S-Persulfidation Analysis – LC-MS/MS Mapping of Protein Persulfide Modifications
Protein S-persulfidation is a reversible process that alters the thiol groups (-SH) of cysteine residues into persulfides (-SSH). This modification helps in boosting antioxidant defenses, controlling redox signaling, and maintaining protein function during oxidative stress. Creative Proteomics offers precise research services aimed at identifying and measuring protein S-persulfidation.
- Comprehensive Detection: Identify and measure S-persulfidated proteins and specific amino acid modifications.
- Advanced Technology: Utilize biotin labeling and enrichment techniques combined with LC-MS/MS for accuracy and depth.
- Functional Insights: Apply bioinformatics tools to analyze motifs, pathways, and network interactions.
- Research Impact: Clarify the regulatory roles of S-persulfidation in signaling pathways and offer new perspectives for understanding mechanisms and identifying therapeutic targets in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Define
- What We Provide
- Technology Platform
- Workflow
- Advantages
- Applications
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case
- Publications
- Sample Requirement
What is S-persulfidation?
Protein S-persulfidation, also known as S-sulfhydration, is a reversible redox modification where the thiol group of cysteine residues is transformed into a persulfide. This process is critical for hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) to perform its biological functions. It mainly occurs when H₂S reacts with oxidized cysteine intermediates or transfers sulfur through small molecule persulfides and sulfur transferases. This modification enhances antioxidant capacity by protecting proteins from damage due to irreversible oxidation, regulates enzyme activity and redox signaling, and helps in maintaining cellular balance. Persulfidation plays a significant role in metabolism, mitochondrial function, cardiovascular and neuroprotection, and its reduction is linked to aging and various diseases. Being a dynamic and reversible post-translational modification, S-persulfidation is a key element connecting H₂S signaling to protein regulation[1].
S-persulfidation Service at Creative Proteomics
