Hydroxylation Analysis – LC-MS/MS Profiling of Protein Hydroxylation
Hydroxylation transfers hydroxyl (-OH) groups to specific amino acid residues and associated with collagen-related disorders, cancer, and hypoxia pathways. Creative proteomics provide high-precision hydroxylation research services focused on the identification and quantification of amino acid hydroxylation modifications.
- Comprehensive detection: Identify and quantify hydroxylated proteins and site-specific amino acid modifications.
- Advanced technology: LC-Ms/Ms + immunoprecipitation enrichment for precision and depth.
- Functional insights: Integrated bioinformatics for motif, pathway, and network interpretation.
- Research impact: Clarify hydroxylation critical roles in protein stability, enzymatic activity, and disease pathogenesis.
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Define
- What We Provide
- Technology Platform
- Workflow
- Advantages
- Applications
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case
- Publications
- Sample Requirement
What Is Hydroxylation?
Hydroxylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an enzyme catalyses the introduction of a hydroxyl (-OH) group onto specific amino acid residues. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) represents the primary oxygen-sensitive regulatory modification involving proline hydroxylation. This modification is primarily catalyzed by 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs), lysyl hydroxylases, and factor inhibiting HIF (FIH). These enzymes require oxygen (O₂), iron (Fe²⁺), α-ketoglutarate (also known as 2-oxoglutarate; 2-OG), and ascorbic acid (vitamin C). PHDs utilize one oxygen atom from O₂ during the oxidative decarboxylation of 2-OG to produce succinate and CO₂, while another directly incorporates into the oxidized amino acid residues of HIF-α. Furthermore, enzymatic hydroxylation reactions have been observed in asparagine, aspartic acid, arginine, histidine, and lysine residues. Hydroxylation plays central roles in oxygen sensing, transcriptional regulation, and protein stability. It controls the hypoxic response through HIF degradation, modulates protein–protein interactions, and influences phase separation and organelle assembly. Collectively, hydroxylation represents a versatile modification linking environmental signals to structural and functional outcomes in diverse proteins[1].
Hydroxylation Service at Creative Proteomics
