- Service Details
- Demo
- Case Study
- FAQ
- Publications
What Is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme, which can be found in all living cells. NAD consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups and it is a dinucleotide, in which the one nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. There are two different NAD forms exist naturally, the one is an oxidized form, which is abbreviated as NAD+ and the other is a reduced form, which is abbreviated as NADH.
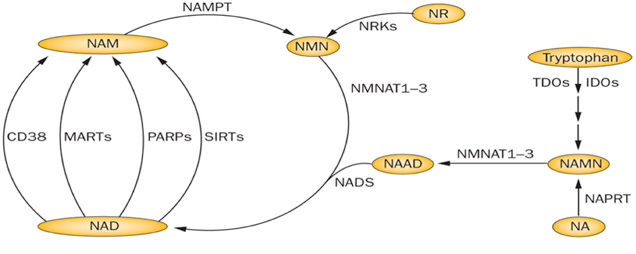
What Is Nad Synthesis Pathway
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems, NAD is synthesized through two pathways: de novo pathway and salvage pathway. In the de novo pathway, NAD is generated from tryptophan through quinolinic acid (QA) and nicotinic acid (NA). In salvage pathway, NAD is synthesized by recycling degraded NAD products such as Nam and nicotinamide. Both pathways play essential roles in cell growth. Under normal physiological condition, the salvage pathway plays a more important role than de novo pathway in NAD synthesis. In yeast, the de novo pathway is making of six enzymatic steps and one non-enzymatic reaction. In the last enzymatic reaction, quinolinate is converted to nicotinic acid mononucleotide by a quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase encoded by the BNA6/ QPT1 gene. This last enzymatic reaction is the converge point of the de novo pathway and the salvage pathway.
Physiological Functions of NAD
NAD takes part in many physiological processes, such as energy metabolism regulation, DNA repair and transcription. Besides acting as a coenzyme, NAD also serves as a substrate such as substrate for NAD-dependent DNA ligases, NAD-dependent oxidoreductases and NAD-dependent deacetylases. At the same time, the reduced form of NAD, NADH, serves as a substrate for the NADH dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial respiratory chain to transfers electrons to coenzyme Q and generate NAD. Calorie restriction accomplished by glucose limitation in wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae can extend replicative lifespan of cells and this process relies on Sir2 and the NAD+ salvage enzymes, nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase and nicotinamidase. Together with glutathione, the derivative of NAD, the NADPH coenzyme, maintains the intracellular redox state and is also involved in many assimilatory pathways. To maintain the proper redox state, NADH needs to be constantly re-oxidised. Mostly, NAD is converted to NADH mostly in catabolic reactions such as glycolysis and TCA cycle. However, both cytosolic and mitochondrial NADH are re-oxidised mainly by the respiratory chain. Since the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable for NAD and NADH, there are several shuttle systems to transport permeable redox equivalents across this barrier. Ethanol-acetaldehyde shuttle is one example.
Though the changes of NAD+ to nicotinamide ratio and the NAD+ to NADH ratio can be anticipated through models to related the effects of calorie restriction. However, the putative alterations of NAD+ metabolism require a sensitive and reliable qualitative and quantitative analysis of NAD+ metabolites.
What Are The Pertinent Small Molecules Within The NAD Metabolic Pathway?
The NAD metabolic pathway encompasses a spectrum of small molecules, prominently featuring the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), its reduced counterpart nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+), the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide riboside (NAR), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Notably, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), alternatively referred to as coenzyme I, plays an indispensable role as a coenzyme in redox processes, actively participating in diverse physiological processes such as DNA repair, cellular substance metabolism, and energy synthesis.
NAD Metabolites Analysis Solution
Creative Proteomics presents a cutting-edge analytical solution tailored to the study of NAD metabolism. This comprehensive platform leverages state-of-the-art GC/MS technology (Agilent 7890A/5975C) and ACQUITY UPLC/TripleQuad5500 instrumentation (Waters/AB Sciex) to facilitate both quantitative and qualitative assessments of a wide spectrum of small molecules involved in the NAD metabolic pathways. Central to this platform is the incorporation of standard reference materials and isotopic standards, enabling precise quantification of nearly 95% of the analytes under investigation.
Sample Requirement
Serum, plasma, urine, bile, and bile acids;
Animal tissues such as cells, liver, brain tissues, etc., and feces;
Plants, yeast, microorganisms, etc.
Blood samples, bile, etc.: 10 microliters
Various tissues: 10 milligrams
Feces, etc.: 10 milligrams
Delivery
A detailed technical report will be provided at the end of the whole project, including the experiment procedure, MS/MS instrument parameters
Analytes are reported as uM or ug/mg (tissue), and CV's are generally<10%
The name of the analytes, abbreviation, formula, molecular weight and CAS# would also be included in the report.
| NAD Metabolites Quantified in This Service | ||
|---|---|---|
| Acetyl-CoA (aCoA) | Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) | Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) |
| Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Citrate/Isocitrate combined (Cit/i-Cit) | Erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P) |
| Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) | Fructose-6-phosphate + glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P) | Fructose-bisphosphate (FBP) |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) | Succinate (Suc) | Malate (Mal) |
| nicotinamide (NAM) | Nicotinic acid (NA) | Nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) |
| Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced (NADH) | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) |
| Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (NADPH) | Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) | Quinolinic acid (QA) |
| Ribulose 5-phosphate/Xylulose 5-phosphate/ribose-5-phosphate combined (R5P/X5P/Ru5P) | Sedoheptulose 7-phosphate (S7P) | 2-Phosphoglycerate/3-Phosphoglycerate combined (2PG/3PG) |
| 6-phosphogluconate (6PG) | ||
With integrated set of separation, characterization, identification and quantification systems featured with excellent robustness & reproducibility, high and ultra-sensitivity, Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid and cost-effective NAD metabolites targeted metabolomics services.

