Niacin/ Nicotinic Acid/Vitamin B3 Quantification Service
Quantify and distinguish niacin forms for nutrition, metabolism, and drug research
Niacin (Vitamin B3), in the form of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide, is an essential cofactor in energy metabolism, lipid regulation, and DNA repair. Accurate quantification is crucial for nutritional assessment, pharmaceutical development, and metabolic pathway studies.
At Creative Proteomics, we offer advanced HPLC and LC-MS-based niacin analysis services with exceptional sensitivity and reproducibility. Our platform enables detection of trace niacin levels and clear separation of niacin derivatives such as NMN, NR, NAD, and NADP.
Service Advantages:
Ultra-Sensitive Detection: LC-MS down to nanogram–picogram levels.
Comprehensive Profiling: Niacin and metabolites in biological & pharmaceutical samples.
Custom Solutions: Tailored workflows for nutrition science, drug discovery, and metabolic research.
Reliable Results: Publication-ready data with strict quality control.
Submit Your Request Now
×
- Overview
- Our Services
- Workflow
- Technology
- Applications
- Sample Requirements
- Deliverables
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Publications
- Demo
What is Niacin / Vitamin B3 Analysis
Did you know that a single vitamin directly supports energy metabolism, lipid balance, and DNA repair? That vitamin is niacin—also known as Vitamin B3 or nicotinic acid. Its simple molecular structure (C₆H₅NO₂), first described in the 19th century, masks its central role in human biology.
Niacin is one of the 13 essential vitamins and acts as a biochemical gateway to NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These two coenzymes regulate redox balance, drive ATP production, and maintain genomic stability. Accurate measurement of niacin and its metabolites enables researchers to explore metabolic health, nutritional status, and therapeutic interventions with confidence.
Niacin is found in common foods such as liver, poultry, fish, cereals, legumes, and peanuts. The body can also synthesise it from tryptophan, although this conversion is limited. A deficiency once led to the widespread disease pellagra, recognised by skin damage, diarrhoea, and neurological symptoms. Today, niacin remains widely used in pharmaceutical formulations targeting cholesterol regulation and metabolic disorders, and its measurement is critical in both nutritional science and drug development. Recent lipidomics studies show that niacin derivatives are increasingly analysed in clinical and preclinical settings to track subtle metabolic changes.
For research teams working in nutrition, metabolism, or pharmaceutical development, precise niacin analysis is indispensable. Partner with Creative Proteomics to access reliable HPLC and LC-MS/MS quantification, tailored reporting, and expert support to advance your next study.
Niacin Analysis Services at Creative Proteomics
Reliable quantification of niacin (Vitamin B3) is essential for nutrition science, metabolic research, and pharmaceutical development. Even minor fluctuations in niacin or its derivatives can significantly affect energy balance and redox pathways, making accurate measurement critical for high-quality data.
At Creative Proteomics, we provide end-to-end niacin analysis services powered by advanced HPLC and LC-MS/MS platforms. Our workflows ensure sensitive, reproducible, and publication-ready results across a wide variety of biological and pharmaceutical matrices. Whether analysing plasma, serum, tissue extracts, or nutritional supplements, our methods are designed for precision and flexibility.
Our niacin assays support both in vitro and in vivo studies, delivering actionable insights into metabolic health and therapeutic applications. Trusted by academic labs, pharmaceutical companies, and biotech partners, our service integrates isotope-labelled standards, strict quality control, and expert bioinformatics to meet diverse research objectives.
Key Niacin Analysis Services We Provide:
- Quantitative Niacin Measurement – Accurate concentration profiling in biological and clinical samples.
- Pharmaceutical and Nutritional Testing – Verification of niacin levels in supplements and drug formulations.
- Customized Niacin Analysis – Flexible study designs tailored from small-scale projects to multi-centre trials.
Whether you are evaluating nutrient absorption, conducting drug efficacy studies, or mapping metabolic pathways, our niacin analysis services provide the sensitivity and reliability needed to advance your research.
