Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
Creative Proteomics delivers trace-level, isomer-specific, and matrix-validated cinnamic acid analysis using LC-MS/MS, HPLC-DAD, and GC-MS platforms. Whether you're developing botanical products, ensuring fragrance quality, or verifying ingredient stability, our analytical services give you data that drives decisions—fast and accurately.
- Sub-ppb sensitivity for label compliance & QC
- trans/cis isomer resolution with full ratio reporting
- Custom matrix prep for food, fragrance, fermentation, and botanicals
- Impurity profiling & stability tracking
- Transferable method files with validated system suitability
Submit Your Request Now
×
- What We Provide
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- FAQ
What is Cinnamic Acid?
Cinnamic acid (trans-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid; C₉H₈O₂, MW 148.16) is a key node in the phenylpropanoid pathway and a widely used building block in flavors, fragrances, UV absorbers, and specialty chemicals. It occurs naturally (often as trans- isomer; cis- forms via photo-isomerization) and coexists with hydroxycinnamic acids (p-coumaric, caffeic, ferulic, sinapic) and cinnamate esters (methyl/ethyl/butyl cinnamates). Measuring it accurately requires methods that tame matrix interferences, resolve isomers, and reach sub-ppb levels when needed.
What Problems We Solve for Our Clients
- Matrix interference & co-elution in botanical extracts, essential oils, and complex formulations.
- Isomer specificity (trans/cis cinnamic acid) and separation from hydroxycinnamates.
- Trace-level detection for labeling claims, migration studies, or impurity control.
- Method transfer into production QC with full parameters, system suitability, and acceptance criteria.
- Stability & photoisomerization control during sample handling and prep.
- Batch comparability with robust calibration, internal standards, and QC trending.
Specific Cinnamic Acid Analysis Services Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Quantitative analysis of cinnamic acid and related compounds across simple and complex matrices, using LC-MS/MS, HPLC-DAD, and GC-MS for reliable, trace-level detection.
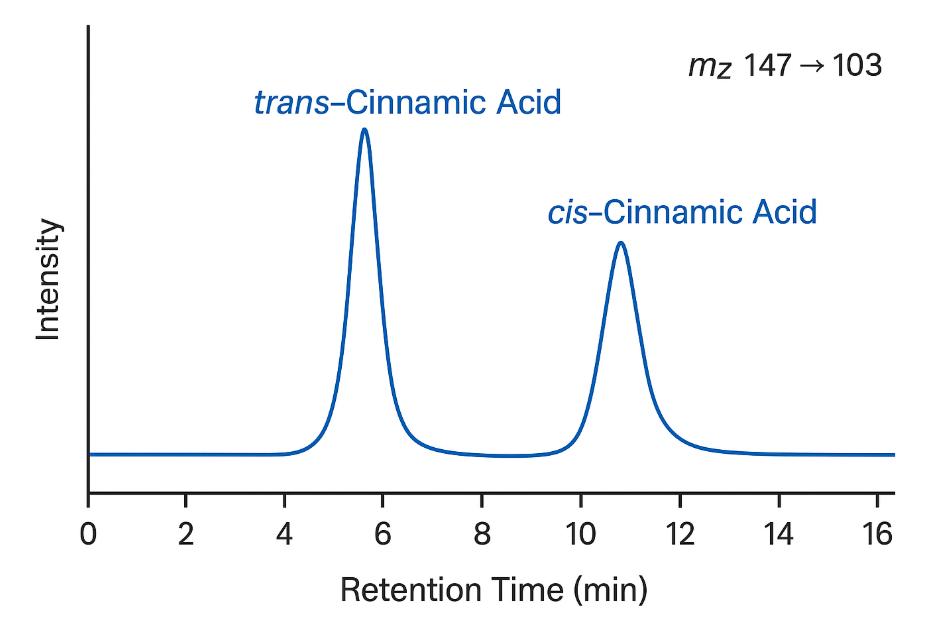
- Isomer-specific analysis services, including trans/cis cinnamic acid separation and ratio reporting, critical for quality control and stability monitoring.
- Impurity profiling and degradation pathway studies, identifying related substances and transformation products through advanced chromatographic and high-resolution MS platforms.