PCA chart

PLS-DA point cloud diagram

Plot of multiplicative change volcanoes

Metabolite variation box plot

Pearson correlation heat map
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α.
Journal: EMBO reports
Published: 2023
Background
Natural Killer (NK) cells are crucial components of the immune system, capable of targeting and destroying virus-infected or malignant cells. They function effectively in low-oxygen (hypoxic) environments, largely mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), particularly HIF-1α. Although NK cells primarily rely on aerobic glycolysis for activation and function, the role of HIF-1α in their metabolism and homeostasis, especially in resting states, is still debated.
Materials & Methods
Mouse Models
Targeted deletions of HIF-1α and VHL in NK cells were achieved as described previously (Krzywinska et al, 2017, 2022). All mice were on a >99% C57Bl/6J background, with both male and female mice (8–12 weeks old) used equally. All procedures followed Swiss animal protection laws.
Pulmonary Metastasis Model
B16F10 melanoma cells were injected intravenously (1 × 10⁵ for HIF1α model, 2 × 10⁵ for VHL model). Lungs were collected 7 days post-injection for NK cell analysis and after 14 days for metastasis assessment.
NK Cell Purification
NK cells were purified from spleen and bone marrow using the EasySep™ Mouse NK Cell Isolation Kit, and from liver following established protocols.
Stimulation and Killing Assays
Splenocytes were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin in normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 6 hours to assess granzyme B and IFN-γ expression. For the killing assay, NK cells were co-cultured with B16F10 melanoma cells and assessed by FACS after 24 hours.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry was performed with antibodies targeting NK1.1, NKp46, CD107a, Granzyme B, IFN-γ, and markers for apoptosis.
Seahorse Metabolic Flux Analysis
OCR and ECAR were measured using Seahorse technology in freshly isolated NK cells. Cells were subjected to sequential injections of metabolic inhibitors for real-time measurements.
ATP and ROS Quantification
ATP levels were determined using an ATP Determination Kit, and mitochondrial ROS were quantified using MitoSOX Red™ by flow cytometry.
Metabolic Assays
Glutamine oxidation and fatty acid oxidation were measured using radioactive substrates, followed by DPM quantification with scintillation counting.
NAD Quantification
NAD⁺/NADH levels were assessed using the NAD/NADH Quantification Kit with absorbance measurements at 450 nm.
Metabolomics
NK cells from 20 mice were pooled for untargeted metabolomics, with sample processing performed by Creative Proteomics.
RNA Isolation and Transcriptomic Analysis
RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Mini Kit, and RNA-sequencing was conducted on pooled NK cells by Novogene Europe.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.1, with statistical significance set at *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
Results
HIF-1α and NK Cell Metabolism
To study the impact of HIF-1α on NK cells, researchers used NK cell-specific HIF-1α knockout (KO) mice. They observed that HIF-1α deficiency led to a reduction in NK cell numbers in the spleen, which is the organ with the lowest oxygen partial pressure, but did not affect NK cell numbers in the bone marrow or liver. This decrease in splenic NK cells was not due to altered maturation or receptor repertoire but was linked to metabolic changes.
Metabolomic analyses of NK cells from HIF-1α KO mice showed decreased levels of glycolytic end products like lactic acid and a reduction in several amino acids, including tryptophan. This suggested a disrupted tryptophan/NAD metabolism. Specifically, levels of tryptophan, methyl-quinoline (a tryptophan metabolite), and NAD precursors were significantly reduced. The mRNA expression of genes involved in tryptophan and NAD metabolism was also decreased in HIF-1α-deficient NK cells. Additionally, these cells exhibited a lower NAD/NADH ratio, indicating a role for HIF-1α in maintaining NAD+ levels in resting NK cells.
 The transcription factor HIF1α contributes to tryptophan/NAD metabolism and maintenance of resting NK cells
The transcription factor HIF1α contributes to tryptophan/NAD metabolism and maintenance of resting NK cells
 HIF1α is involved in tryptophan/NAD metabolism of splenic NK cells
HIF1α is involved in tryptophan/NAD metabolism of splenic NK cells
