De Novo Peptides/Proteins Sequencing Service
Creative Proteomics employs advanced technologies like FTICR-MS, Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, Edman degradation, and multiple fragmentation methods to deliver accurate de novo sequencing for proteins and antibodies. Services include sequence determination, PTM localization, and non-standard amino acid identification, with comprehensive technical reports provided.
Submit Your Request Now
×- Define
- Strategies
- What We Provide
- Advantage
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirements
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case Study
- Publications
What is De Novo Peptides/Proteins Sequencing?
The sequence of peptide/protein is important to study the biological function of the peptide/protein. However, complete characterization of peptides/proteins, including post-translational modifications (PTMs), sequence mutations and variants, is very challenging. There are two approaches to determine the sequence of peptide/protein by mass spectrometry: database search and de novo sequencing. Database search approach compares acquired mass spectra to a database of known protein sequences to identify the protein sequences. De novo sequencing is a process in which amino acid sequences are directly interpreted from tandem mass spectra without the assistance of a database.
Although database search identification of proteins by mass spectrometry is well established, the method does not apply if the protein sequence does not exist in the current database. Therefore, de novo sequencing is the only method for identifying novel peptides, unsequenced organisms, and antibodies drugs, which database search methods were not able to detect. However, de novo sequencing poses more challenging than the traditional database search approach, such as, ambiguous assignments of fragment ions, insufficient product ions generated in incomplete fragmentation leading to low sequence coverage and difficulty in distinguishing ion series, notably N-terminal from C-terminal MS/MS product ions (b ions from y ions).
De Novo Peptides/Proteins Sequencing Strategies in Creative Proteomics
1. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Using Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR-MS) with a 7T SolariX XR instrument, we achieve the highest mass resolution and accuracy, which helps minimize false positives caused by lower resolution. With a resolving power up to 10,000,000, higher mass accuracy ensures more confident ion assignments.
2. Combination of Bottom-Up and Top-Down Mass Spectrometry
We use both bottom-up and top-down mass spectrometry techniques to analyze the same sample:
- Bottom-up MS involves enzyme digestion to generate overlapping peptides, facilitating sequence determination.
- Top-down MS offers intact mass data and provides protein fragmentation details.
By combining these complementary approaches, we can confirm peptide/protein sequences more effectively.
3. Diverse Fragmentation Techniques
We employ four fragmentation techniques to enhance sequence coverage:
- Collision Induced Dissociation (CID)
- Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD)
- Electron Capture Dissociation (ECD)
- High-Energy Collisional Dissociation (HCD)
These techniques provide complementary fragment ion data, which helps improve ion assignments. For example, in ECD, we can distinguish C-terminal (z•) from N-terminal (c') product ions based on their respective ion abundances.
4. Chemical Derivation for Ion Series Identification
We use chemical derivation methods to identify ion series more accurately. For instance, introducing bromide at the C-terminus via oxazolone chemistry allows for the identification of y ions by their distinct bromide isotope peaks. Similarly, guanidination enhances ion selectivity and identification possibilities.
Protein De Novo Sequencing Services at Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics offers high-quality protein de novo sequencing services using the Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer, complemented by Edman degradation for sequence determination (up to 67 amino acids from the N-terminal). Here's how the process works:
- Protein Fragmentation: After receiving the protein sample, we fragment it using six commonly used proteases (Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Asp-N, Glu-C, Lys-C, and Lys-) to generate a variety of peptide sequences for full protein sequence coverage.
- Sequencing and Analysis: Peptide sequences obtained through MS are assembled using PEAKs Studio and PEAKs Ab software, with manual assistance for correct sequence assembly.
- Final Report: A comprehensive technical report will be provided, including details on sample preparation, MS parameters, and the final sequence with FDR < 1%.
Advantages of De Novo Peptides/Protein Sequencing
- Determination of the amino acid sequence of unknown peptides from scratch, independent of known peptide sequence databases.
- Ability to localize the post-translational processing or chemical modification of side chain motifs without the restriction of N-terminal closure.
- Enables the identification of non-standard amino acids.
- Improved detection sensitivity.
Technology Platform for De Novo Peptides/Protein Sequencing