Hydroxylation is an important post-translational modification of proteins, and its dysregulation is associated with collagen-related disorders, cancer, and hypoxia pathways. Systematic investigation of hydroxylated proteins is essential for understanding their biological and pathological functions. Our hydroxylation analysis service provides precise identification and quantification of hydroxylated peptides using high-resolution LC–MS/MS and immunoprecipitation enrichment. This service enables researchers to explore enzyme-specific hydroxylation events and uncover their biological significance across different models.
Hydroxylation Research Platforms

Thermo Fisher Easy-nLC 1000 and Thermo Fisher LTQ Obitrap ETD
(Figure from Thermo Scientific)
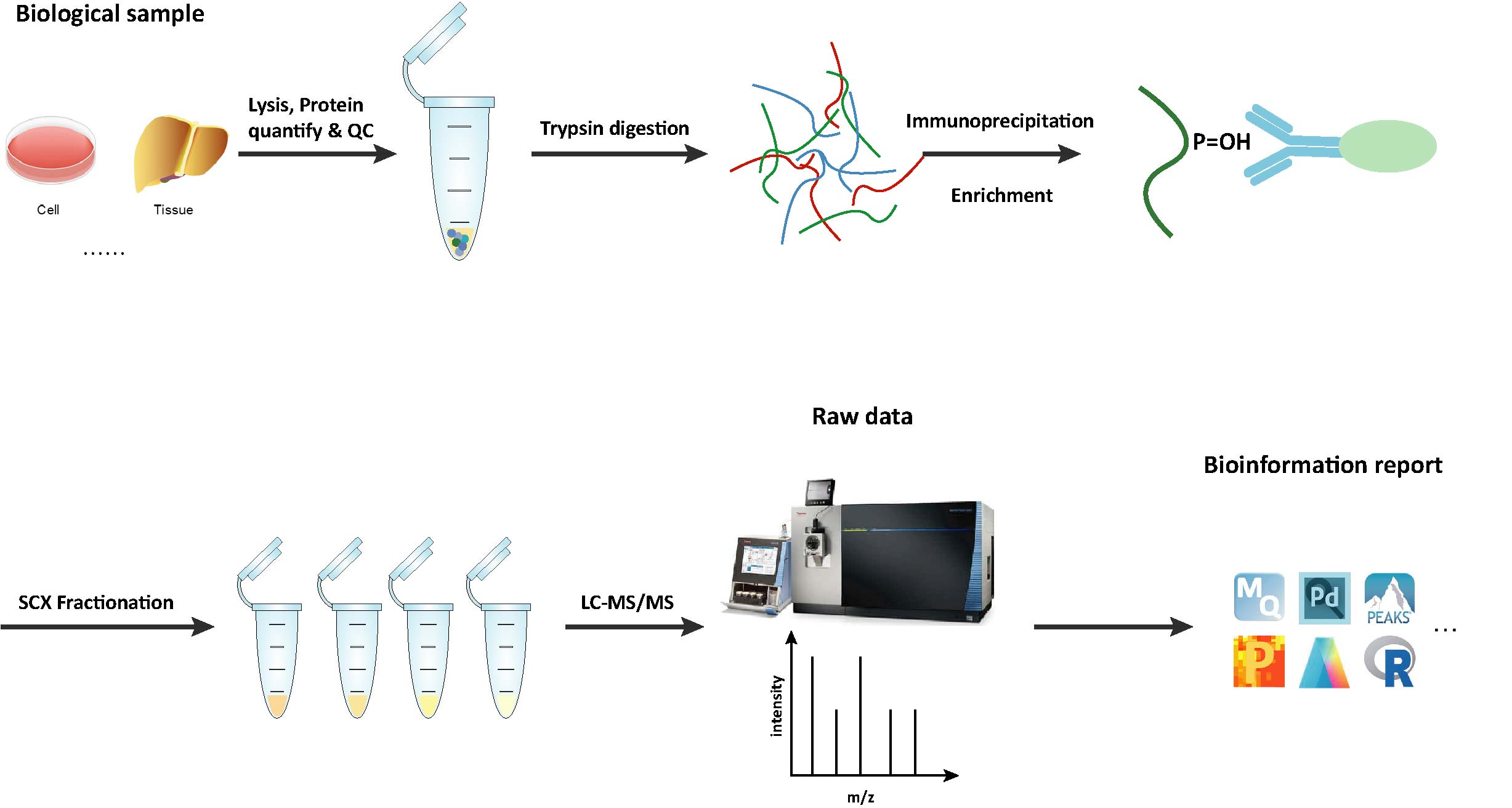
Workflow of Hydroxylation Analysis
Advantages Our Hydroxylation Service
- Professional detection and analysis capability: Supported by an experienced research team and well-established, rigorously validated methodologies.
- Broad Sample Compatibility: Proficient in handling protein samples derived from diverse sources, including cells, animal and plant tissues, and microorganisms.
- High specificity and accuracy: Advanced quantitative proteomics techniques combined with robust PTM enrichment strategies ensure precise and reliable measurements.
- High stability and reproducible: Consistently delivers robust and reproducible results with excellent inter- and intra-assay consistency, enabling reliable downstream data analysis.
- Advanced Analytical Platforms: Use of high-sensitivity mass spectrometry and state-of-the-art tools, ensuring precise, repeatable results.
- End-to-End Support: Offer full-spectrum services from design to data interpretation, with continuous technical support throughout the research process.
Applications of Hydroxylation



Protein interactions and regulations
JMJD family enzymes catalyze lysine hydroxylation on histones and non-histone proteins, linking hydroxylation to transcriptional regulation, RNA processing, and cancer-related signaling pathways.[2].
Therapeutic Targeting
Pharmacological inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases stabilizes HIF and enhances erythropoiesis, demonstrating hydroxylation as a therapeutic target for anemia in chronic kidney disease[3].
Physiological state of animals
Hydroxyproline modulation supports collagen synthesis, antioxidant defense, and signal regulation in response to nutritional and hypoxic conditions[4].
