Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service
Gain comprehensive insights into mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and nutrient absorption efficiency.
Our service provides precise quantification of both ubiquinone and ubiquinol, along with key intermediates in the CoQ10 biosynthetic pathway.
- Suitable for metabolic studies, supplement assessment, functional food analysis, and pharmacokinetic research.
- Based on validated LC-MS/MS and HPLC platforms, compatible with plasma, CSF, tissues, and complex sample types.
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You Will Receive
- Absolute CoQ10 quantification (0.5 ng/mL LOD)
- Ubiquinone / Ubiquinol redox ratio
- Biosynthesis pathway coverage (4-HB, FPP, HMG-CoA, etc.)
- Multi-sample support: plasma, CSF, tissues, supplements
- Full report with chromatograms, stats & raw data
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirements
- Demo
- FAQs
- Case Study
Overview of Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), also known as ubiquinone, is a fat-soluble, vitamin-like compound naturally present in mitochondria. It plays a critical role in the electron transport chain, facilitating aerobic cellular respiration and ATP production. Beyond energy metabolism, CoQ10 functions as a potent antioxidant, modulating oxidative stress, stabilizing cell membranes, and regulating gene expression linked to lipid and energy homeostasis.
CoQ10 exists primarily in two redox states: ubiquinone (oxidized) and ubiquinol (reduced). The redox cycling between these two forms is essential to mitochondrial and cellular function. Due to its dual role in bioenergetics and redox regulation, CoQ10 has become a focal biomarker in metabolic research, pharmacokinetics, food science, and anti-aging applications.
Why Analyze Coenzyme Q10?
Quantitative CoQ10 analysis provides valuable insights into metabolic status, mitochondrial function, nutritional evaluation, and oxidative stress. Variability in CoQ10 levels may reflect alterations in lipid metabolism, statin response, mitochondrial dysfunction, or nutritional absorption efficiency.
Creative Proteomics offers a robust, high-sensitivity CoQ10 analysis service to support:
- Nutritional and dietary supplement evaluation
- Functional food development
- Lipidomic and metabolomic profiling
- Pharmacokinetic studies of CoQ10-containing formulations
- Quality control in bioactive compound manufacturing
- Mitochondrial research and cellular bioenergetics assessment
Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Quantitative CoQ10 (Ubiquinone-10) Detection: Accurate measurement of CoQ10 concentration in plasma, serum, tissue, and other biological samples using LC-MS/MS or HPLC-ECD.
- Ubiquinol-10 Detection: Independent analysis of the reduced form of CoQ10 to assess redox balance and antioxidant status.
- Redox Ratio Analysis (Ubiquinol/Ubiquinone): Evaluation of oxidative stress through the ratio of reduced to oxidized CoQ10 forms.
- CoQ10 Biosynthetic Precursor Profiling: Targeted detection of key intermediates such as 4-hydroxybenzoate, mevalonic acid, IPP, and FPP.
- Mevalonate Pathway Metabolite Profiling: Expanded analysis of pathway components including HMG-CoA and geranyl pyrophosphate related to CoQ10 synthesis.
- Subcellular CoQ10 Distribution Analysis: Quantification of CoQ10 levels in mitochondrial vs. cytosolic fractions to support mitochondrial function research.
- Pharmacokinetic Analysis of CoQ10 Supplements: Time-course monitoring of CoQ10 levels post-intake for bioavailability and formulation studies.
- Matrix-Compatible Multi-Sample Testing: Compatible with a wide range of sample types, including CSF, cell lysates, and functional foods.
- Pathway Modeling and Data Visualization: Integration of quantitative data into metabolic pathway maps for systems biology analysis.
- Custom Method Development & Validation: Optional assay customization with validation of accuracy, precision, recovery, and detection limits.
