Linoleic Acid Analysis Service
As industries face rising demands for product authenticity, nutritional precision, and quality assurance, linoleic acid analysis has become essential for revealing vital biochemical and industrial insights. Creative Proteomics offers advanced LC-MS/MS and GC-MS solutions to quantify, characterize, and authenticate linoleic acid and related compounds, empowering your research, manufacturing, and regulatory compliance.
- Ultra-low detection limits down to 0.5 fg for trace analysis
- Precise cis/trans isomer separation for authenticity testing
- Comprehensive profiling across 20+ fatty acids
- Customized methods for diverse matrices and regulatory needs
- Expert data interpretation supporting lipidomics research
Submit Your Request Now
×
Download Our Lipidomics Solution Brochure
What You'll Receive
- Quantitative results for linoleic acid and key lipid compounds
- Clear chromatograms and mass spectra for your records
- Comprehensive method details upon request
- Expert support to help apply findings in research and production
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- FAQ
- Case
What Is Linoleic Acid?
Linoleic acid (LA) is an essential polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid (C18:2, cis-9,12) crucial for maintaining cellular membrane fluidity, signal transduction, and eicosanoid biosynthesis. As a significant component of dietary fats and biological systems, LA influences inflammatory pathways, lipid metabolism, and overall health. Variations in linoleic acid levels are increasingly studied in contexts ranging from metabolic disorders to food quality control and agricultural research.
Why Analyze Linoleic Acid?
Analyzing linoleic acid is essential for diverse research and industrial applications, such as:
- Nutritional Research and Food Science: Monitoring fatty acid composition in oils, food products, and nutritional supplements to ensure product quality and label compliance.
- Quality Control in Manufacturing: Verifying raw materials and final products in the food, cosmetics, and personal care industries for consistency and authenticity.
- Agricultural and Plant Research: Evaluating oilseed crops for breeding programs and assessing feed quality in animal nutrition studies.
- Product Development: Formulating products with specific lipid profiles to enhance texture, stability, or other functional properties.
- Process Optimization: Supporting industrial processes where precise lipid composition impacts yield, efficiency, or product performance.
Accurate measurement of linoleic acid ensures product integrity, supports research objectives, and provides valuable data for innovation in multiple sectors.
Linoleic Acid Analysis Service Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Quantitative Determination of Linoleic Acid: Precise measurement of absolute or relative linoleic acid content in samples such as food products, plant oils, cosmetics, and biological specimens.
- Comprehensive Fatty Acid Profiling: Simultaneous analysis of multiple fatty acids to determine the proportion of linoleic acid within the overall lipid composition, supporting formulation optimization and raw material quality assessment.
- Isomer Separation and Quantification: Separation and quantification of cis/trans isomers of linoleic acid, essential for authenticity testing and detection of adulteration, particularly in edible oils.
- Trace-Level Detection: High-sensitivity assays for detecting low concentrations of linoleic acid in complex or limited-volume samples, suitable for specialized research and premium product testing.
- Custom Method Development and Validation: Development of tailored analytical methods specific to unique sample types or regulatory requirements, complete with method validation and documentation.
- Batch Consistency Testing: Analysis of linoleic acid content across production batches to ensure consistency and support quality control and product release processes.
- Lipidomics Data Analysis Services: Professional bioinformatics and data interpretation services to help clients integrate linoleic acid data into broader lipidomics studies and understand its impact on product characteristics or biological pathways.