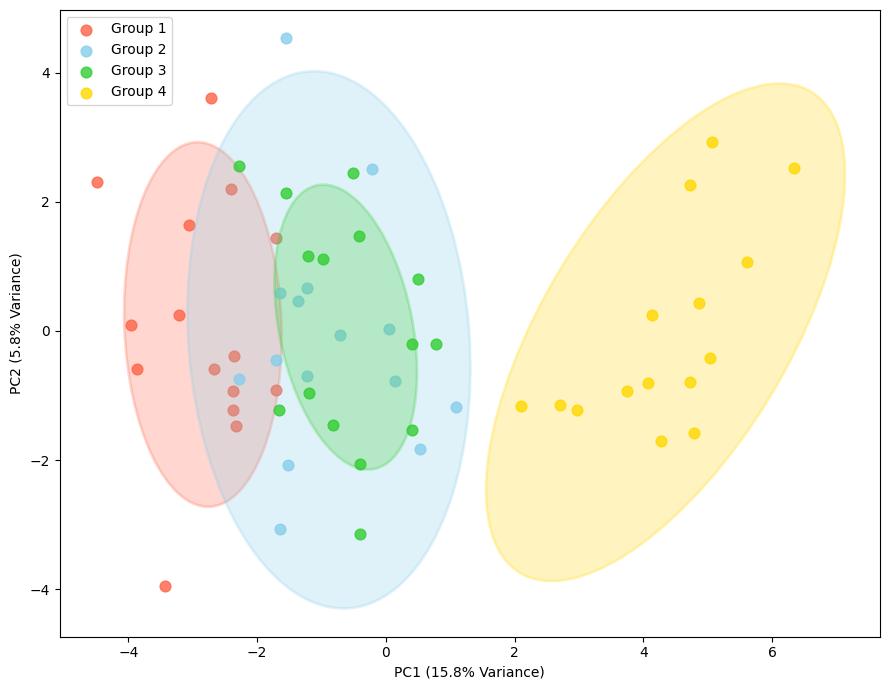
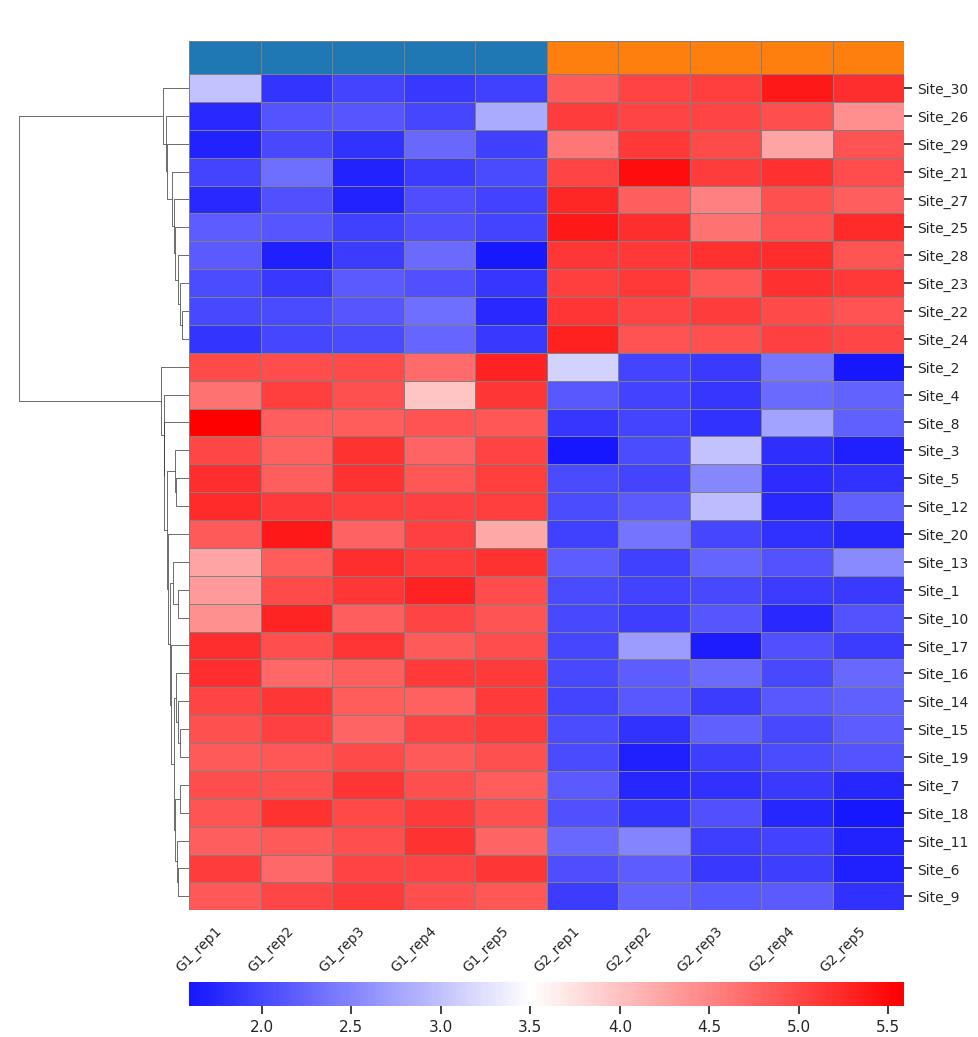
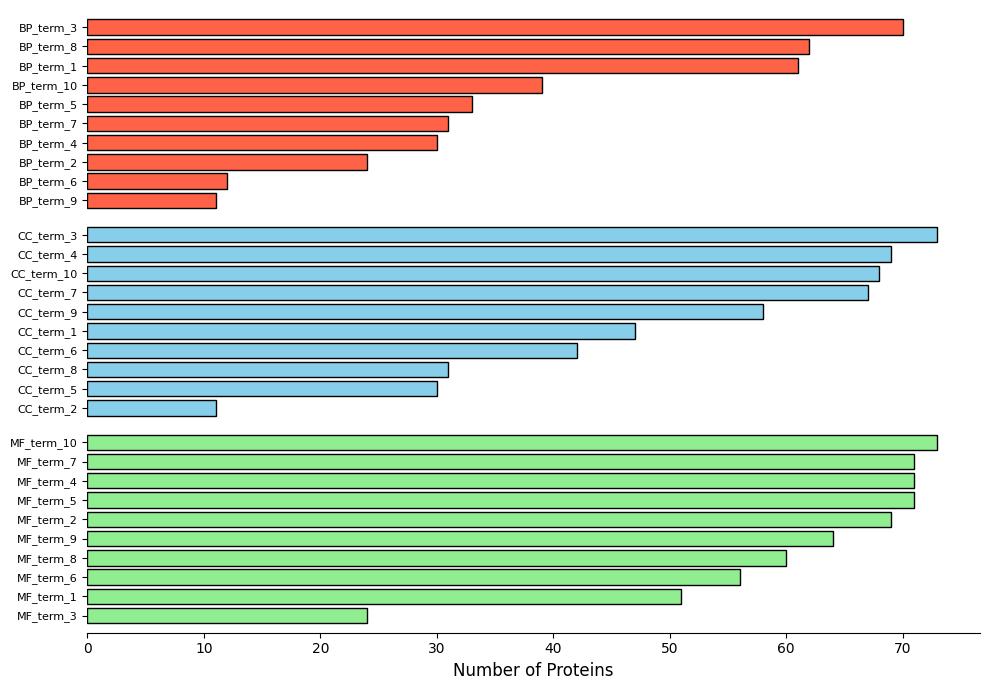
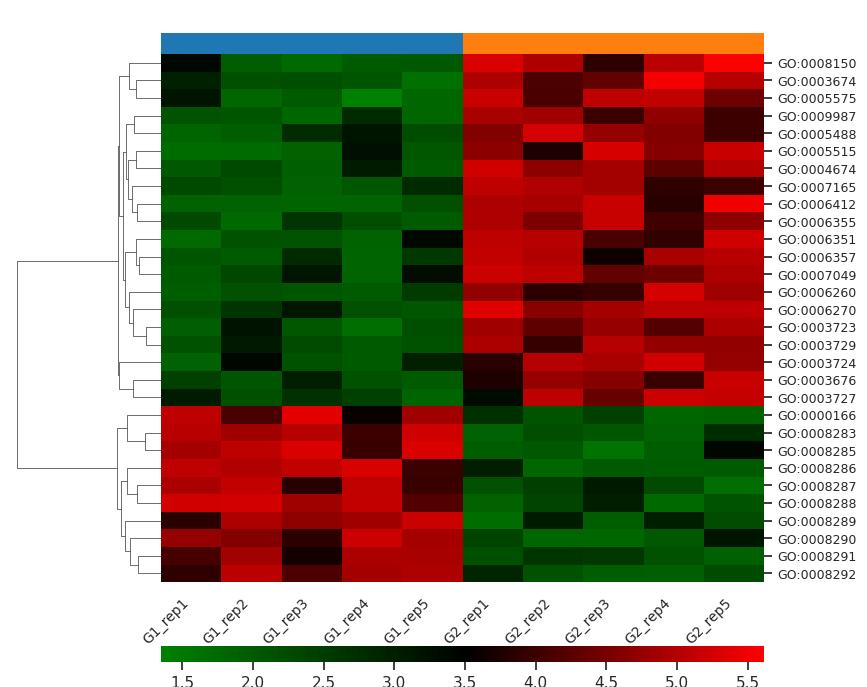
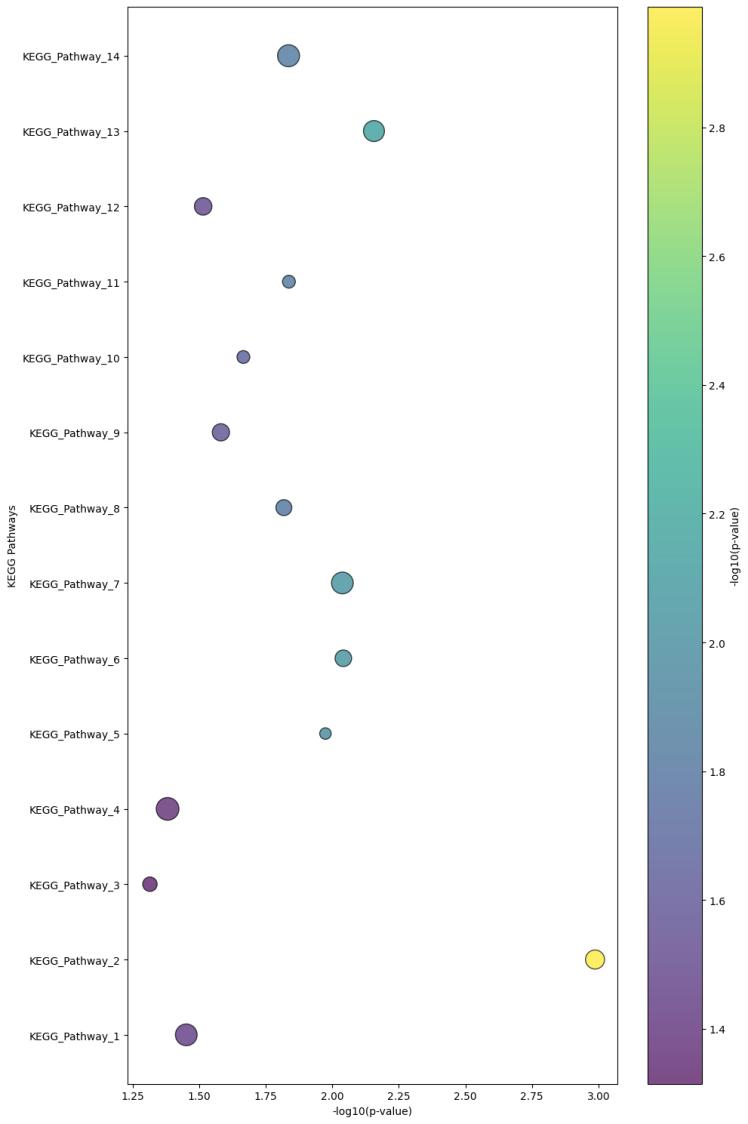
Demo Result of Hydroxylation Service
FAQs of Hydroxylation Service
Which sample types are accepted by the service?
We accept a variety of sample types including cells, tissues, plant tissue and more. If you have other special sample types, please consult in advance.
Whether the sample needs pretreatment?
We recommend that customers provide fresh or frozen samples, which should avoid repeated freezing and thawing, and we will be responsible for subsequent protein extraction and pretreatment. If you have already extracted the protein, please communicate with us in advance about the sample handling method.
What are the common targets for hydroxylation detection?
We can detect hydroxylation modifications of various amino acid residues such as proline (Pro), lysine (Lys), asparagine (Asn), and histidine (His), and it is particularly suitable for studies on HIF pathway proteins, collagen family proteins, and metabolic-related enzymes.
