Progesterone Analysis Service
Creative Proteomics specializes in high-precision progesterone and metabolite analysis using advanced LC-MS/MS platforms. We provide quantitative and pathway-level insights across diverse biological matrices to support endocrine research, toxicology studies, and systems biology. Our service delivers reproducible, low-CV data with full transparency—empowering researchers to decode hormonal dynamics with confidence.
Submit Your Request Now
×- What We Provide
- Advantage
- Workflow
- Technology Platforms
- Sample Requirements
- FAQ
- Publication
What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a naturally occurring C21 steroid hormone synthesized primarily in the corpus luteum of the ovaries, as well as in the adrenal glands and placenta. It is structurally defined by a cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene backbone, featuring a ketone group at C3 and a double bond between C4 and C5.
Functionally, progesterone plays a central role in regulating reproductive and endocrine physiology. In mammals, it is essential for establishing uterine receptivity, supporting embryo implantation, and maintaining pregnancy by inhibiting myometrial contractions. Beyond its reproductive functions, progesterone contributes to neuroendocrine regulation, immune modulation, and transcriptional control through binding to nuclear progesterone receptors (PR-A and PR-B isoforms).
Progesterone also acts as a metabolic precursor in steroid biosynthesis, giving rise to hormones such as cortisol, aldosterone, and estrogens via enzymatic conversion in the steroidogenic pathway. Interestingly, its presence has also been reported in plants and marine organisms, underscoring its evolutionary conservation across biological kingdoms.
Progesterone Analysis Service Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Progesterone Quantification: Measurement of progesterone concentrations in various biological samples including plasma, serum, urine, and saliva.
- Progesterone Metabolite Profiling: Identification and quantification of progesterone metabolites in serum, urine, and other fluids, utilizing advanced LC-MS/MS methods.
- Hormonal Disruption Studies: Analysis of progesterone levels in the context of exposure to environmental toxins, pharmaceuticals, or endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
- Pharmacokinetic Studies: Measurement of progesterone concentration over time in drug development or clinical trial settings to assess the pharmacodynamics of progesterone analogs or treatments.
- Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Mapping of progesterone's metabolic pathways and its interaction with other hormones like estrogen, cortisol, and testosterone.
List of Detected Progesterone and Related Metabolites
| Metabolite | Description | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnanediol | Primary urinary metabolite of progesterone, used as a biomarker for luteal function | LC-MS/MS |
| 17α-OHP | Intermediate in adrenal steroidogenesis, commonly studied in endocrine research | LC-MS/MS |
| Allopregnanolone | Neuroactive steroid influencing GABA-A receptor activity; key in neuroendocrinology | LC-MS/MS |
| Pregnenolone | Precursor molecule in the steroid hormone biosynthesis pathway | LC-MS/MS |
| 5α-Dihydroprogesterone | Peripheral metabolite with implications in uterine and neurological pathways | LC-MS/MS |
| Progesterone sulfate | Sulfated form of progesterone; part of phase II metabolism | LC-MS/MS |
| Androstenedione | Intermediate in androgen and estrogen biosynthesis; cross-pathway relevance | LC-MS/MS |
| Corticosterone | Glucocorticoid precursor involved in adrenal hormone pathways | LC-MS/MS |
| 20α-Dihydroprogesterone | Inactive metabolite formed via reduction; indicates progesterone deactivation | LC-MS/MS |
| 11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC) | Mineralocorticoid precursor derived from progesterone metabolism | LC-MS/MS |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) | Key precursor in both androgen and estrogen pathways; intersects with progesterone metabolism | LC-MS/MS |
| Cortisol | Major stress hormone synthesized downstream from progesterone | LC-MS/MS |
| Estrone (E1) | Primary estrogen metabolite; part of hormone balance analysis alongside progesterone | LC-MS/MS |
| 3α,5α-Tetrahydroprogesterone (THP) | Allopregnanolone precursor; exhibits potent neurosteroid effects | LC-MS/MS |
| 3β,5α-Tetrahydroprogesterone | Isomer of THP with differing receptor activity in the nervous system | LC-MS/MS |
| 17β-Estradiol | Principal estrogen involved in reproductive hormone balance | LC-MS/MS |
| Androsterone | Androgen metabolite; reflects interplay between androgen and progesterone pathways | LC-MS/MS |
Advantages of Progesterone Assay
- Precision & Reproducibility: All quantifications are performed with a coefficient of variation (CV) below 10%, ensuring high reliability and reproducibility of data across replicates and sample batches.