List of Detected Linoleic Acid and Related Metabolites
| Analyte Name | Abbreviation | Typical Detection Range (µg/mL or % total FA) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linoleic Acid | LA | 0.1 – 500 µg/mL or 0.1 – 80% | Essential omega-6 fatty acid; main target analyte. |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid | CLA | 0.05 – 50 µg/mL | Various positional and geometric isomers. |
| γ-Linolenic Acid | GLA | 0.05 – 30 µg/mL | Omega-6 fatty acid derived from linoleic acid. |
| α-Linolenic Acid | ALA | 0.05 – 40 µg/mL | Essential omega-3 fatty acid, metabolic counterpart. |
| Arachidonic Acid | AA | 0.05 – 30 µg/mL | Derived from linoleic acid; involved in eicosanoid pathways. |
| Eicosadienoic Acid | EDA | 0.02 – 10 µg/mL | Elongation product of linoleic acid. |
| Dihomo-γ-linolenic Acid | DGLA | 0.02 – 10 µg/mL | Omega-6 intermediate between GLA and AA. |
| Stearidonic Acid | SDA | 0.02 – 15 µg/mL | Omega-3 fatty acid linked to ALA metabolism. |
| Oleic Acid | OA | 0.1 – 70% (of total FA) | Major monounsaturated fatty acid in oils and tissues. |
| Palmitic Acid | PA | 0.1 – 60% (of total FA) | Common saturated fatty acid. |
| Stearic Acid | SA | 0.1 – 30% (of total FA) | Saturated fatty acid often measured alongside LA. |
| Myristic Acid | MA | 0.01 – 10% (of total FA) | Minor saturated fatty acid in some oils and fats. |
| Lauric Acid | LAU | 0.01 – 20% (of total FA) | Significant in certain plant oils like coconut oil. |
| Capric Acid | C10:0 | 0.01 – 5% (of total FA) | Medium-chain fatty acid in specific plant/fat sources. |
| Caprylic Acid | C8:0 | 0.01 – 5% (of total FA) | Medium-chain fatty acid relevant in food products. |
| Trans-Linoleic Acid Isomers | t-LA | 0.01 – 20 µg/mL | Important for authenticity testing in edible oils. |