List of Detected Coenzyme Q10 and Related Metabolites
| Category | Detected Compounds |
|---|---|
| Core Coenzyme Q10 Molecules | Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone-10), Ubiquinol-10 |
| Redox Indicators | Ubiquinol-10/Ubiquinone-10 ratio, Total CoQ10, Oxidized/Reduced CoQ10 ratio |
| Biosynthetic Precursors | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HB), Mevalonic acid, Mevalonate-5-phosphate, Mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate |
| Isoprenoid Intermediates | Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) |
| Mevalonate Pathway Markers | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), Acetyl-CoA, Acetoacetyl-CoA |
| Cholesterol Linkage Metabolites | Cholesterol, Lanosterol, Squalene |
| Mitochondrial Co-Factors | NAD⁺/NADH, FAD/FADH₂, Coenzyme A, Cytochrome c, ATP |
| Oxidative Stress Markers | Glutathione (GSH/GSSG), Malondialdehyde (MDA), Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity |
| TCA Cycle Intermediates | Citrate, Succinate, Fumarate, Malate, α-Ketoglutarate (for mitochondrial context) |
| Supplement Tracking Markers | Formulation excipients (lipid carriers, emulsifiers), Labelled CoQ10 isotopes (if applicable) |
Advantages of Coenzyme Q10 Assay
- Ultra-Low Detection Limit: Capable of detecting Coenzyme Q10 at concentrations as low as 0.5 ng/mL, ensuring high sensitivity in low-abundance biological samples.
- Wide Linear Quantification Range: Delivers accurate quantification across a broad dynamic range from 0.5 ng/mL to 10 µg/mL, suitable for both physiological and supplemented levels.
- Exceptional Analytical Precision: Intra- and inter-assay coefficient of variation (CV) maintained below 10%, ensuring reproducibility across sample batches.
- High Sample Throughput: Supports batch analysis of over 200 samples per run, ideal for population studies, time-course experiments, and screening trials.
- Redox Ratio Resolution: Accurately differentiates and quantifies oxidized (ubiquinone) and reduced (ubiquinol) forms with<5% deviation, enabling reliable oxidative stress assessment.
- Multi-Matrix Compatibility: Optimized for use with plasma, serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), liver, heart, muscle tissue, cell cultures, and dietary supplement matrices—validated in 10+ biological matrices.
- Pathway Integration Capability: Supports simultaneous detection of 20+ related metabolites across the CoQ10 and mevalonate biosynthetic pathways.
- Stable Isotope Internal Standards: Use of deuterated or 13C-labelled CoQ10 internal standards ensures accuracy and compensates for matrix effects.
Workflow for Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service
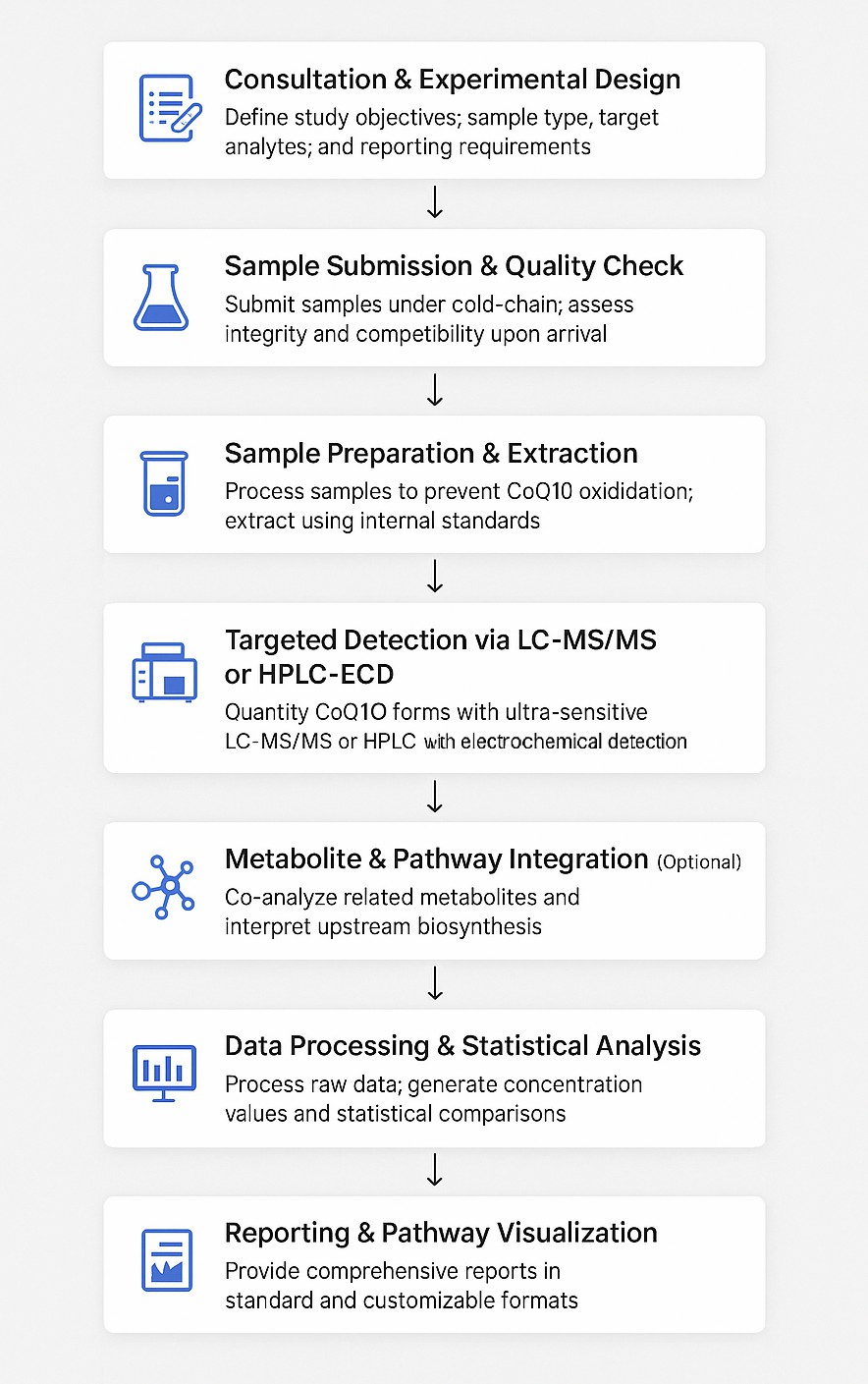
Technology Platform for Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service
Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole LC/MS
Highly suitable for CoQ10 analysis, especially using LC-MS/MS for sensitive and selective quantification of CoQ10 and its metabolites.
Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC System
Well-suited for CoQ10 analysis with UV or electrochemical detection. Widely used for routine quantification in supplements, food, and biological samples.

Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)

Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC (Fig from Agilent)
Sample Requirements for Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Sample Volume/Amount | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma / Serum | ≥ 200 µL | Prefer EDTA tubes; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| Whole Blood | ≥ 500 µL | Anticoagulant-treated; separate plasma promptly |
| Tissue (animal or plant) | ≥ 50 mg (wet weight) | Store at -80°C; homogenize under cold conditions |
| Cell Pellets | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | Washed with PBS; snap-freeze immediately after collection |
| Cultured Medium | ≥ 500 µL | Serum-free if possible; include antioxidant additives if applicable |
| Food / Oil Samples | ≥ 100 mg or 200 µL | Homogenized; provide full formulation or matrix info |
| Nutritional Supplements | ≥ 1 capsule / tablet (or ≥ 200 mg) | Provide ingredient label and formulation type (softgel, powder, etc.) |
Demo Results
FAQ of Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service
Why is HPLC preferred for CoQ10 analysis, and are there other methods?
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is preferred for CoQ10 analysis due to its high precision, sensitivity, and ability to distinguish between oxidized and reduced forms of CoQ10. HPLC offers accurate quantification even in complex biological matrices such as plasma, tissue, and cells. Alternative methods like mass spectrometry (MS) or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) can also be used, especially when higher specificity or multiplexing with other metabolites is required. However, HPLC remains the gold standard due to its robustness and reliability in routine CoQ10 quantification.
Which form of CoQ10 do you quantify—oxidized (ubiquinone) or reduced (ubiquinol)?
Our platform supports independent and simultaneous quantification of both forms, provided the redox status is preserved during sample collection and shipping.
Is derivatization required for CoQ10 detection?
No derivatization is required. Our methods use direct extraction and LC-MS/MS quantification, preserving the native form of CoQ10 and improving analytical stability.
What's the typical coefficient of variation (CV) for replicate CoQ10 measurements?
In our optimized LC-MS/MS protocol, intra-batch CV is typically<5%, and inter-batch CV is <10%, based on internal standard calibration.