Understanding S-persulfidation is essential for exploring redox-based regulatory processes and discovering new biomarkers or therapeutic targets related to oxidative stress diseases. Therefore, identifying S-persulfidated proteins and their specific amino acid sites in biological tissues or cells is crucial. We provide complete proteomics services for analyzing S-persulfidated proteins, including high-resolution mass spectrometry, site-specific identification, quantitative profiling, and advanced bioinformatics analysis. Our services assist researchers in systematically studying S-persulfidated proteins, exploring their pathway connections, and uncovering their clinical and therapeutic significance.
S-persulfidation Research Platforms

Thermo Fisher Easy-nLC 1000 and Thermo Fisher LTQ Obitrap ETD
(Figure from Thermo Scientific)
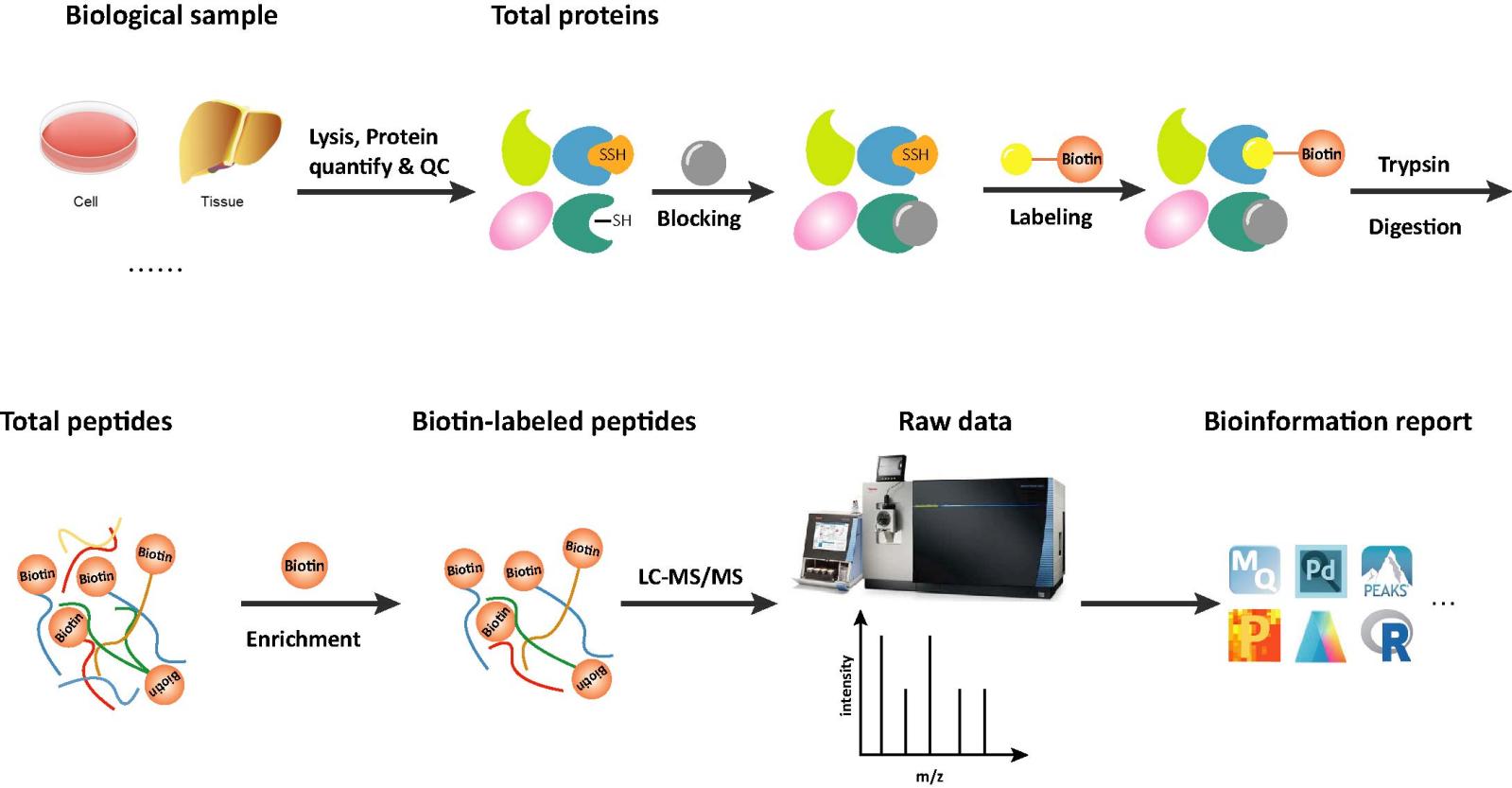
Workflow of S-persulfidation Analysis
Advantages of Our S-persulfidation Service
- Professional Detection and Analysis: Experienced research team with reliable and established techniques.
- Broad Applicability: We can handle protein samples from a wide range of sources such as cells, animal and plant tissues, microorganisms, etc.
- High Specificity and Accuracy: Use of skilled quantification proteomics techniques and PTMs enrichment methods.
- Consistent and Reproducible Results: Obtain stable and repeatable inter- and intra-assay results for data analysis.
- Advanced Analytical Platforms: Utilization of high-sensitivity mass spectrometry and state-of-the-art technologies to ensure precise and repeatable results.
- End-to-End Support: Provide full-service from design to data interpretation with continuous technical support throughout the research process.
Applications of S-persulfidation





Neurodegenerative disease
In neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, lower levels of protein S-persulfidation lead to reduced activity, abnormal phosphorylation, and increased aggregation of proteins such as Parkin and GSK3β, thereby promoting neuronal damage and the progression of disease[2][3].
Macrophages and inflammation
In activated macrophages involved in inflammation, protein S-persulfidation helps by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activity, reducing inflammatory cell death[4].
Senescence and Sarcopenia
During aging, the production of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) decreases due to reduced expression of H₂S-producing enzymes, such as cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), leading to lower levels of protein S-persulfidation. This reduction weakens antioxidant defenses, impairs mitochondrial function, and interferes with proteostasis, accelerating aging and contributing to the loss of muscle mass and function (sarcopenia)[3].