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) species | PC-FA | Varies by chain length and saturation | Major phospholipid containing LA in cell membranes. |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) species | PE-FA | Varies by chain length and saturation | Lipid class often analyzed with LA in lipidomics. |
| Triacylglycerols containing LA | TAG-LA | Varies by matrix | Key lipid species in oil and fat matrices. |
| Free Fatty Acids (total) | FFA-total | Varies widely | Includes LA among other fatty acids. |
Advantages of Linoleic Acid Assay
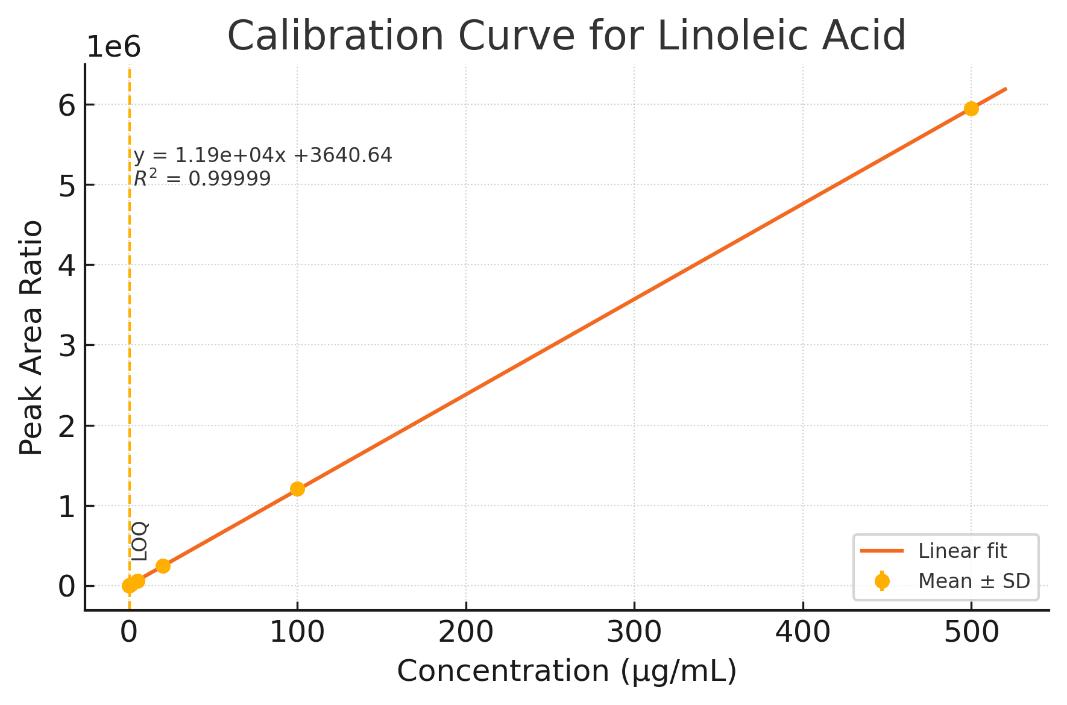
- Ultra-Low Detection Limits: Down to 0.4 ppb (LC-MS/MS) or 0.02 µg/mL (GC-FID), ideal for trace-level detection
- Broad Quantification Range: 0.05 to 500 µg/mL with excellent linearity (R² ≥ 0.995)
- High Precision & Accuracy
- Intra- and inter-batch RSD < 5 %
- Spike recovery between 90–110 % across diverse matrices
- Isomer Resolution
- Cis/trans separation with Rs > 1.5 (GC-FID)
- Chiral LC achieves > 98 % baseline separation when needed
- Low Sample Requirements: As little as 200 µL plasma or 50 mg tissue sufficient for analysis
- Robust Structural Confirmation: MS/MS analysis with ≥ 4 diagnostic fragments ensures high specificity
- Excellent Method Reproducibility
- Retention time drift ≤ 0.05 min over long-term runs
- Cross-lab bias within ±10 % validated for method transfer
Workflow for Linoleic Acid Analysis Service
Sample Receipt & Inspection
- Check integrity and assign tracking IDs
Sample Preparation
- Lipid extraction and optional derivatization
- Cleanup to reduce matrix effects
Instrumental Analysis
- GC-FID, GC-MS, or LC-MS/MS based on sample and sensitivity needs
- Targeted monitoring of linoleic acid and related compounds
Data Processing & Quality Control
- Quantification using certified standards
