Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service
Creative Proteomics offers expert Salvianolic Acid B (Sal B) analysis services using advanced LC-MS/MS technology. Our comprehensive solutions include accurate quantification, metabolite profiling, pharmacokinetics, stability testing, and metabolic pathway analysis. We specialize in providing high-sensitivity and reproducible results for research, product development, and clinical studies. Whether you need to monitor bioavailability, ensure consistency in herbal products, or explore the pharmacokinetic behavior of Sal B, our services meet the highest scientific standards to support your projects efficiently and reliably.
Submit Your Request Now
×- What We Provide
- Advantage
- Workflow
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirements
- FAQ
- Case Study
What is Salvianolic Acid B?
Salvianolic Acid B (Sal B) is a major bioactive polyphenolic compound extracted primarily from Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen), a cornerstone of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Structurally characterized by multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups, Sal B exhibits potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective properties. It plays a critical role in vascular protection, platelet aggregation inhibition, and modulation of cellular signaling pathways such as MAPK and TGF-β. Due to its high polarity and complex molecular structure (C₃₆H₃₀O₁₆, MW: 718.61 g/mol), precise quantification and metabolomic mapping of Sal B remain a scientific priority in drug discovery, herbal pharmacology, and functional food research.
Why Analyze Salvianolic Acid B?
Enabling Pharmacological Validation and Process Optimization
Precise Salvianolic acid B analysis is essential for:
- Pharmacokinetics & Bioavailability: Monitoring absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in preclinical or clinical models.
- Herbal Product Standardization: Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency in botanical formulations and dietary supplements.
- Metabolite Profiling: Characterizing in vivo or in vitro biotransformation pathways of Sal B.
- Stability Testing: Assessing compound degradation under various processing or storage conditions.
- Therapeutic Targeting: Supporting mechanism-of-action studies and pathway-level insights.
Creative Proteomics delivers robust and reproducible Salvianolic Acid B analysis services that meet regulatory and scientific requirements for high-impact research and development.
Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Quantitative Analysis – Accurate measurement of Salvianolic Acid B concentrations in plasma, tissue, urine, and plant extracts using LC-MS/MS.
- Metabolite Profiling – Identification and quantification of Sal B-related metabolites including oxidative, sulfated, and glucuronidated forms.
- Pharmacokinetics Study – Time-point analysis of Sal B to evaluate absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
- Stability Testing – Assessment of Sal B stability and degradation under conditions such as heat, light, pH, and long-term storage.
- Metabolic Pathway Analysis – Mapping of biosynthetic and downstream metabolic pathways using integrated MS and bioinformatics.
- Tissue and Biofluid Analysis – Detection of Sal B in blood, urine, liver, kidney, brain, and other biological matrices.
- Plant and Herbal Extract Testing – Comprehensive profiling of Sal B in raw herbs, extracts, powders, and formulated products.
- Toxic Metabolite Screening – Detection of potentially toxic or reactive metabolites for safety and risk assessment.
- Precursor and Derivative Identification – Analysis of structurally related compounds such as Danshensu, caffeic acid, and other salvianolic acids.
List of Detected Salvianolic Acid B and Related Metabolites
| Category | Compound / Metabolite Name | Description / Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Target | Salvianolic Acid B | Main bioactive compound extracted from Salvia miltiorrhiza |
| Precursors | Caffeic Acid | Biosynthetic precursor of Sal B |
| Danshensu | Intermediate metabolite in Sal B biosynthesis | |
| Rosmarinic Acid | Structurally related compound with similar pharmacological activities | |
| Derivatives / Analogues | Salvianolic Acid A | Structural analogue with different antioxidant profiles |
| Salvianolic Acid C, D, E | Other natural analogues found in Danshen | |
| Lithospermic Acid | Related polyphenol co-existing in Salvia miltiorrhiza | |
| Phase I Metabolites | Hydroxylated Sal B | Products of oxidative modification |
| Demethylated Sal B | Formed via O-demethylation pathway | |
| Phase II Metabolites | Glucuronidated Sal B | Result of conjugation with glucuronic acid (detoxification) |
| Sulfated Sal B | Phase II metabolite formed by sulfotransferases | |
| Oxidative Products | Quinone Derivatives | Reactive intermediates formed during oxidative stress |
| Hydroquinone Derivatives | Reduced forms indicating redox activity | |
| Related Pathways | Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway | Central metabolic route for polyphenol production |
| Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway | Source of precursors such as caffeic acid | |
| Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathway | Shared intermediates and enzymes with Sal B synthesis | |
| TCA Cycle Intermediates (e.g., fumarate, succinate) | Monitored in pharmacokinetics to assess systemic metabolic impact |
Advantages of Salvianolic Acid B Assay
- Ultra-Sensitive Detection: Detection limit as low as 5 pg/mL using Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC/MS, suitable for trace-level quantification in complex matrices.