Impact of HIF-1α Deficiency on NK Cell Function
HIF-1α-deficient NK cells displayed increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damage, particularly in the spleen, correlating with enhanced mitochondrial respiration and proton leakage. Despite increased OxPhos, these cells generated less ATP, suggesting mitochondrial dysfunction.
Furthermore, HIF-1α deficiency led to enhanced fatty acid oxidation, contributing to ROS production. However, glutamine oxidation remained unaffected. In terms of NK cell activation, HIF-1α was dispensable for glycolysis under normoxic conditions but crucial for glycolysis under hypoxic conditions. HIF-1α-deficient NK cells showed impaired activation and effector functions, such as reduced degranulation and IFN-γ production. Supplementing with NAD+ or nicotinamide did not restore NK cell activation, likely due to an anti-glycolytic effect.
In vivo, HIF-1α KO mice exhibited increased pulmonary metastasis of B16 melanoma cells. This was associated with decreased NK cell frequency and functionality in the lungs, demonstrating HIF-1α's role in NK cell infiltration into metastatic sites. Despite this, HIF-1α did not affect NK cell-mediated killing of B16 cells in vitro.
Constitutive Activation of HIF-1α Enhances NK Cell Function
To investigate the effect of constitutive HIF activation, researchers generated NK cell-specific VHL knockout (VHL KO) mice. Loss of VHL stabilizes HIF-1α, leading to increased NK cell glycolysis and enhanced effector functions, including greater Granzyme B expression. In contrast, deletion of HIF-2α did not produce significant effects on NK cell function or numbers, highlighting HIF-1α as the main regulator of hypoxic responses in NK cells.
Reference
- Pelletier, Abigaelle, et al. "Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α." EMBO reports 24.6 (2023): e56156.
What is the difference between NAD+ and NADH, and why is it important to measure both?
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and NADH are two forms of the same molecule, crucial for redox reactions within cells. NAD+ acts as an electron acceptor, while NADH is a donor. Measuring both forms is vital because their balance reflects the cellular redox state, influencing energy production, oxidative stress, and various metabolic pathways. Disruptions in this balance can impact cellular function and are linked to numerous diseases, including metabolic disorders and cancer. Therefore, precise measurement of both NAD+ and NADH provides a comprehensive view of cellular metabolism and health.
Can NAD analysis be used to monitor changes in NAD+ levels over time, and how often should samples be collected?
Yes, NAD analysis can track changes in NAD+ levels over time, which is useful for longitudinal studies assessing the impact of treatments, diet, or disease progression. The frequency of sample collection depends on the specific study objectives and the dynamics of the biological system being investigated. For instance, in clinical trials or metabolic studies, samples may be collected at regular intervals (e.g., weekly, monthly) to observe trends or changes.
What are the benefits of analyzing niacin and nicotinamide in the context of NAD+ metabolism?
Analyzing niacin (Vitamin B3) and nicotinamide is crucial for understanding NAD+ biosynthesis and metabolism. Niacin is a precursor to NAD+, and its levels can influence NAD+ production. Nicotinamide, another NAD+ precursor, is involved in maintaining NAD+ levels and regulating cellular stress responses. By measuring these compounds, researchers can gain insights into NAD+ synthesis, evaluate deficiencies or imbalances, and study their implications for metabolic health and disease.
Resting natural killer cell homeostasis relies on tryptophan/NAD+ metabolism and HIF‐1α.
Pelletier, Abigaelle, et al.
Journal: EMBO reports
Year: 2023
https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202256156
Metabolites and Genes behind Cardiac Metabolic Remodeling in Mice with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Kambis, Tyler N., Hamid R. Shahshahan, and Paras K. Mishra.
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year: 2022
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031392
Enhance trial: effects of NAD3® on hallmarks of aging and clinical endpoints of health in middle aged adults: a subset analysis focused on blood cell NAD+ concentrations and lipid metabolism.
Roberts, Michael D., et al.
Journal: Physiologia
Year: 2022
https://doi.org/10.3390/physiologia2010002