- Internal QC for precision and accuracy
Report Delivery
- Clear reports with data, chromatograms, and optional expert consultation

Technology Platform for Linoleic Acid Analysis Service
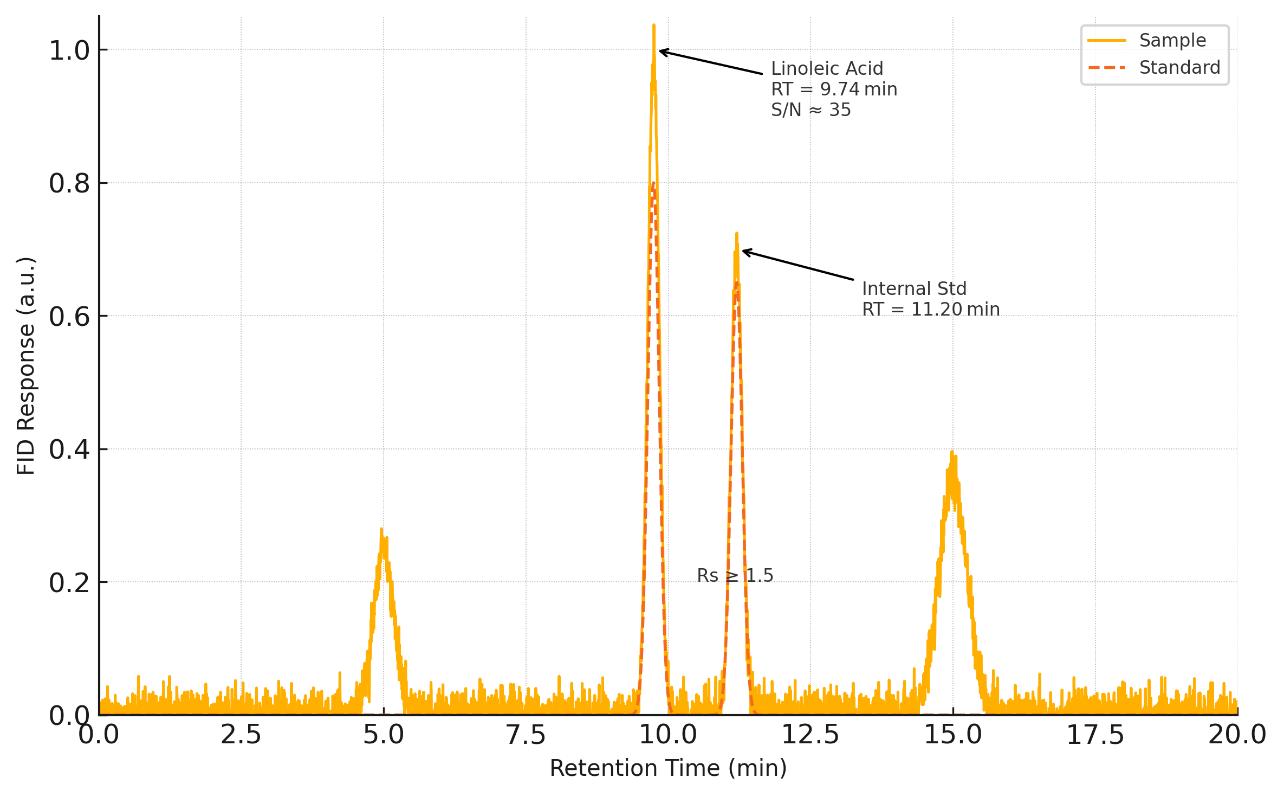
Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detection (GC-FID)
- Instrument: Agilent 7890B GC System
- Column: DB-23 or equivalent, 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm
- Temperature Program: 50–250°C
- Detection Limit: ~0.02 µg/mL
- Ideal for fatty acid profiling in oils, food products, and biological samples after derivatization to fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs).
 Agilent 7890B (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 7890B (Figure from Agilent)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
- Instrument: Agilent 7890B coupled with 5977A MS
- Selected Ion Monitoring (SIM) for enhanced specificity in complex matrices
- Detection Limit: ~0.01 µg/mL
- Suitable for confirming fatty acid identities and detecting trace levels in diverse matrices.
 Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
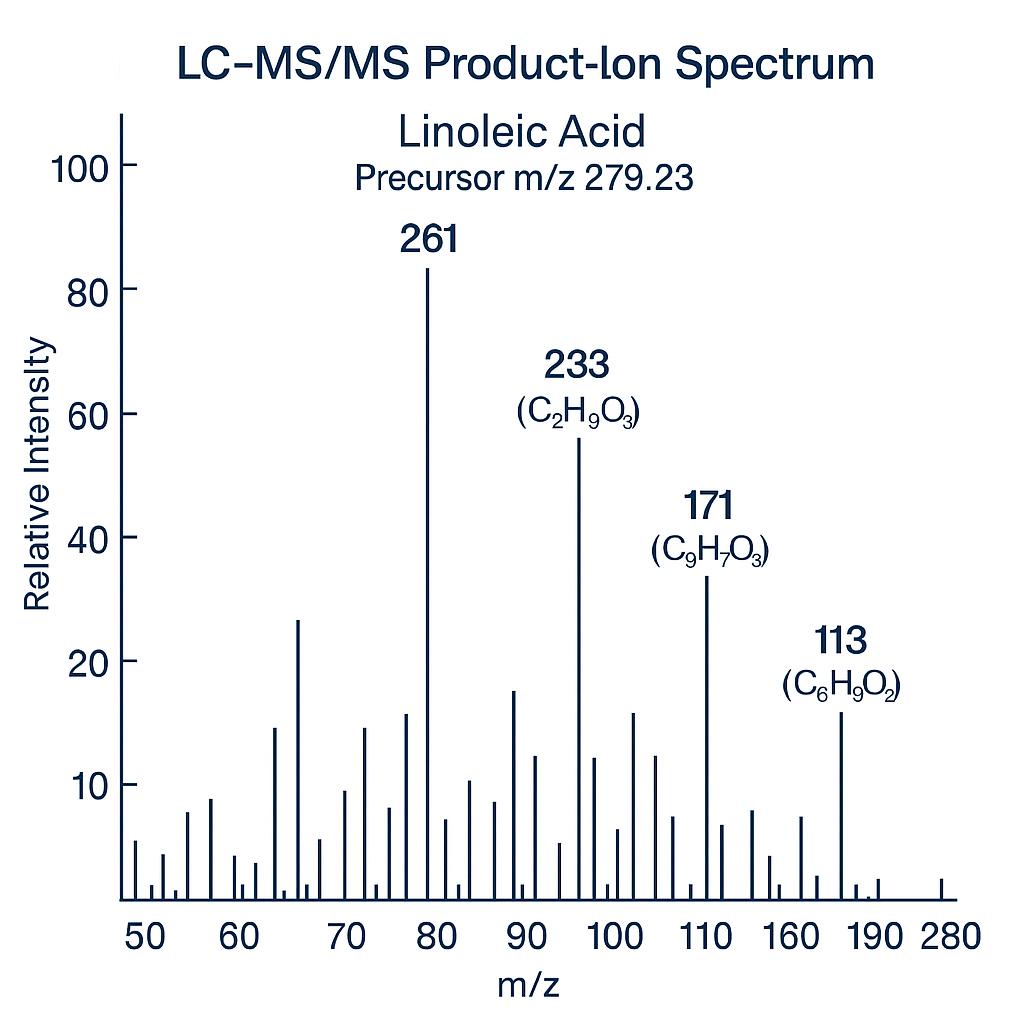
Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
- Instrument: Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole
- Operating Mode: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM)
- Detection Limit: As low as ~0.5 fg on column for optimized conditions
- Excellent for direct analysis of free linoleic acid without derivatization, especially in complex matrices like plasma, cosmetics, or low-level biological samples.
- Provides high selectivity to distinguish linoleic acid from structurally similar compounds, including cis/trans isomers.
 Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Sample Requirements for Linoleic Acid Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount Needed | Container & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Serum / Plasma | ≥ 200 µL | EDTA or heparin tubes; ship on dry ice |
| Whole Blood | ≥ 300 µL | EDTA tube; keep refrigerated or frozen |
| Plant Oils / Edible Oils | ≥ 100 mg | Amber glass vial to prevent oxidation |
| Animal or Plant Tissue | ≥ 50 mg | Snap-frozen in liquid N₂; delivered on dry ice |
| Feed / Food Products | ≥ 1 g | Vacuum-sealed bag or sterile container |
| Cosmetic Formulations | ≥ 200 mg | Clean, airtight jar; avoid light/heat |
| Microbial Culture Broth | ≥ 10 mL | Sterile tube; cool pack transport |
| Cell Pellets (Mammalian) | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | Frozen pellet in cryovial |
| Plant Seeds or Grains | ≥ 1 g | Dry, sealed pouch; room-temperature okay |
Demo Results
FAQ of Linoleic Acid Analysis Service
How do you evaluate and mitigate matrix effects in difficult sample types?
We run post-extraction spike-recovery experiments at three concentration levels and calculate absolute matrix factors. If suppression or enhancement exceeds ±15 %, we switch to isotopic-dilution calibration or standard-addition to eliminate bias.
Which isotopically-labeled internal standards are accepted?
Our default calibrant is ¹³C₁₈-linoleic acid. We can also accommodate D₄-LA or closely related ¹³C-labeled C18:1 standards, provided purity is ≥ 98 % and a certificate of analysis accompanies the shipment.
How is artifactual oxidation of linoleic acid prevented during sample prep?
All extractions are performed on ice under nitrogen. We add 50 µM butylated hydroxytoluene as an antioxidant and use silanized glassware to suppress metal-catalyzed peroxidation. Process blanks routinely confirm in-lab oxidation stays below 2 % of native LA.