- Superior Sensitivity: Utilizing UHPLC-MS/MS technology, our platform achieves detection limits as low as 0.09 μg/L for 8-OHdG and 0.04 μg/L for related oxidative DNA damage metabolites—enabling detection even in trace-level samples.
- High Throughput Metabolomics Integration: Capable of simultaneous profiling of over 500 endogenous metabolites, including oxidized nucleotides, base excision repair intermediates, and purine metabolism products—ideal for systems biology and oxidative stress network analysis.
- Matrix Versatility: Our methods are validated across a comprehensive range of biological matrices.
- Internal Standard Normalization: All quantifications employ stable isotope-labeled internal standards, significantly improving data accuracy and compensating for matrix effects.
- End-to-End Data Transparency: All results are reported with raw chromatograms, standard curves, and quantification metrics for full scientific traceability.
Workflow for Progesterone Analysis Service
Technology Platform for Plasmalogen Analysis Service

Thermo Fisher Q Exactive (Figure from Thermo Fisher)

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)

Agilent 7890B-5977B (Figure from Agilent)
Sample Requirements for Progesterone Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Required Volume | Storage Condition | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | ≥ 100 µL | -80°C | Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| Plasma (EDTA/Heparin) | ≥ 100 µL | -80°C | Centrifuge immediately after collection |
| Urine | ≥ 500 µL | -80°C or -20°C (short-term) | First morning urine preferred for hormone studies |
| Saliva | ≥ 500 µL | -20°C | Collect using validated saliva collection kits |
| Tissue | ≥ 50 mg | Snap frozen in liquid nitrogen; store at -80°C | Provide tissue type and treatment details |
| Cell Lysate | ≥ 100 µL | -80°C | Include total protein concentration if available |
| CSF (Cerebrospinal Fluid) | ≥ 100 µL | -80°C | For neurosteroid analysis applications |
| Cultured Media | ≥ 1 mL | -20°C or -80°C | Serum-free media recommended to avoid interference |
Applications of Progesterone Assay Service
Endocrine Disruption Research
Analyze progesterone fluctuations in response to environmental toxins, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), and xenobiotics in toxicology studies.
Reproductive Biology and Fertility Studies (Non-Clinical)
Investigate progesterone's regulatory role in ovulation cycles, implantation models, and reproductive physiology in animal or in vitro systems.
Steroidogenesis Pathway Mapping
Quantify progesterone alongside other steroid intermediates to study the regulation and flux of steroid hormone biosynthesis pathways.
Neurosteroid Research and Brain-Gut Axis Studies
Explore the impact of progesterone and its metabolites (e.g., allopregnanolone) on neuronal function, stress response, and neuroendocrine signaling.
Agricultural and Veterinary Research
Measure progesterone levels in livestock and animal models to monitor hormonal changes related to estrus cycles and reproductive management.
Pharmacokinetic and Hormonal Compound Evaluation
Assess the absorption, distribution, and metabolic behavior of progesterone or progesterone-modulating compounds in preclinical models.
Demo
FAQ of Progesterone Analysis Service
Can your platform distinguish progesterone from isobaric compounds (e.g., 17α-OHP)?