How do you prevent CoQ10 oxidation during sample handling?
We recommend immediate snap-freezing and the optional addition of antioxidants such as BHT during sample preparation. For particularly sensitive samples, our lab can implement redox-stabilized workflows.
Can you analyze CoQ10 content in oily or fatty matrices like fish oil, olive oil, or lipid emulsions?
Yes. We have validated extraction protocols for lipid-rich samples, including fortified food matrices and dietary supplements.
How is quantification achieved—relative or absolute?
Quantification is absolute, using isotopically labeled CoQ10 internal standards and multi-point calibration curves to ensure accuracy across a wide dynamic range.
Do you provide CoQ10 content normalized to protein or lipid levels?
Yes, if total protein or lipid content data is provided or requested as an additional service, we can normalize CoQ10 content accordingly (e.g., ng/mg protein or ng/mg lipid).
Are there any specific anticoagulants or additives to avoid when collecting plasma samples?
Avoid citrate-based anticoagulants, as they may interfere with downstream redox chemistry. EDTA and heparin tubes are preferred for most CoQ10 applications.
What's the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for CoQ10?
Our validated LLOQ is approximately 10 pg/mL in plasma, depending on the matrix, with a signal-to-noise ratio ≥10:1.
Can your method distinguish CoQ10 from structurally similar quinones or degradation products?
Yes. Our LC-MS/MS platform provides baseline separation and high-resolution mass detection, ensuring specific identification of CoQ10 over other isobaric or interfering compounds.
What types of quality controls are used during analysis?
Each batch includes method blanks, matrix-matched calibration standards, internal standards, and QC replicates to ensure accuracy and reproducibility.
Can I request custom detection of related metabolites in the CoQ10 biosynthesis or degradation pathway?
Yes. We support targeted method development for CoQ biosynthesis precursors (e.g., polyprenyl compounds) and downstream redox-active metabolites upon request.
Learn about other Q&A.
Coenzyme Q10 Analysis Service Case Study

Title: Simultaneous Analysis of Retinol, Carotenoids, Tocopherols, and Coenzyme Q10 from Human Plasma by HPLC
Journal: Journal of Chromatography B
Published: 2020
- Background
- Methods
- Results
- Reference
Lipophilic antioxidants—including retinol (vitamin A), carotenoids, tocopherols (vitamin E), and coenzyme Q10—are critical modulators of oxidative stress and metabolic homeostasis. Their accurate quantification in human plasma provides key insights into nutritional status, antioxidant capacity, and disease risk profiles. However, analytical challenges persist due to the structural similarity among carotenoid isomers, redox sensitivity, and matrix complexity.
To overcome these limitations, the study aimed to develop a high-resolution, robust HPLC-UV method that enables simultaneous quantification of multiple lipid-soluble antioxidants, including coenzyme Q10, in plasma samples.
Sample Preparation
Human plasma samples were deproteinized with ethanol and subjected to liquid-liquid extraction using hexane. To enhance phase separation, a 0.9% NaCl solution was added. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) served as an antioxidant to minimize oxidative degradation during processing.
Chromatographic Conditions
The method employed a C30 reversed-phase column, which offered enhanced resolution of structurally similar carotenoids such as lutein and zeaxanthin. UV detection was performed at four selective wavelengths, optimized for retinol, tocopherols, carotenoids, and CoQ10.
Internal Standards
Three class-specific internal standards were used: Q4 for CoQ10, α-tocopherol nicotinate for vitamin E, and echinenone for carotenoids. These ensured precise correction for recovery efficiency and instrument variation.
Relevance to Metabolomics and Nutritional Research
This method is highly suitable for metabolomics workflows that require precise quantification of redox-active lipophilic compounds. Its application spans nutritional epidemiology, clinical biomarker studies, and oxidative stress profiling.
Creative Proteomics Lipidomics Platform
Simultaneous quantification of omega-3/6-derived isoprostanoids via LC-MS/MS.
- LOD < 1 ng/mL
- Validated SPE-based extraction
- Custom method & statistical analysis support
- The method achieved excellent chromatographic resolution, particularly between challenging carotenoid pairs (e.g., lutein vs. zeaxanthin) and between α- and γ-tocopherol.