Workflow
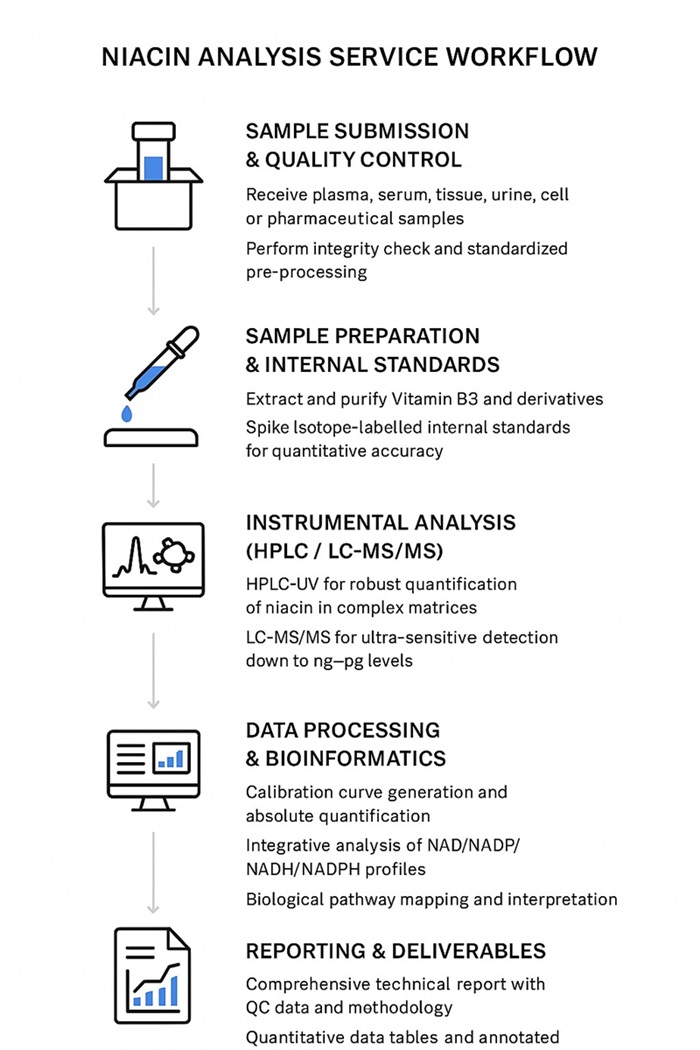
Technology Platforms for Niacin (Vitamin B3) Analysis
Choosing the right analytical platform is critical for accurate niacin quantification. Subtle differences between nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and newer derivatives require sensitive and reproducible technologies.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with UV Detection
HPLC coupled with UV detection at 261 nm provides a robust, widely adopted method for niacin quantification. It is particularly effective for separating polar, non-volatile compounds such as Vitamin B3 in complex sample matrices.
Why Use HPLC for Niacin Analysis?
- High Sensitivity – Detects low niacin concentrations in plasma, serum, and tissue extracts.
- Wide Application Range – Suitable for both nutritional and pharmaceutical investigations.
- Quantitative Accuracy – Delivers reproducible results, ideal for routine clinical and laboratory studies.
Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
LC-MS/MS integrates liquid chromatography separation with the ultra-sensitive detection of tandem mass spectrometry, making it the gold standard for niacin and derivative profiling. It enables detection of trace metabolites and clear identification in complex biological systems.
Why Use LC-MS/MS for Niacin Analysis?
- Unmatched Sensitivity – Detects niacin down to nanogram or picogram levels.
- High Specificity – Differentiates nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, NMN, NR, and related metabolites.
- Versatile Application – Applicable to drug formulations, biological samples, and fortified foods.
Applications of Niacin Analysis
Niacin and its derivatives play critical roles in cellular metabolism, making accurate profiling valuable across multiple research areas:
Nutritional Science – Assess dietary intake, monitor vitamin status, and evaluate niacin bioavailability in functional foods and supplements.
Pharmaceutical Development – Support drug discovery by tracking NAD+ pathway modulation, lipid regulation, and redox balance.
Clinical & Translational Research – Explore niacin's role in healthy aging, cardiovascular health, and metabolic disease progression.