Cardiometabolic health
In the cardiovascular system, S-persulfidation helps maintain vasodilation, mitochondrial balance, and antioxidant capacity by modifying key enzymes and signaling proteins. A deficiency or decrease in this modification worsens inflammation, increases oxidative damage accumulation, and raises the risk of myocardial structural changes and heart failure[2].
COVID-19
During a COVID-19 infection, the body's reduced production of H₂S and lower levels of S-persulfidation disrupt redox balance, impair mitochondrial function, and amplify inflammatory responses, which facilitate viral replication, lung injury, and vascular or coagulation issues[2].
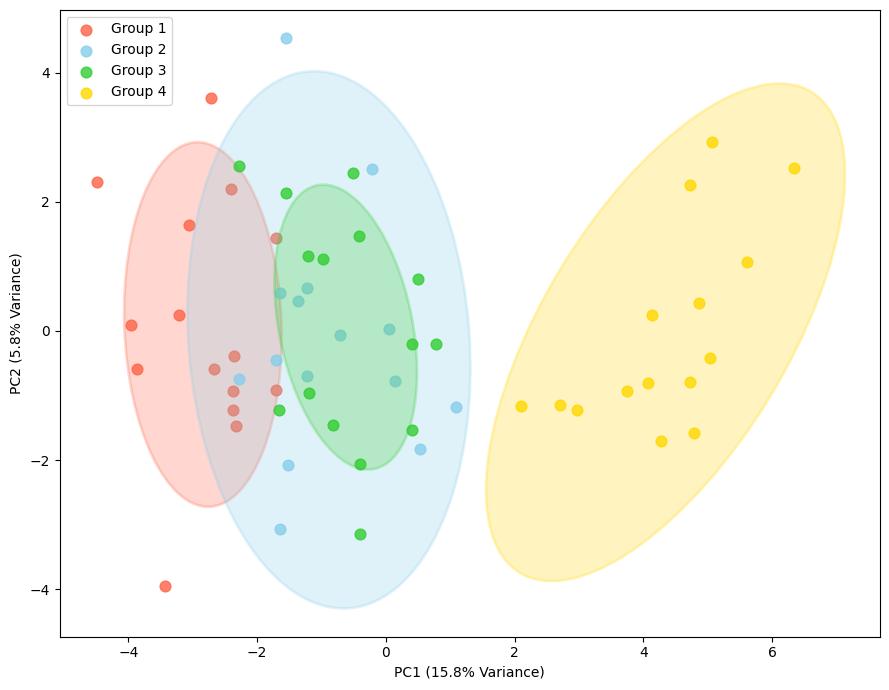
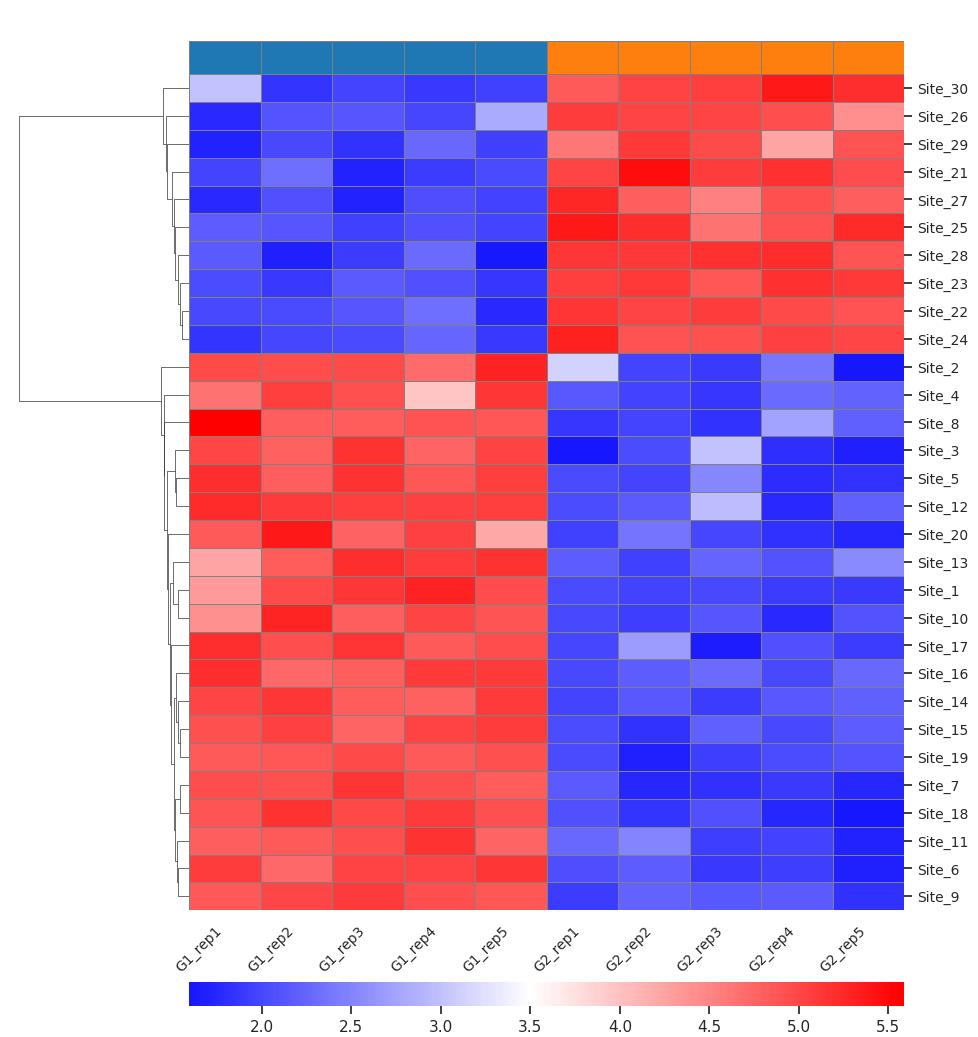
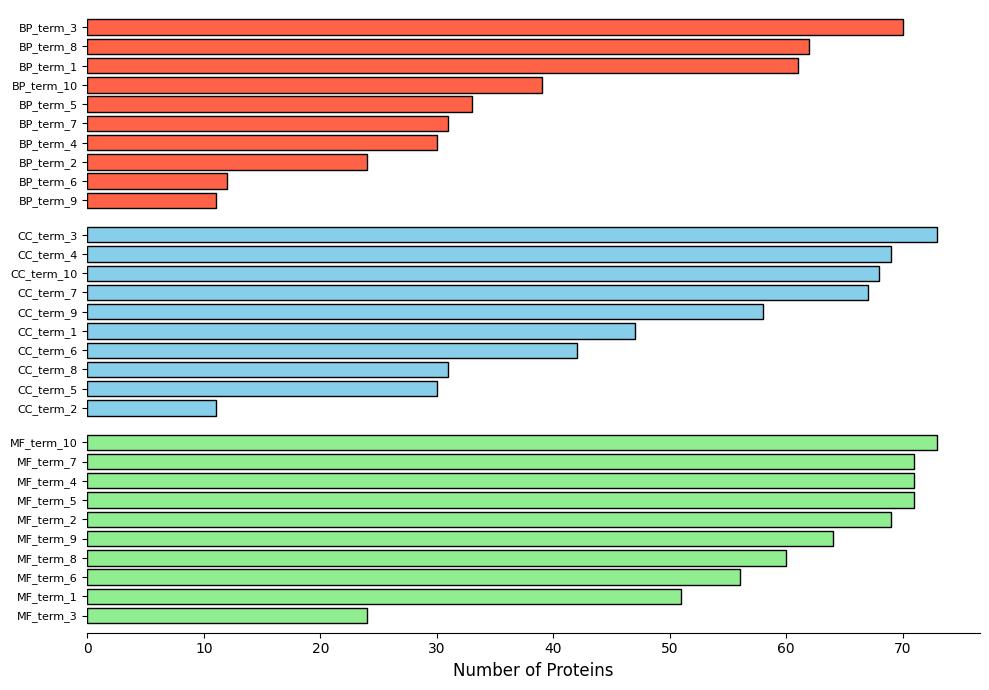
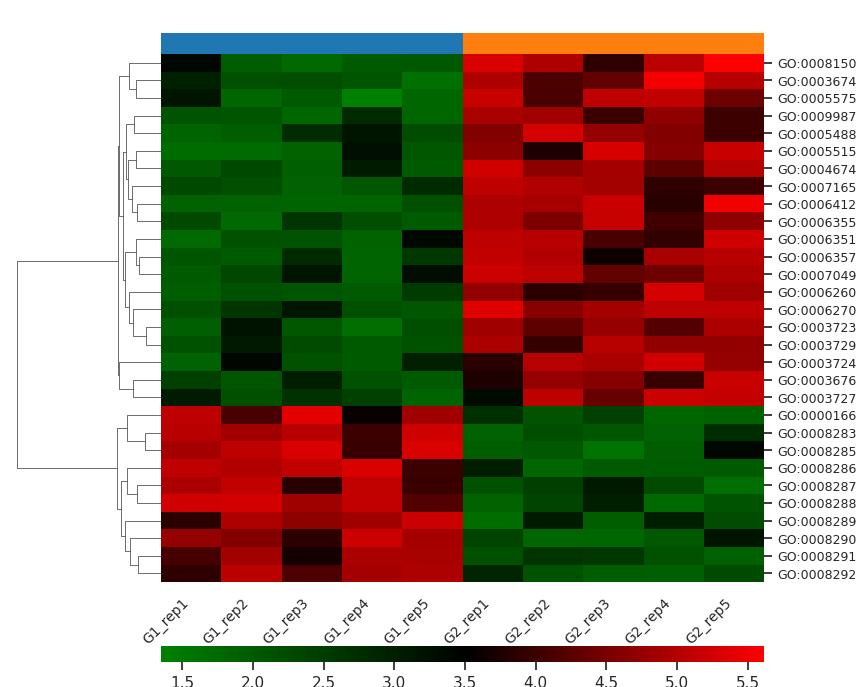
Demo Result of S-persulfidation Service
FAQs of S-persulfidation Service
Which sample types are accepted by the service?
We accept a variety of sample types including cells, tissues, plant tissue and more. If you have other special sample types, please consult in advance.
Whether the sample needs pretreatment?