- Batch-to-batch comparability testing to support raw material qualification, product release, and sourcing decisions.
- Stability and shelf-life studies, evaluating cinnamic acid integrity under varying conditions including light, pH, and storage environment.
- Custom multi-analyte panels tailored to your project, integrating cinnamic acid analysis within broader phenolic or volatile profiling strategies.
Target Analyte Panel – Cinnamic Acid and Related Compounds
| Class | Analyte | Primary Mode | Typical LOQ* | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamic Acids | Cinnamic acid (trans/cis) | LC-MS/MS, HPLC-DAD | 0.5–2 ng/mL | Isomer-resolved; key analyte |
| 3-Phenylpropionic acid | LC-MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Hydrogenation product; degradation marker | |
| Hydroxycinnamic Acids | p-Coumaric acid | LC-MS/MS, DAD | 0.5–2 ng/mL | Common in food and plants |
| Caffeic acid | LC-MS/MS, DAD | 0.5–2 ng/mL | Antioxidant-rich matrices | |
| Ferulic acid | LC-MS/MS, DAD | 0.5–2 ng/mL | Widely used in cosmeceuticals | |
| Sinapic acid | LC-MS/MS, DAD | 0.5–2 ng/mL | Requires retention control | |
| Isoferulic acid | LC-MS/MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Structural isomer of ferulic acid | |
| 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid | LC-MS/MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Related to caffeic acid | |
| Cinnamate Esters | Methyl cinnamate | GC-MS, LC-MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Common in flavors |
| Ethyl cinnamate | GC-MS, LC-MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Used in fragrances | |
| Butyl cinnamate | GC-MS, LC-MS | 2–10 ng/mL | Non-polar applications | |
| Benzyl cinnamate | GC-MS | 2–10 ng/mL | Present in cosmetics | |
| Phenethyl cinnamate | GC-MS | 2–10 ng/mL | High-end perfumery | |
| Conjugated Forms | Cinnamic acid glucoside | LC-MS/MS | 2–5 ng/mL | Plant-derived or biotransformed |
| Cinnamic acid glucuronide | LC-MS/MS | 2–5 ng/mL | Metabolic derivative | |
| Cinnamic acid sulfate | LC-MS/MS | 2–5 ng/mL | Often seen in metabolism | |
| Polyphenolic Co-occurrents | Chlorogenic acid | LC-MS/MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Common in coffee, fruits |
| Rosmarinic acid | LC-MS/MS | 2–10 ng/mL | Herbal antioxidant marker | |
| Ellagic acid | LC-MS/MS | 2–10 ng/mL | Antioxidant polyphenol | |
| Related Volatiles | Cinnamaldehyde | GC-MS, LC-MS | 1–5 ng/mL | Aroma component, optional |
| Cinnamyl alcohol | GC-MS, LC-MS | 2–10 ng/mL | Fragrance-related alcohol |
*Typical LOQs based on standard matrices and validated methods. Actual detection limits may vary by sample type and prep method.
Advantages of Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
- Sensitivity built for labels and traceability: LOQ ≤0.5–2 ng/mL for cinnamic acid and key hydroxycinnamates by LC-MS/MS; ≤20–50 ng/mL by HPLC-DAD for cost-efficient routine QC.
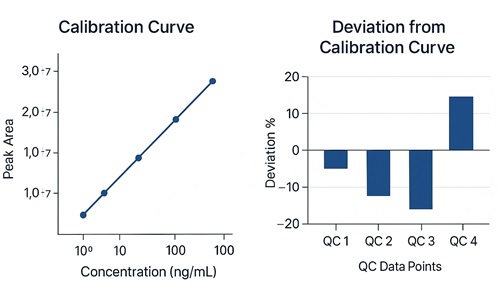
- Linearity you can trust: Typical calibration R² ≥ 0.999 over 3–4 orders of magnitude (matrix-matched where needed).
- Precision & accuracy: Intra-day %RSD ≤ 5%, inter-day %RSD ≤ 8%; spike-recovery 85–115% in validated matrices.
- Isomer resolution: Baseline separation (Rs ≥ 1.5) of trans/cis cinnamic acid on sub-2-µm C18 columns.
