comparing experimental and control groups, this approach provides valuable insights into lipid function and regulation.
Key Applications:
Lipid Identification: Comprehensive detection of lipid species in biological samples
Functional Lipidomics: Investigating lipid functions and their role in metabolic regulation
Lipidomics Pathway & Network Analysis: Mapping lipid metabolism pathways and interactions
Biomarker Discovery: Identifying lipid-based biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis
Deliverables
1. Experiment Procedures
2. Parameters of Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometer
3. MS Raw Data Files
4. MS Data Quality Checks
5. Metabolites Quantification Data
6. Bioinformatics Analysis (PCA, KEGG, etc)
Sample Requirement
| Sample Type | Normal Sample Volume | Minimum Sample Volume | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell | Cell | ≥ 107 | ≥ 107 |
| Animal tissue | Liver, kidney, etc. | ≥ 100 mg | ≥ 60 mg |
| Body fluids | Plasma/serum, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. | ≥ 200μL | ≥ 100μL |
| Special samples | Please inquire separately | ||
Lipidomics Results Interpretation
Our untargeted lipidomics workflow leverages LipidSearch software for lipid identification, peak extraction, and data alignment. The processed dataset undergoes quality control and statistical analysis to generate meaningful insights.
Case Study: Client Success Stories
Lipidomic Profiling Services by Creative Proteomics Inc. in Deciphering Metabolic Adaptations of Mitochondrial-Deficient Nematodes
- Background
- Methodology
- Results and Conclusion
Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a variety of metabolic and age-related diseases. In a recent study, researchers investigated the role of insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS) inhibition in rescuing mitochondrial-deficient Caenorhabditis elegans. The study aimed to understand the metabolic adaptations that enable survival under compromised mitochondrial conditions. A key aspect of this research was the identification of lipidomic changes associated with IIS inhibition, necessitating a precise and comprehensive lipidomic analysis.
To gain a deeper understanding of the lipid alterations, the research team partnered with Creative Proteomics Inc., a leading provider of lipidomic profiling services. Using state-of-the-art ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS), Creative Proteomics conducted a high-throughput lipidomic analysis on C. elegans mutants, including wild-type, IIS-inhibited, and mitochondrial-deficient strains. The analysis provided:
Comprehensive Lipid Profiling: Identification and quantification of diverse lipid species, including triacylglycerols (TAGs) and phospholipids.
Comparative Analysis: A detailed comparison of lipid compositions between different mutant strains to uncover metabolic shifts.
Statistical Interpretation: Advanced data processing to highlight significantly altered lipid pathways.
The lipidomic analysis by Creative Proteomics Inc. revealed that IIS inhibition did not significantly reduce storage lipid levels, such as triacylglycerols, in mitochondrial-deficient nematodes. This finding suggested that lifespan extension in these mutants was driven by alternative metabolic adaptations rather than enhanced lipid catabolism. Furthermore, the study identified xanthine accumulation as a key metabolic signature associated with IIS inhibition, providing a novel therapeutic target for mitochondrial disorders.
 Figure 4A illustrating the lipidomic profiling results comparing gas-1 and age-1; gas-1 mutants.
Figure 4A illustrating the lipidomic profiling results comparing gas-1 and age-1; gas-1 mutants.
By leveraging the lipidomic expertise of Creative Proteomics Inc., the research team successfully elucidated critical metabolic changes underlying mitochondrial dysfunction. This case highlights the essential role of advanced lipidomic profiling in uncovering novel biochemical pathways and potential therapeutic strategies in metabolic disease research.