We recommend that customers provide fresh or frozen samples, which should avoid repeated freezing and thawing, and we will be responsible for subsequent protein extraction and pretreatment. If you have already extracted the protein, please communicate with us in advance about the sample handling method.
Learn about other Q&A.
Case Study

Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- The yeast protein Mam33 functions in the assembly of the mitochondrial ribosome. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008476
- Molecular signature of the ontogenic development of the prawn Macrobrachium tenellum. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.16344
- Impact of alanyl-tRNA synthetase editing deficiency in yeast. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab766
- Immunoproteomics characterization of Leishmania panamensis proteins for potential clinical diagnosis of mucosal Leishmaniasis. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12824
- Extracellular vesicles regulate metastable phenotypes of lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells via shuttling ATP synthesis to pseudopodia and activation of integrin adhesion complexes. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.09.611297
S-persulfidation Service Sample Requirements
| Sample | Sample Quantity | |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue | animal tissue | 200-500mg |
| fresh plant | 200-500mg | |
| Cell | suspension cell | > 3x108 |
| adherent cell | > 3x108 | |
| microorganism | > 50 mg or 3 × 108 cells | |
| Protein | Total protein > 5mg and concentration >1 μg/μL | |
References
- Andrés, C. M. C., Lobo, F., Lastra, J. M. P., Munguira, E. B., Juan, C. A., & Pérez Lebeña, E. (2025). Reactive Sulfur Species and Protein Persulfidation: An Emerging Redox Axis in Human Health and Disease. Current issues in molecular biology, 47(9), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090765
- Petrovic, D., Kouroussis, E., Vignane, T., & Filipovic, M. R. (2021). The Role of Protein Persulfidation in Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 13, 674135. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.674135
- Salti, T., Braunstein, I., Haimovich, Y., Ziv, T., & Benhar, M. (2024). Widespread S-persulfidation in activated macrophages as a protective mechanism against oxidative-inflammatory stress. Redox biology, 72, 103125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2024.103125