- Carryover control: Post-blank response <0.1% of calibration high point.
- Throughput & robustness: 96-well compatible prep; routine run-to-run retention time RSD <0.2% and mass accuracy <5 ppm (HRAM).
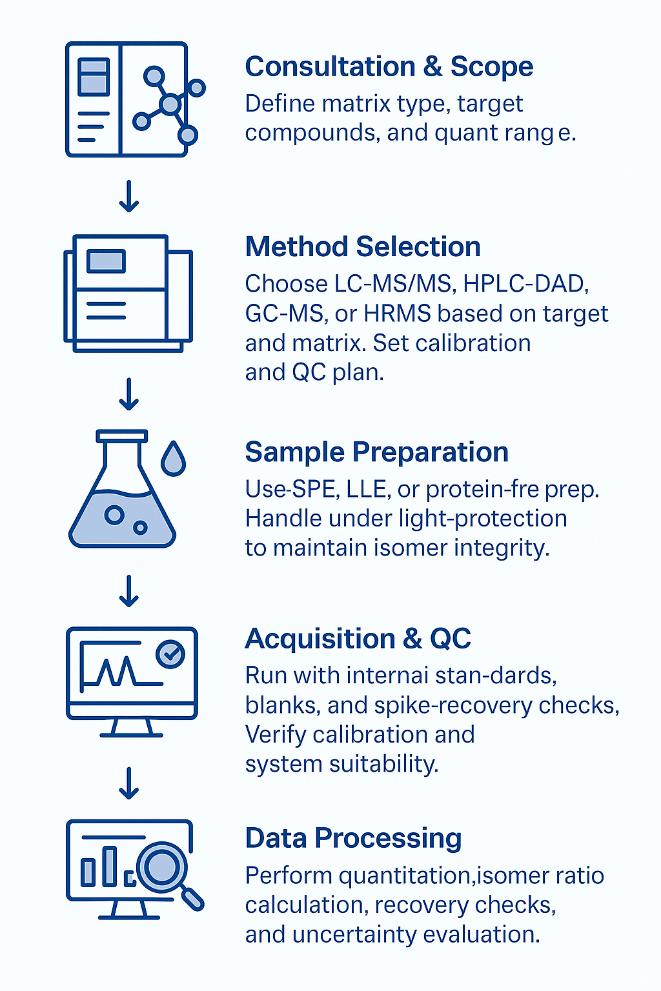
Workflow for Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
1. Consultation & Scope — Define matrices, targets (acids, esters, isomers), ranges, and acceptance criteria.
2. Method Selection — Choose UHPLC-DAD, LC-MS/MS, GC-MS, HRAM, or combined paths; set calibration/QA plan.
3. Sample Preparation — Matrix-specific extraction (SPE, LLE, protein-free precipitation for non-clinical bio-matrices, or solid-phase cleanup), light-protected handling to control isomerization.
4. Acquisition & QC — System suitability, blanks, matrix spikes, duplicates, and continuing calibration verification.
5. Data Processing — Isotope-dilution or external-standard quant, isomer ratioing, recovery/precision checks, and uncertainty estimation.
6. Reporting & Review — Concentrations (with units), chromatograms/spectra, calibration curves, QC summary, and actionable interpretation; optional method transfer pack.