Nano HPLC- 7T solariX XR FTICR-MS
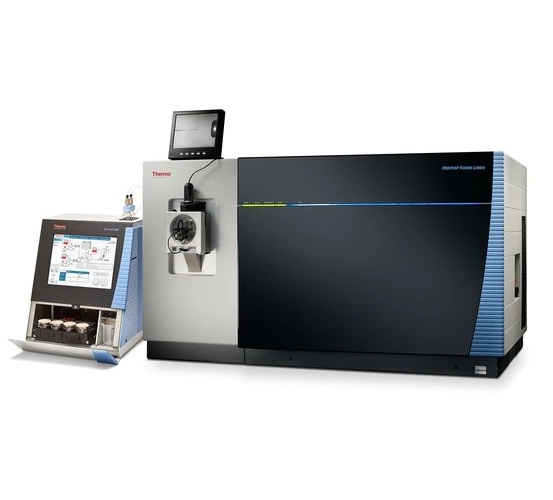

Nano HPLC- Orbitrap Fusion™ Lumos™ Tribrid™ MS
Sample Requirements for De Novo Protein Sequencing
| Sample Type | Description | Recommended Sample Amount | Minimum Sample Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purified Protein | High-quality, purified proteins with minimal contamination with purity >95% | 300 µg/protein | 200 µg/protein |
| Peptide | Purified peptide with purity >95% | 150 µg/peptide | 100 µg/peptide |
| antibody | Purified antibodies with purity >95% for sequencing (typically used in monoclonal antibody studies) | 300 µg/antibody | 200 µg/antibody |
Demo for De Novo Protein Sequencing

Figure from Mignone, Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2022.
FAQs
What is the difference between de novo sequencing and Edman degradation sequencing for protein sequencing?
De novo sequencing of proteins utilizes algorithms to directly deduce the peptide sequence from ion information in mass spectrometry spectra. On the other hand, Edman degradation sequencing is generally suitable for peptides composed of 15-20 amino acids and requires relatively high sample purity, at least 97% purity. It also involves protein digestion, peptide separation, purification, and individual peptide testing. Additionally, the time and economic costs of performing Edman degradation sequencing on a monoclonal antibody are relatively high.
Compared to the traditional Edman degradation method, mass spectrometry-based de novo sequencing is more efficient, high-throughput, and cost-effective. In cases where the amino acid sequence of a protein is already known, de novo sequencing can also identify new protein variants arising from unknown mutations, splicing events, and various post-translational modifications, providing more comprehensive information about the antibody sequence.
What types of samples can be used for de novo sequencing of protein?
De novo sequencing of proteins is not dependent on the size or length of the protein. It can be performed on monoclonal antibodies, Fab/Fc, bispecific antibodies, multispecific antibodies, recombinant proteins, peptides, fluorescently labeled antibodies, cross-linked antibodies, and other types of proteins.
Can fluorescently labeled or cross-linked antibodies be subjected to de novo sequencing?
Proteins that are cross-linked on beads or those that are fluorescently labeled, such as flow cytometry antibodies labeled with FITC, Cy5, PE, etc., can also undergo de novo sequencing.
Do the sample buffer components affect the sequencing results?
For standard sample submission, it is recommended to use PBS or Tris buffer system for protein dissolution. If there are components like glycerol, BSA, detergents, salts, etc., appropriate purification methods will be applied, ensuring that they do not affect the sequencing results.
Will sample glycosylation and post-translational modifications affect the sequencing?
During data analysis, possible post-translational modifications and glycosylation will be taken into consideration, and they will not affect the sequencing results of the sample itself.
What does the report of protein de novo sequencing include?
The report includes the following:
Complete amino acid sequence of the protein, including heavy and light chain sequences for antibodies, constant and variable regions.
Verification of the complete molecular weight, comparing the measured molecular weight to the theoretical sequence weight to validate sequence accuracy.
Peptide coverage map of the complete sequence, with support from over ten different peptide fragments at each amino acid position.
Supportive secondary mass spectrometry data for variable region peptide segments of antibodies.
Reliability analysis of I/L identification.
How accurate are the results of protein de novo sequencing?
The sequencing results guarantee full sequence coverage and 100% sequence accuracy. Each amino acid position is supported by over ten different peptide fragments in the mass spectrometry data, providing strong evidence. The sequencing results are obtained through a combination of software algorithms and manual verification, ensuring the accuracy of the sequence.
Learn about other Q&A of De Novo Peptides/Proteins Sequencing.
Case Study