- Coenzyme Q10 recovery rate was 93.1%, with overall compound recoveries ranging from 93.1% to 108.0%.
- Intra-assay precision was below 5% for most analytes, except for γ-tocopherol and zeaxanthin; inter-assay CVs were within 15%, meeting biological validation standards.
- Limit of quantification (LOQ) for CoQ10 and other analytes was comparable to published reference methods, ensuring method reliability.
- In a large French adult cohort (n = 2307), the measured mean plasma concentrations were 2.1 µmol/L for retinol and 27.2 µmol/L for α-tocopherol, with carotenoid levels consistent with known population norms.
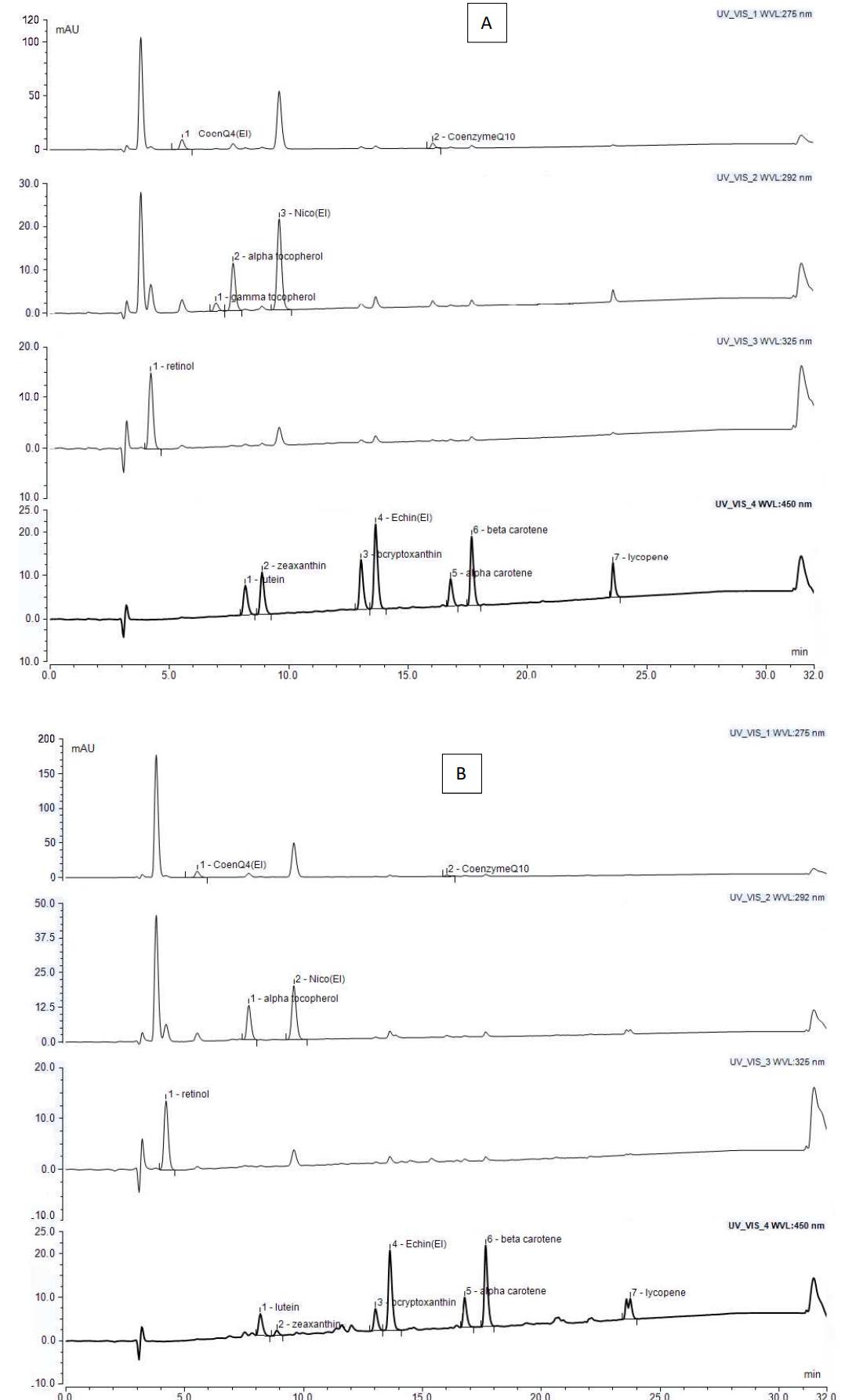 Representative HPLC chromatograms of standards and plasma samples showing retinol, tocopherols, carotenoids, and coenzyme Q10 detected at four UV wavelengths.