Metabolic Pathway Studies – Quantify NAD/NADP/NADH/NADPH to link niacin metabolism with energy production and mitochondrial function.
Nutraceutical and Food Industry – Verify label claims, ensure batch consistency, and perform regulatory-compliant quality control.
By integrating niacin profiling into broader lipidomics and metabolomics workflows, Creative Proteomics helps researchers generate actionable insights that connect nutritional inputs with metabolic and therapeutic outcomes.
Sample Requirements for Niacin Analysis
| Sample Type | Required Volume/Weight | Storage Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma/Serum | 200 μL | Store at -80°C | Use heparin or EDTA as anticoagulants. Avoid hemolysis. |
| Blood | 500 μL | Store at -20°C | Whole blood samples should be collected in EDTA tubes. |
| Tissue Samples | 50 mg | Store at -80°C | Freeze tissue samples immediately after collection. |
| Urine | 500 μL | Store at -80°C | Ensure samples are free from particulates or debris. |
| Cell Culture Samples | 1 x 10⁶ cells | Store at -80°C | Freeze cell pellets rapidly after harvesting. |
| Pharmaceuticals | 5-10 mg | Store at room temperature or 4°C | Provide detailed product information for context-specific testing. |
Deliverables: What You Receive
Every niacin analysis project is delivered with a complete reporting package designed to support publication and regulatory needs:
Detailed Technical Report – Experimental design, sample preparation details, and instrument parameters (HPLC/LC-MS/MS).
Calibration Curves & QC Data – Standard curves, detection limits, and internal QC metrics for method validation.
Quantitative Data Tables – Absolute and relative concentrations of niacin and derivatives across your samples.
Annotated Chromatograms & Spectra – Clear visual outputs including HPLC peak profiles and LC-MS/MS spectra.
Interpretative Summary – Expert commentary linking results to biological relevance, metabolic pathways, and research implications.
Publication-Ready Outputs – Figures, graphs, and formatted tables suitable for inclusion in scientific manuscripts or regulatory submissions.
Optional Raw Data Files – Complete datasets available for reanalysis or in-depth review.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How sensitive is niacin analysis using HPLC and LC-MS, and how does it impact my research?
HPLC-based niacin analysis can reliably detect Vitamin B3 in the low microgram range, which is suitable for nutritional studies and pharmaceutical testing, while LC-MS/MS provides greater sensitivity, detecting niacin and its derivatives down to nanogram or even picogram levels. This capability is critical in pharmacokinetic studies and low-concentration matrices such as cerebrospinal fluid, where small concentration changes must be tracked precisely, making LC-MS/MS the recommended method for complex research requiring differentiation of niacin derivatives.
Can your niacin analysis distinguish between different forms of Niacin, such as nicotinic acid and nicotinamide?
Yes, our LC-MS/MS workflows can separate and quantify nicotinic acid, nicotinamide (niacinamide), and emerging derivatives including nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), which is valuable because each form plays a unique role in human metabolism, such as nicotinamide in DNA repair and nicotinic acid in cholesterol regulation, allowing targeted insights for nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and metabolic research projects.
How stable is niacin in biological samples, and what precautions should I take during sample collection and storage?
Niacin is stable when stored correctly, but degradation can occur through heat, light, or enzymatic activity; plasma and serum should be stored at -80°C immediately after collection, tissues must be rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and cell culture pellets should also be frozen quickly at -80°C, while pharmaceutical samples should be kept in cool, dry conditions and shipped on dry ice to maintain stability.
Can Creative Proteomics analyze niacin levels in supplements and food products?
Yes, our niacin analysis service covers both supplements and food matrices, enabling precise quantification of Vitamin B3 content for quality control and regulatory compliance, as well as bioavailability studies that assess how effectively niacin is absorbed and utilized, which is crucial for product formulation in the nutraceutical and functional food industry.
What is the typical turnaround time for niacin analysis, and can it be expedited?