- Wide Dynamic Range: Linear quantification across ≥4 orders of magnitude, enabling accurate measurement from low to high concentrations without repeated dilutions.
- High Precision: Intra- and inter-batch variability <10% RSD, ensuring consistent and reproducible results across multiple runs.
- Excellent Recovery: Optimized extraction yields >95% recovery in plasma, tissue, urine, and plant matrices.
- Comprehensive Target Panel: Simultaneous quantification of 15+ related compounds, including Danshensu, caffeic acid, and salvianolic acids A–E.
- Fast Turnaround: Standard reports delivered in 14–28 business days; expedited services available.
- Validated Quantification: All assays performed with ≥6-point calibration curves, achieving R² ≥ 0.995 for quantitative accuracy.
Workflow for Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service

Technology Platform for Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC
Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry: Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC/MS

Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)

Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC (Fig from Agilent)
Sample Requirements for Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma / Serum | ≥ 200 μL | Collected in EDTA or heparin tubes; store at -80°C |
| Urine | ≥ 500 μL | First morning urine preferred; store at -80°C |
| Tissue (e.g., liver, kidney, brain) | ≥ 50 mg (wet weight) | Flash-freeze in liquid nitrogen; store at -80°C |
| Cell Pellets | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | Washed with PBS; store at -80°C |
| Plant Extracts | ≥ 200 μL or ≥ 20 mg dried powder | Indicate extraction solvent used (e.g., methanol, ethanol) |
| Herbal Raw Materials | ≥ 200 mg (dried weight) | Ground to fine powder; protect from light and moisture |
| Formulated Products | ≥ 100 mg | Tablets, capsules, or granules; provide excipient information if known |
| Culture Media / Supernatant | ≥ 500 μL | Filtered or centrifuged; store at -80°C |
FAQ of Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service
What is the detection limit for Salvianolic Acid B in biological samples?
Using the Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC/MS, our method achieves a lower limit of detection (LOD) down to 5 pg/mL in plasma and other biofluids, depending on matrix complexity.
Can you analyze Salvianolic Acid B in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulations?
Yes. We can analyze Sal B in complex herbal formulations, including tablets, granules, decoctions, and concentrated extracts. Please provide formulation details and excipient information when possible.
How do you ensure accuracy and reproducibility across batches?
We use matrix-matched calibration curves, isotope-labeled internal standards, quality control (QC) samples at multiple concentration levels, and perform replicate injections for key samples.
Do I need to provide standards for Salvianolic Acid B?
No. We maintain certified reference standards of Salvianolic Acid B and its major metabolites in-house. However, if you have a specific standard you'd like us to use, we can accommodate it.
Can you quantify Salvianolic Acid B in tissue samples like liver or brain?
Yes. We routinely quantify Sal B in various tissues, including liver, brain, kidney, and heart. Homogenization and extraction protocols are adapted to preserve compound integrity.
What is the typical turnaround time for a Salvianolic Acid B analysis project?
Standard projects are typically completed within 10–15 business days after sample receipt. Rush services are available upon request for time-sensitive studies.
Is it possible to simultaneously analyze other salvianolic acids or related compounds?
Yes. Upon request, we can design multi-target panels to include Salvianolic Acids A, C, D, E, lithospermic acid, danshensu, caffeic acid, and others using multiplex LC-MS/MS methods.
What type of documentation and data will I receive?
You will receive a comprehensive report including method details, sample preparation summary, chromatograms, raw and processed data, QC validation, and quantified results (ng/mL or ng/g).
How should I ship samples to ensure stability?
Samples should be shipped on dry ice in clearly labeled, leak-proof containers. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. For plant or formulated samples, protect from light and humidity.
Do you offer method development for custom sample types?
Yes. We can develop and validate customized methods for unique matrices or regulatory purposes. Please contact us to discuss project-specific requirements.
Learn about other Q&A.