Learn about other Q&A.
Case Study

Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Calcium homeostasis and stable fatty acid composition underpin heatwave tolerance of the keystone polychaete Hediste diversicolor. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.110885
- APOB100 transgenic mice exemplify how the systemic circulation content may affect the retina without altering retinal cholesterol input. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.61.13.19
- Assessment of Fasciola hepatica glutathione S-transferase as an antigen for serodiagnosis of human chronic fascioliasis. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.07.002
- Characterizing the proteome of bullous pemphigoid blister fluid utilizing tandem mass tag labeling coupled with LC–MS/MS. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-021-02253-8
- Impact of alanyl-tRNA synthetase editing deficiency in yeast. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab766
Hydroxylation Service Sample Requirements
| Sample | Sample Quantity | |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | animal tissue | 200-500mg |
| fresh plant | 200-500mg | |
| Cell | suspension cell | > 3x108 |
| adherent cell | > 3x108 | |
| microorganism | > 50 mg or 3 × 108 cells | |
References
- Zurlo, G., Guo, J., Takada, M., Wei, W., & Zhang, Q. (2016). New Insights into Protein Hydroxylation and Its Important Role in Human Diseases. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1866(2), 208–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.09.004
- Oh, S., & Janknecht, R. (2024). Versatile JMJD proteins: juggling histones and much more. Trends in biochemical sciences, 49(9), 804–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2024.06.009
- Ren, S., Yao, X., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Tong, C., & Feng, Y. (2023). Efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor treatment for anemia in chronic kidney disease: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Frontiers in pharmacology, 14, 1296702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1296702
- Hu, S., He, W., & Wu, G. (2022). Hydroxyproline in animal metabolism, nutrition, and cell signaling. Amino acids, 54(4), 513–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03056-x.