Antigen Presentation Profiling Reveals Recognition of Lymphoma Immunoglobulin Neoantigens
Journal: Nature
Published: 2017
- Background
- Results
Cancer cells can produce neoantigens through somatic mutations, which enable the immune system to distinguish malignant cells from normal ones. Identifying and validating these neoantigens, however, is a significant challenge due to their variability and complexity. In mantle cell lymphoma, neoantigens are presented on MHC class I and class II molecules, providing potential immunotherapeutic targets. While somatic mutations in various genes occur in cancer, immunoglobulin variable regions appear to be a primary source of neoantigens in lymphoma. These findings underscore the importance of integrated genomic and proteomic approaches in advancing neoantigen discovery and cancer immunotherapy development.
The article integrated genomic and proteomic strategies to directly analyze tumor antigen peptides presented by MHC I and MHC II from tumor cells. It was found that these tumor neoantigen peptides originated from the variable regions of immunoglobulin light chains or heavy chains of lymphomas. For the MHC-bound tumor neoantigen peptides, over 24,000 unique peptides bound to MHC-I were identified through immunoprecipitation (IP) and mass spectrometry, while over 12,500 unique peptides bound to MHC-II were identified. Additionally, a protein sequence database was constructed for comprehensive proteomic analysis of the MCL cell line.
In terms of data analysis methods, the team employed a combination of de novo sequencing and database search, with improvements to the percolator algorithm. The PEAKS Studio 7.0 software was used to execute de novo sequencing and database search, maximizing the identification of peptides.
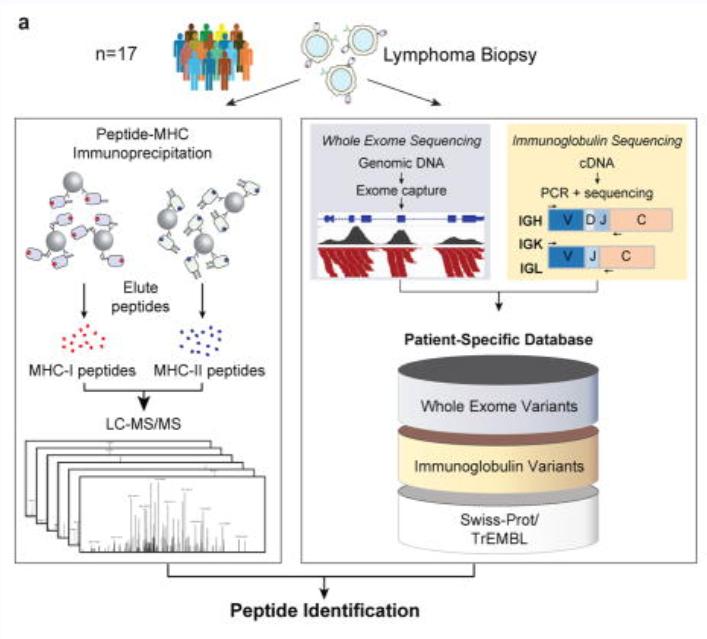
The analysis method based on de novo sequencing in the study used a credibility filtering approach to obtain de novo tags for database search. By combining de novo sequencing with database search, the efficiency of peptide identification was maximized, leading to improved sensitivity and accuracy in the database search. This approach facilitated the identification of a greater number of modifications, sequence mutations, and entirely novel peptides.
Reference
- Khodadoust M S, Olsson N, Wagar L E, et al. Antigen presentation profiling reveals recognition of lymphoma immunoglobulin neoantigen. Nature, 2017, 543(7647):723-727.
Publications
Here are some publications in Proteomics research from our clients:

- Chemoproteomic identification of CO2-dependent lysine carboxylation in proteins. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-022-01043-1
- Functional Characterization of Propeptides in Plant Subtilases as Intramolecular Chaperones and Inhibitors of the Mature Protease. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.744151
- Isolation of the mustard Napin protein Allergen Sin a 1 and characterisation of its antifungal activity. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101208