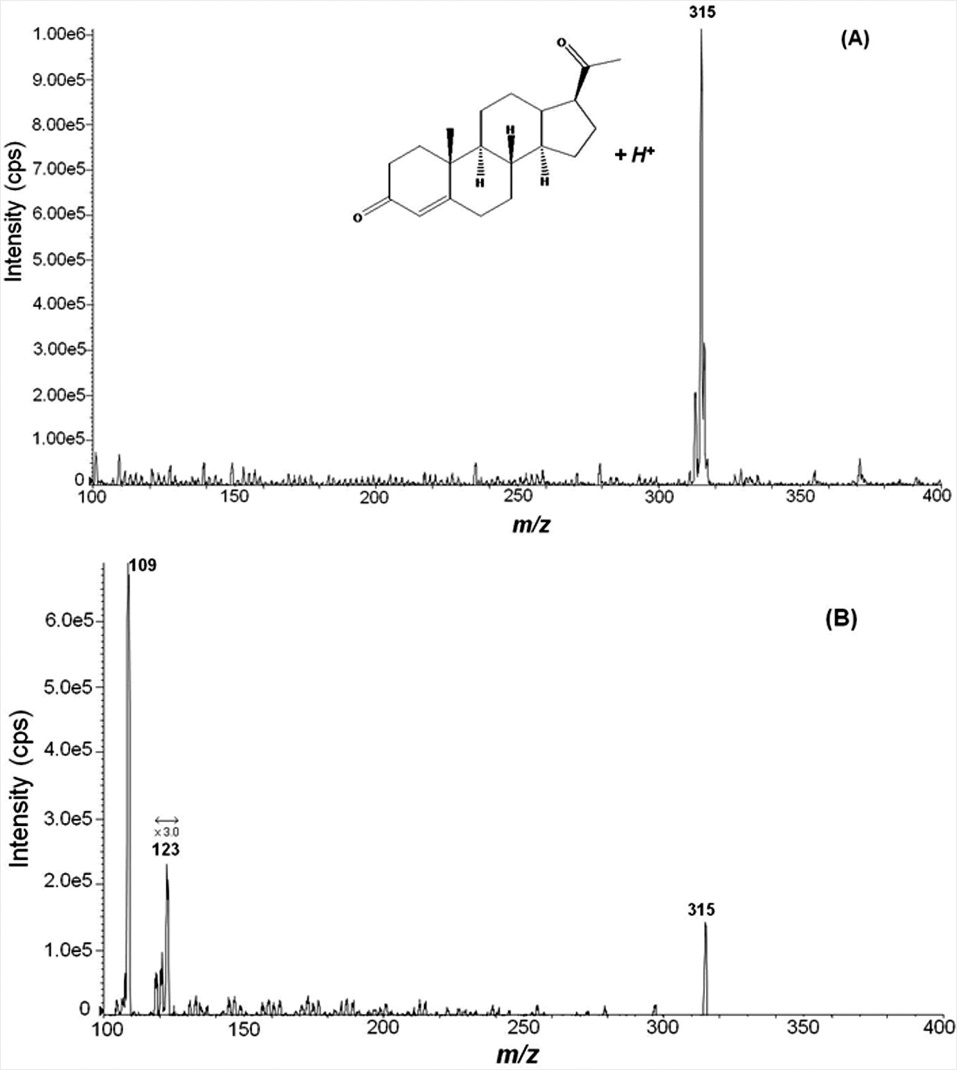
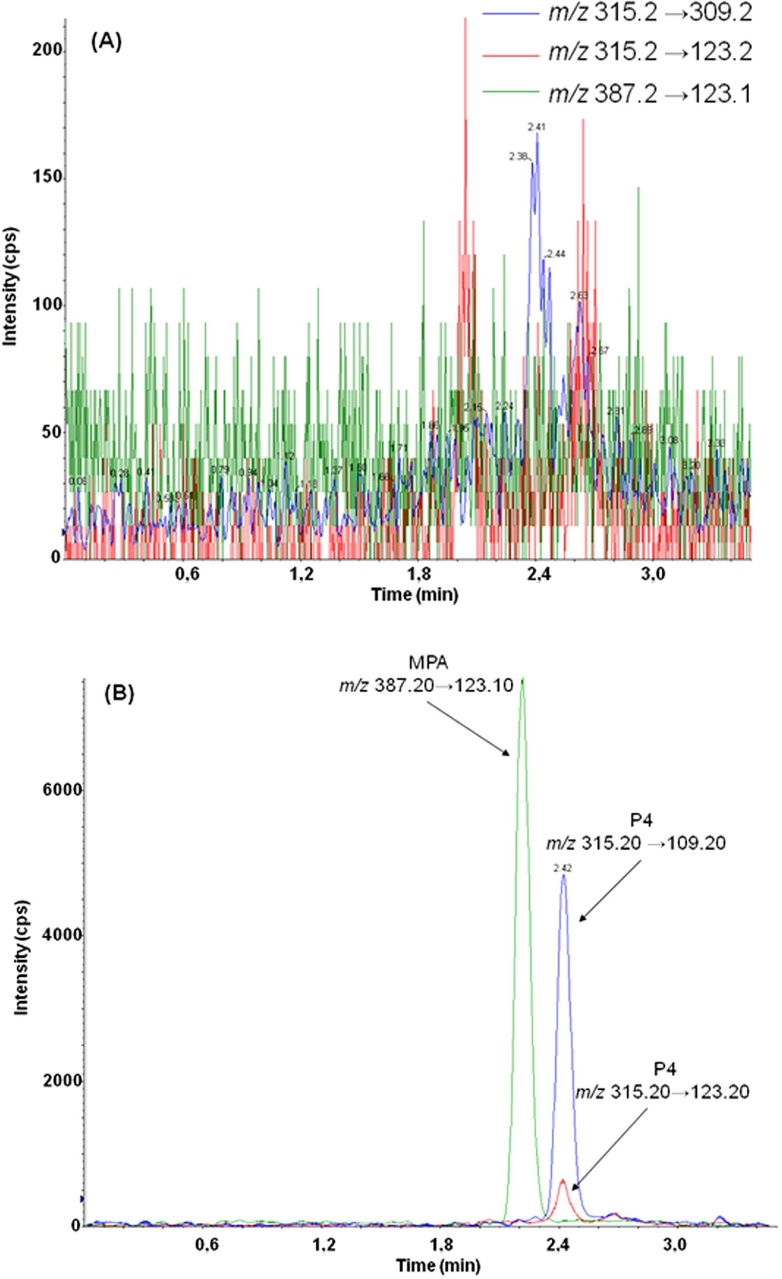
Yes. We use compound-specific MRM transitions and chromatographic separation (C18 column, 1.8 µm, 2.1×100 mm). For example, progesterone (315.3 → 97.1 m/z) and 17α-OHP (331.3 → 109.1 m/z) elute with >1.2 min retention time separation under our standard LC gradient.
What internal standards are used in quantification?
We employ stable isotope-labeled standards such as progesterone-d9 and allopregnanolone-d4 to ensure accurate normalization. These correct for matrix suppression and extraction efficiency across diverse sample types.
Can Creative Proteomics support time-course or dose-response studies?
Absolutely. Our analytical pipeline supports high-throughput profiling with robust inter-run consistency (CV<7%). Batch-to-batch comparability is ensured through the use of pooled QC samples and shared calibration curves.
Is metabolite stability during storage a concern?
Yes, particularly in biological fluids. We recommend storing samples at -80°C and avoiding >2 freeze-thaw cycles. For sensitive metabolites (e.g., tetrahydroprogesterones), sample stabilization with BHT or immediate extraction is advisable.
Can you perform absolute quantification with standard curves?
Yes. Quantification is achieved using external standard curves with 5–8 concentration points, fitted by linear regression (R² > 0.998). Calibration curves are matrix-matched wherever possible.
Do you offer metabolite pathway visualization or statistical analysis?
Yes. For multi-group studies, we offer optional bioinformatics services, including PCA, heatmaps, and pathway enrichment visualization (KEGG/SMPDB) to contextualize progesterone and its metabolites in broader biological networks.