Standard turnaround time is 5 to 10 business days depending on sample type and complexity, but expedited niacin analysis can be requested for urgent studies, with results typically delivered within 3 to 5 business days, making this service especially useful for clinical trials, drug development timelines, or regulatory submissions.
Can Creative Proteomics assist in method development and validation for niacin analysis?
Yes, we provide method development and validation tailored to sample type, matrix, and concentration range, following strict regulatory guidelines for accuracy, precision, linearity, sensitivity, and specificity, ensuring that validated workflows can be used confidently in both research and GMP-compliant regulatory submissions.
Does Creative Proteomics offer niacin metabolite analysis?
Yes, our LC-MS/MS platform quantifies key niacin metabolites including NAD, NADP, and their reduced forms (NADH, NADPH), which are essential for energy metabolism and redox balance, providing researchers with deeper insights into cellular health, metabolic pathways, and therapeutic strategy development.
What if I have a very small sample size? Can you still perform niacin analysis?
Yes, even microliter volumes of plasma or small tissue biopsies can be analysed, as LC-MS/MS is highly sensitive to trace analytes, and we adjust protocols to maximize detection accuracy, which benefits studies with limited material such as paediatric trials, rare sample research, or biopsy-based investigations.
Can niacin analysis be performed on genetically modified organisms (GMOs) or transgenic models?
Yes, our platform supports analysis of samples from GMOs and transgenic models, enabling accurate quantification of Vitamin B3 in both plant and animal systems, which is valuable for research on how genetic modifications alter metabolic pathways, including studies using CRISPR or other transgenic approaches.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Client Case Study

NAD3® Supplementation Enhances Cellular NAD+ and Lipid Metabolism
- Project Background
- Client Challenges
- How Creative Proteomics Helped
- Results
Auburn University and The Center for Applied Health Sciences launched the Enhance Trial to evaluate how NAD3® supplementation influences metabolic health and aging biomarkers in middle-aged adults. Specifically, the team investigated whether 12 weeks of NAD3® intake could alter serum lipid levels and cellular NAD+ metabolism in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). NAD3® is a proprietary blend containing Wasabia japonica, theacrine, and cuprous niacin chelate, all hypothesised to impact lipid metabolism and NAD+ pathways.
The researchers faced three major challenges:
- Trace metabolite detection: NAD+, NADH, and related niacin metabolites exist at extremely low concentrations in PBMC lysates.
- Data reproducibility: Small sample sizes demanded rigorous analytical consistency to ensure results were statistically meaningful.
- Complex biological matrices: Differentiating subtle changes in NAD+ redox balance and lipid biomarkers required high sensitivity and specificity beyond standard clinical assays.
Creative Proteomics provided the targeted NAD+ metabolomics analysis using LC-MS/MS.
- We developed a workflow with isotope-labelled internal standards and a calibration range as low as 0.0025 nM, ensuring detection of ultra-trace metabolites.
- PBMC lysates were processed with ethanol-based extraction, protein normalization, and reconstitution before analysis on a Waters Acquity UPLC–Sciex QTRAP 6500 Plus platform.
- Data were delivered with calibration curves, quantitative accuracy, and replicate reproducibility, enabling the client to confidently link NAD3® supplementation to metabolic outcomes.
The study reported two major findings:
Improved Serum Lipid Profile
- NAD3® supplementation reduced total cholesterol by 11.1% and LDL cholesterol by 15.2% over 12 weeks, while control participants showed no such improvement (Figure 1).
- No significant changes were observed in triglycerides or HDL cholesterol.
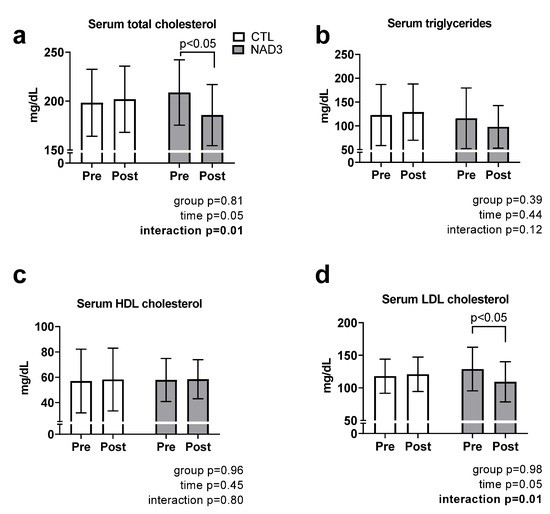 Figure 1. Effects of supplementation on serum lipids. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation values for 15 CTL and 13 NAD3 participants. Abbreviations: CTL, control group; NAD3, supplementation group.