Technology Platform for Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
LC-MS/MS — For Trace-Level Quantification and Complex Matrices
Instruments: Thermo TSQ Altis, AB Sciex QTRAP 6500+
Key Features:
- Quantification down to 0.5 ng/mL
- High selectivity for structurally related compounds
- Supports isotope-dilution and scheduled MRM
Ideal For: Biological samples, complex botanical matrices, formulation QA
HPLC-DAD — For Cost-Efficient Routine Testing
Instruments: Waters ACQUITY UPLC with Photodiode Array Detection
Key Features:
- UV detection at 270–325 nm
- Baseline separation of trans/cis isomers
- Robust, high-throughput workflows
Ideal For: Food, plant extracts, fragrance raw materials
GC-MS — For Volatile Esters and Aromatic Compounds
Instruments: Agilent 7890B GC + 5977B MSD (EI)
Key Features:
- Detection of cinnamate esters and related volatiles
- LOQs typically 1–5 ng/mL
- Suitable for fragrance, essential oils, and migration studies
Ideal For: Cosmetic ingredients, aroma profiling, product integrity
HRAM LC-MS — For Structural Confirmation and Unknown Impurities
Instruments: Thermo Q Exactive Orbitrap
Key Features:
- High-resolution accurate mass (≤ 5 ppm)
- Formula confirmation and unknown ID
Ideal For: R&D, degradation pathway studies, structural elucidation

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+

Agilent 5977B GC/MSD

Waters ACQUITY UPLC System

Thermo Fisher Q Exactive
Sample Requirements for Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
| Matrix Type | Minimum Amount | Container | Storage/Transport | Preparation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure substance / API / intermediate | 5–10 mg | Amber glass vial, PTFE-lined cap | Dry, cool, protected from light | Provide CoA if available |
| Liquid formulation / fragrance / flavor base | 2 mL | Amber glass vial | 2–8 °C, protect from light | Indicate solvent system |
| Plant material (dried) | 0.5 g | Zip-seal bag or vial | Dry, cool, protected from light | Avoid high humidity |
| Plant material (fresh) | 2 g | Sealed bag | ≤ 4 °C, protected from light | Do not add preservatives |
| Fermentation broth / process sample | 10 mL | Polypropylene tube | ≤ −20 °C for storage | Note pH and additives |
| Food/beverage | 50 g / 50 mL | Food-grade container | 2–8 °C | Indicate fat/sugar content |
| Environmental water | 50 mL | Amber bottle | 2–8 °C; optional pH ≈ 3 (HCl) | Avoid headspace if volatile esters |
| Soil/sediment | 50 g | Sampling jar | ≤ 4 °C | Note moisture content |
Demo Results
FAQ of Cinnamic Acid Analysis Service
What is the best method for analyzing cinnamic acid in complex matrices?
The most suitable method depends on matrix complexity and detection goals. LC-MS/MS is typically preferred for trace-level quantification in botanical, food, and fermentation samples due to its high sensitivity and selectivity.
Can this analysis distinguish between trans- and cis- cinnamic acid?
Yes. Our platform supports full isomer resolution with accurate ratio reporting. This is particularly important for stability monitoring, photochemical behavior studies, and product authenticity.
Is cinnamic acid analysis relevant for natural product verification?
Absolutely. Cinnamic acid and its derivatives are common marker compounds in natural extracts. Their presence, ratios, and related profiles can support source authentication and formulation integrity.
How is method reliability ensured across different sample types?
We apply matrix-matched calibrations, internal standards, and system suitability protocols. This ensures reproducibility, accuracy, and transferability of the method across various applications.
Can the results support regulatory or quality audits?
Yes. We provide fully documented analytical reports with quantitative data, chromatographic evidence, QC results, and method outlines—ready to be used in technical files, supplier audits, or internal validation.
What types of samples are suitable for cinnamic acid testing?
Common matrices include plant extracts, essential oils, food/beverage products, cosmetics, fermentation broths, and raw materials. Our extraction and prep protocols are adapted to suit each.
How is isomerization during analysis prevented?
We implement light-protected handling and validated sample preparation workflows to preserve the native trans/cis isomer ratio and ensure accurate reporting.
Can multiple related compounds be analyzed in the same run?
Yes. Depending on the method, cinnamic acid, hydroxycinnamic acids, and esters can be quantified simultaneously, allowing for comprehensive profiling of phenylpropanoids or flavor markers.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Publications
Here are some of the metabolomics-related papers published by our clients:

- MS-CETSA functional proteomics uncovers new DHODH interactors and new ways to inhibit pyrimidine biosynthesis. 2024.
- High Levels of Oxidative Stress Early after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Correlate with Cognitive Impairment in Survivors. 2024.
- Serum metabolites as potential biomarkers in patients with schizophrenia: A targeted metabolomics study. 2024.
- Metabolic signatures of liver fibrosis progression in NAFLD revealed by targeted plasma metabolomics. 2023.
- Quantitative profiling of amino acid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease using LC-MS/MS. 2023.