Our Untargeted Lipidomics Review

- White matter lipid alterations during aging in the rhesus monkey brain. Dimovasili, C., Vitantonio, A. T., Conner, B., Vaughan, K. L., Mattison, J. A., & Rosene, D. L. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-024-01353-3
- Annexin A2 Controls Lipid Composition Necessary for Junctional Stability in Response to Sphingosine 1-Phosphate (Doctoral dissertation). Sveeggen, T. 2022. https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/handle/1969.1/198138
- Characterising Chinese Hamster Ovary cell extracellular vesicle production in biopharmaceutical manufacturing (Doctoral dissertation, University of Sheffield). O'Donnell, F. 2022. https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/33062/
- Multi‐omics identify xanthine as a pro‐survival metabolite for nematodes with mitochondrial dysfunction. Anna Gioran et al. 2019. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899558
Choosing the Right Metabolomics Approach for Your Research
Creative Proteomics has established a first-class metabolomics and lipidomics research platform. Based on mass spectrometry technology, the platform integrates the advantages of untargeted, targeted, or broad-targeted MS analysis to achieve high-throughput, high-sensitivity, and broad-coverage omics analysis.
Here's a breakdown of their differences in molecular detection, quantification methods, analytical techniques, and applications. It supports various omics studies in biomedical research.
1. Key Differences Among Metabolomics Approaches
| Feature | Untargeted Metabolomics | Targeted Metabolomics | Broad-Targeted Metabolomics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Metabolites | Highest (thousands) | Lowest (dozens to hundreds) | Moderate (hundreds to thousands) |
| Quantification Type | Relative quantification (peak area) | Absolute quantification (ng/mL, µM) | Semi-quantitative or relative quantification |
| Analytical Technique | High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) | Triple quadrupole MS (QqQ) in MRM/SRM mode | Combination of HRMS and QqQ |
| Key Advantage | Discover new metabolites, explore metabolic networks | Highly precise quantification for clinical and validation studies | Balances high-throughput screening and quantification accuracy |
2. Quantification Methods
Untargeted metabolomics: Measures relative metabolite abundance based on ion intensity (peak area/height); Ideal for exploratory research, biomarker discovery, and metabolic pathway analysis.
Targeted metabolomics: Uses calibration curves from authentic standards for absolute concentration measurement; Best for clinical validation, pharmacokinetic studies, and precise metabolite quantification.
Broad-targeted metabolomics: Incorporates internal standards or calibration curves to provide semi-quantitative data; Suitable for in-depth mechanistic studies, offering both breadth and accuracy.
References
- Jia Z, Qiu Q, He R, Zhou T, Chen L. Identification of Metabolite Interference Is Necessary for Accurate LC-MS Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Anal Chem. 2023;95(20):7985-7992. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00804
- Chen L, Lu W, Wang L, et al. Metabolite discovery through global annotation of untargeted metabolomics data. Nat Methods. 2021;18(11):1377-1385. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01303-3
- Jang C, Chen L, Rabinowitz JD. Metabolomics and Isotope Tracing. Cell. 2018;173(4):822-837. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.055
- Li F, Song J, Zhang Y, et al. LINT-Web: A Web-Based Lipidomic Data Mining Tool Using Intra-Omic Integrative Correlation Strategy. Small Methods. 2021;5(9):e2100206. doi:10.1002/smtd.202100206
- Gioran A, Piazzesi A, Bertan F, Schroer J, Wischhof L, Nicotera P, Bano D. Multi-omics identify xanthine as a pro-survival metabolite for nematodes with mitochondrial dysfunction. EMBO J. 2019 Mar 15;38(6):e99558. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899558. Epub 2019 Feb 22. PMID: 30796049; PMID: 30796049
- Yamada, Y., Akita, H., Kamiya, H., Kogure, K., Yamamoto, T., Shinohara, Y., Yamashita, K., Kobayashi, H., Kikuchi, H., & Harashima, H. (2008). MITO-Porter: A liposome-based carrier system for delivery of macromolecules into mitochondria via membrane fusion. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.11.002
- Liang Z. Assessment of the Construction of a Climate Resilient City: An Empirical Study Based on the Difference in Differences Model. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 21;18(4):2082. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18042082. PMID: 33669915; PMCID: PMC7924589.