Figure 1. Effects of supplementation on serum lipids. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation values for 15 CTL and 13 NAD3 participants. Abbreviations: CTL, control group; NAD3, supplementation group.
Stabilisation of Cellular NAD+/NADH Balance
- In control participants, the PBMC NAD+/NADH ratio declined during the study, consistent with aging-associated metabolic decline.
- In contrast, NAD3® supplementation increased NAD+/NADH ratios by ~35%, supporting healthier cellular redox balance (Figure 2c–e).
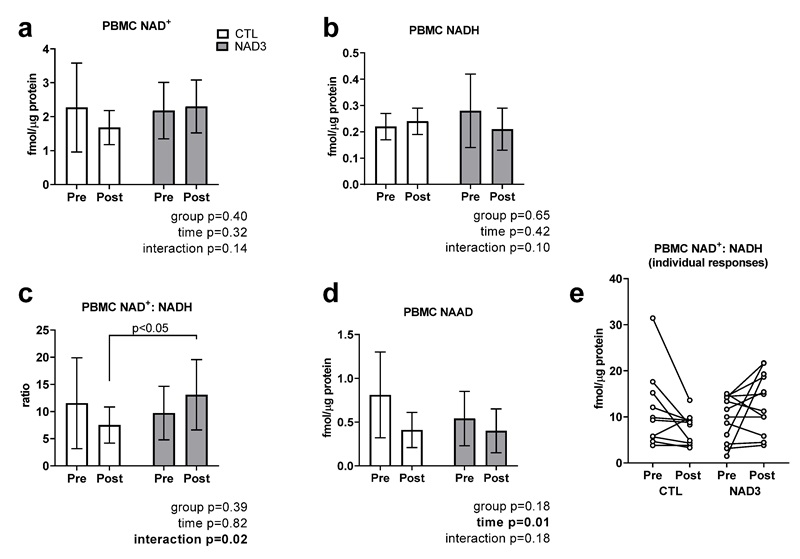 Figure 2. Targeted NAD+ metabolome data. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation values for 15 CTL and 13 NAD3 participants. Abbreviations: CTL, control group; NAD3, supplementation group.
Figure 2. Targeted NAD+ metabolome data. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation values for 15 CTL and 13 NAD3 participants. Abbreviations: CTL, control group; NAD3, supplementation group.
Research Impact
With Creative Proteomics' specialised NAD+ metabolite analysis, the trial was able to:
- Provide the first human evidence that a theacrine- and niacin-based supplement can favourably alter NAD+ metabolism and lipid biomarkers.
- Demonstrate the value of sensitive LC-MS/MS assays in capturing subtle but meaningful changes in cellular metabolism.
- Generate publication-ready data for Physiologia (2022), advancing research into nutritional strategies for healthy aging and cardiometabolic health.
This project underscores how Creative Proteomics supports clinical and nutritional research by delivering high-precision niacin and NAD+ metabolite profiling for both discovery and translational applications.
Publication

- Pelletier A, Boulay LM, Beaudoin M, Champagne EA, Drouin A, Côté JF, Roux P. Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α. EMBO Reports. 2023.
- Roberts MD, O'Neill L, Tinsley G, Colombo A, Wilson JM. Enhance trial: effects of NAD3® on hallmarks of aging and clinical endpoints of health in middle aged adults: a subset analysis focused on blood cell NAD+ concentrations and lipid metabolism. Physiologia. 2022.
- Kambis TN, Shahshahan HR, Mishra PK. Metabolites and genes behind cardiac metabolic remodeling in mice with type 1 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022.