Salvianolic Acid B Analysis Service Case Study

Title: Simultaneous Quantification of Aspirin, Its Metabolite Salicylic Acid, and Salvianolic Acid B in Human Plasma Using UPLC-MS/MS
Journal: International Journal of Analytical Chemistry
Published: 2021
- Background
- Methods
- Results
- Conclusion
- Reference
Salvianolate injection, derived from danshen (a widely used Chinese medicinal herb), is frequently combined with aspirin (ASA) in clinical practice to treat coronary heart disease, particularly in patients with stable angina. Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is the major active component of salvianolate injection and has demonstrated cardiovascular protective effects, including anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet properties.
Previous studies suggest potential drug-drug interactions (DDIs) between ASA and danshen, which may influence their pharmacokinetic profiles and therapeutic outcomes. However, there has been no existing bioanalytical method capable of simultaneously quantifying ASA, its metabolite salicylic acid (SA), and Sal B in human plasma due to differences in their chemical and physical properties.
To address this gap, the authors developed and validated a rapid, sensitive UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of ASA, SA, and Sal B. This method enables accurate pharmacokinetic analysis in clinical DDI studies and supports the safe and rational combined use of salvianolate injection and aspirin in cardiovascular therapy.
- Sample Preparation: Human plasma samples processed via liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate, dried under nitrogen, and reconstituted before injection.
- Chromatography: Separation on a BEH C18 column using gradient elution (0.5% formic acid in water and acetonitrile), 0.4 mL/min flow rate, 2 μL injection volume.
- Detection: Negative ESI mode with MRM transitions for Sal B, ASA, SA, and internal standard (IS).
- Linearity & Sensitivity: Calibration curves (r > 0.99); LLOQ at 5 ng/mL.
- Validation Parameters: Method validated for specificity, accuracy, precision, matrix effect, recovery, and stability per regulatory standards.
- Clinical Application: Successfully applied in a 16-subject PK-DDI clinical trial to evaluate interactions between salvianolate injection and aspirin.
UPLC-MS/MS Optimization
- Negative ion mode selected for better signal intensity.
- Optimized MRM transitions:
- Sal B: m/z 717.2→519.1
- ASA: m/z 179.1→137.0
- SA: m/z 136.8→65.0
- IS: m/z 321.0→152.0
- Chromatographic separation resolved ASA-SA overlap (resolution > 1.5).
- Peak shapes improved by lowering mobile phase pH (0.5% formic acid outperformed 0.1%).
Sample Preparation
- Liquid-liquid extraction chosen over protein precipitation to ensure sensitivity, especially for low ASA levels.
- Final reconstitution solvent: MeOH/ACN/H₂O (40:40:20, v/v/v) optimized for linear calibration curves of all analytes.
Extraction Recovery & Matrix Effect
- High recoveries: Sal B: ~85%, ASA: ~95%, SA: ~94%.
- Minimal matrix effect after IS normalization (RSD < 4.6%).
Precision & Accuracy
- Intra-/inter-day accuracy within ±11%; precision <10% for all analytes—compliant with bioanalytical standards.
Stability
- Analytes stable for 4 h at room temp (with acidifier), 60 days at −80°C, and 24 h in autosampler at 4°C.
- Acidification required to prevent ASA degradation to SA during plasma handling.
Clinical Application
- Applied to plasma samples from 16 subjects.
- Most Sal B and SA levels quantifiable; ASA often below LLOQ due to fast metabolism.
- PK data showed reduced drug exposure and altered absorption/elimination in the aspirin + salvianolate group, indicating a drug-drug interaction (DDI).