Representative HPLC chromatograms of standards and plasma samples showing retinol, tocopherols, carotenoids, and coenzyme Q10 detected at four UV wavelengths.
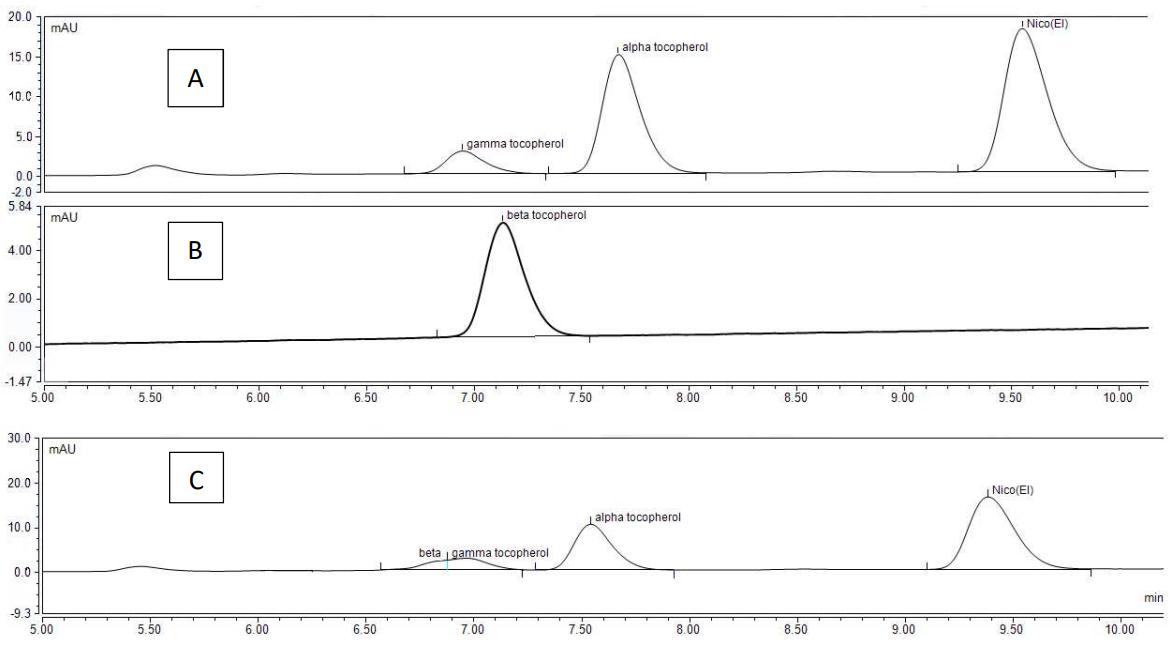 HPLC chromatograms at 292 nm for individual and mixed tocopherols: gamma, alpha, and beta forms.
HPLC chromatograms at 292 nm for individual and mixed tocopherols: gamma, alpha, and beta forms.
Reference
- Boulet, Lysiane, et al. "Simultaneous analysis of retinol, six carotenoids, two tocopherols, and coenzyme Q10 from human plasma by HPLC." Journal of Chromatography B 1151 (2020): 122158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122158
Publications
Here are some of the metabolomics-related papers published by our clients:

- Comparative metabolite profiling of salt sensitive Oryza sativa and the halophytic wild rice Oryza coarctata under salt stress. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1002/pei3.10155
- The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475
- Regulation of host metabolism and defense strategies to survive neonatal infection. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167482
- White matter lipid alterations during aging in the rhesus monkey brain. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-024-01353-3
- Multiomics of a rice population identifies genes and genomic regions that bestow low glycemic index and high protein content. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2410598121
- The Brain Metabolome Is Modified by Obesity in a Sex-Dependent Manner. 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063475