Can I analyze progesterone metabolites from archived FFPE tissues?
Yes, with limitations. While steroid recovery is lower than in frozen tissues, we have optimized extraction protocols using deparaffinization and LC-compatible solvents. Please consult us before submission for sample-specific guidance.
Do you support non-targeted detection of unknown steroid metabolites?
Yes. Using high-resolution Orbitrap LC-MS (Q Exactive™), we provide untargeted steroid profiling and post-acquisition data mining (mzCloud, MassBank) for novel compound annotation.
Learn about other Q&A.
Progesterone Analysis Service Case Study
Publications
Here are some publications in Metabolomics research from our clients:

- The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475
- Methyl donor supplementation reduces phospho‐Tau, Fyn and demethylated protein phosphatase 2A levels and mitigates learning and motor deficits in a mouse model of tauopathy. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12931
- Nutritional analysis of commercially available, complete plant-and meat-based dry dog foods in the UK. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.11.612409
- Lipid droplet-associated lncRNA LIPTER preserves cardiac lipid metabolism. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-023-01162-4
- Ketone bodies are mildly elevated in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and are inversely associated with insulin resistance as measured by the lipoprotein insulin resistance index. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9020321
Reference
- Fernandes, R. M. T., et al. "LC-MS/MS quantitation of plasma progesterone in cattle." Theriogenology 76.7 (2011): 1266-1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2011.05.033