Can the method be transferred to a sponsor's laboratory?
Yes. We supply a full transfer dossier—SOP, column spec, MRM table, system-suitability criteria, and cross-validation data. A bridging validation with ≤ 6 % precision and ± 10 % accuracy is typically sufficient for adoption.
How do you monitor long-run stability during batches exceeding 400 injections?
A system-suitability sample is injected every 20 runs. Acceptance limits are ≤ 0.05 min RT drift and ≤ 5 % peak-area RSD. Control charts trigger automatic re-tune if thresholds are breached.
Can you provide orthogonal confirmation (FID + MS) for regulatory dossiers?
Absolutely. We split the GC effluent to FID for quantitative traceability and to MS (SIM mode) for structural confirmation; the two detectors agree within ± 3 % for linoleic acid.
How are carry-over and dilution integrity validated?
Carry-over is checked by injecting solvent after the highest calibrator; signal must be < 0.1 % of that standard. Dilution linearity is demonstrated up to 1:100 with accuracy maintained between 95 % and 105 %.
Do you support incurred-sample reanalysis (ISR) for regulated studies?
Yes. We select ISR pairs around C_max and the median concentration; re-measured values must fall within ± 15 % of the originals. Any deviation triggers root-cause investigation and, if necessary, batch re-integration.
Can results be integrated with broader lipidomics datasets you generate?
We deliver mzTab-M files aligned to your sample IDs and provide ISA-Tab metadata, allowing seamless import into LipidSuite, Skyline, or custom bioinformatics pipelines for pathway-level analysis.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Linoleic Acid Analysis Service Case Study

Title: LC-MS/MS Profiling of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu
Journal: Metabolites
Published: 2025
- Study Summary
- Background
- Methods
- Results
- Reference
This study highlights linoleic acid oxide profiling as a powerful tool for verifying product age and quality, helping producers maintain brand trust and meet regulatory standards.
Aging significantly influences the quality and market value of Baijiu, a traditional Chinese spirit. Identifying reliable chemical markers to assess storage time is crucial for product authentication.
Analytes:
- 9,12,13-TriHOME
- 9,10-DiHOME
- 9-OxoODE
- 9-HODE
- 13-HODE
The researchers developed and validated an LC-MS/MS method operating in negative electrospray ionization (ESI) mode, with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions for precise quantification. Key parameters included:
- Limits of detection (LOD): as low as 0.4 ppb
- Limits of quantification (LOQ): 1.0 ppb
- Calibration curve linearity: R² > 0.9990 across 1.0–100.0 ppb
- Recovery rates: 87.25–119.44% across three spiking levels
- Intra- and inter-day precision: RSD below 6.96%
In strong-aroma Baijiu, 9,12,13-TriHOME and 9,10-DiHOME exhibited significant positive correlations with storage time, suggesting their suitability as aging markers.
Light-aroma Baijiu showed more complex trends, indicating that oxidative pathways and storage conditions can vary significantly depending on product type.
The method provided excellent sensitivity and reproducibility, capable of detecting trace levels of linoleic acid oxides in complex alcoholic matrices.
Reference
- Fang, Cheng, et al. "LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time." Metabolites 15.4 (2025): 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040246
Publications
Here are some of lipidomics-related papers published by our clients:

- White matter lipid alterations during aging in the rhesus monkey brain. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-024-01353-3
- Characterization of Dnajc12 knockout mice, a model of hypodopaminergia. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.06.602343
- Evidence for phosphate-dependent control of symbiont cell division in the model anemone Exaiptasia diaphana. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01059-24
- The olfactory receptor Olfr78 promotes differentiation of enterochromaffin cells in the mouse colon. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44319-023-00013-5
- Annexin A2 modulates phospholipid membrane composition upstream of Arp2 to control angiogenic sprout initiation. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202201088R
- Lipid Membrane Engineering for Biotechnology. 2023. https://doi.org/10.48780/publications.aston.ac.uk.00046663