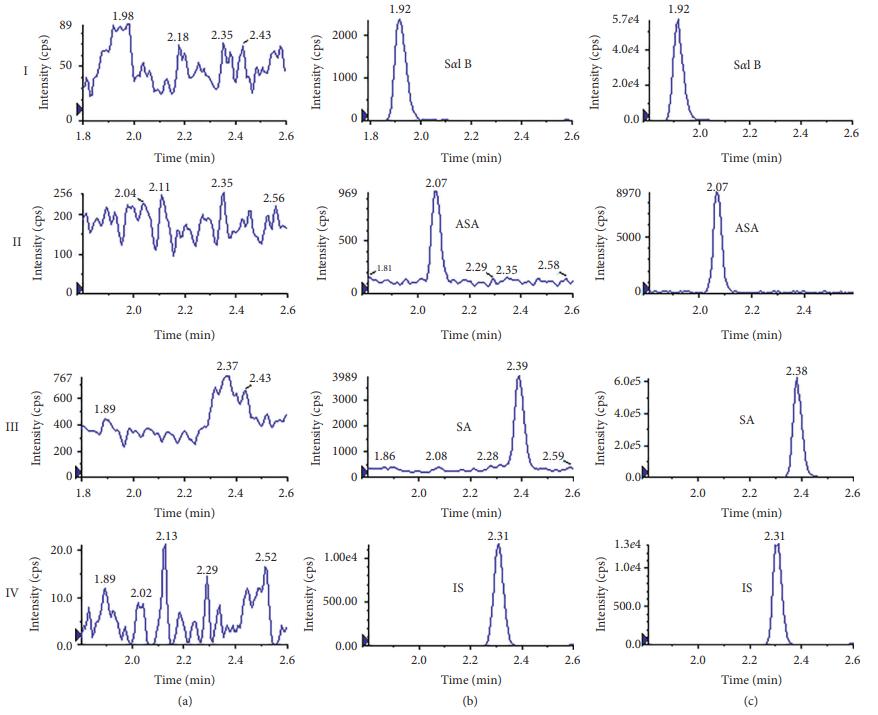 Representative MRM chromatograms of Sal B ASA, SA, and IS in plasma. (a) Blank plasma. (b) LLOQ sample (Sal B ASA, and SA at 5 ng/mL; IS at 20 ng/mL). (c) Plasma sample 4 h after administration.
Representative MRM chromatograms of Sal B ASA, SA, and IS in plasma. (a) Blank plasma. (b) LLOQ sample (Sal B ASA, and SA at 5 ng/mL; IS at 20 ng/mL). (c) Plasma sample 4 h after administration.
Table 1: MS/MS ion acquisition parameters of Sal B, ASA, SA, and IS
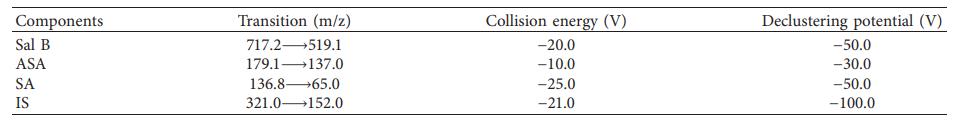
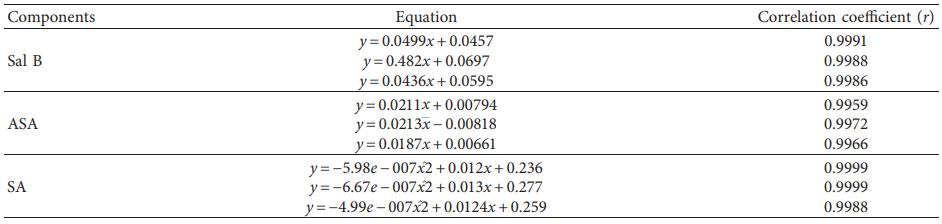
Table 2: Calibration curves and correlation coefficients of Sal B, ASA, and SA.
Developed a robust, sensitive, and validated UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of Sal B, ASA, and SA in human plasma. Method is suitable for clinical pharmacokinetic studies, especially DDI assessments involving traditional Chinese medicine and Western drugs. Provides a reference for future in vivo analysis of similar compound combinations in integrated medicine research.
Reference
- Cao, Weiyi, et al. "Simultaneous Quantification of Aspirin, Its Metabolite Salicylic Acid, and Salvianolic Acid B in Human Plasma Using UPLC‐MS/MS." International Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2021.1 (2021): 6620868. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6620868
Publications
Here are some publications in Metabolomics research from our clients:

- Elevated SLC7A2 expression is associated with an abnormal neuroinflammatory response and nitrosative stress in Huntington’s disease. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-024-03038-2
- Lipin-1 regulates lipid catabolism in pro-resolving macrophages. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.03.121293
- Physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic insights of three extremophyte woody species living in the multi-stress environment of the Atacama Desert. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04484-1
- Fatty Acid and Antioxidant Profile of Eggs from Pasture-Raised Hens Fed a Corn- and Soy-Free Diet and Supplemented with Grass-Fed Beef Suet and Liver. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213404
- NUDT22 promotes cancer growth through pyrimidine salvage and the TCA cycle. 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1491465/v1






