Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis Service
Central carbon metabolism sits at the heart of cellular energy and biosynthesis—and even subtle pathway shifts can reveal decisive biology. Our LC-MS/MS–based Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis delivers high-confidence, quantitative coverage across glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and the pentose phosphate pathway, helping you pinpoint pathway bottlenecks, redox changes (NAD(P)H), and energy states (ATP/ADP/AMP) with clarity. Whether you're studying cancer metabolism, immunometabolism, neurodegeneration, or metabolic disease, we turn complex metabolite data into actionable insight—so you can move from observation to mechanism faster.
Why choose our service
- Broad pathway coverage: ~80 targeted analytes across Glycolysis / TCA / PPP
- High sensitivity & accuracy: reliable quantitation down to ng/mL level (sample-efficient)
- Actionable interpretation: PCA/PLS-DA, pathway mapping, enrichment & (optional) flux-style insights
- Flexible panels: fully customizable metabolite list to match your project
- End-to-end support: experimental design → sample prep → data delivery & consultation
Submit Your Request Now
×
- What is
- Our Service
- Instruments
- Work flow
- Applications
- Sample Requirements
- Our Advantages
- Demo
- FAQ
- Case Study
- Publication
What is Central Carbon Metabolism?
Central carbon metabolism refers to a series of key metabolic pathways in organisms, which mainly involve the decomposition and synthesis of carbohydrates and are the central hub of cellular energy production and biosynthesis. These metabolic pathways are highly conserved in all organisms and are essential for maintaining normal cell function and growth. The following are the key pathways in central carbon metabolism.
Glycolysis pathway (EMP): Glycolysis is a metabolic process that converts glucose into pyruvate, generating ATP and NADH. It serves as a key energy-producing pathway under anaerobic conditions and initiates aerobic respiration.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA): As the cornerstone of energy metabolism, the TCA cycle oxidizes acetyl-CoA in mitochondria, producing NADH and FADH₂. These molecules then transfer electrons to the respiratory chain, culminating in ATP generation.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP): The PPP is another important pathway of glucose metabolism, which mainly produces NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate.
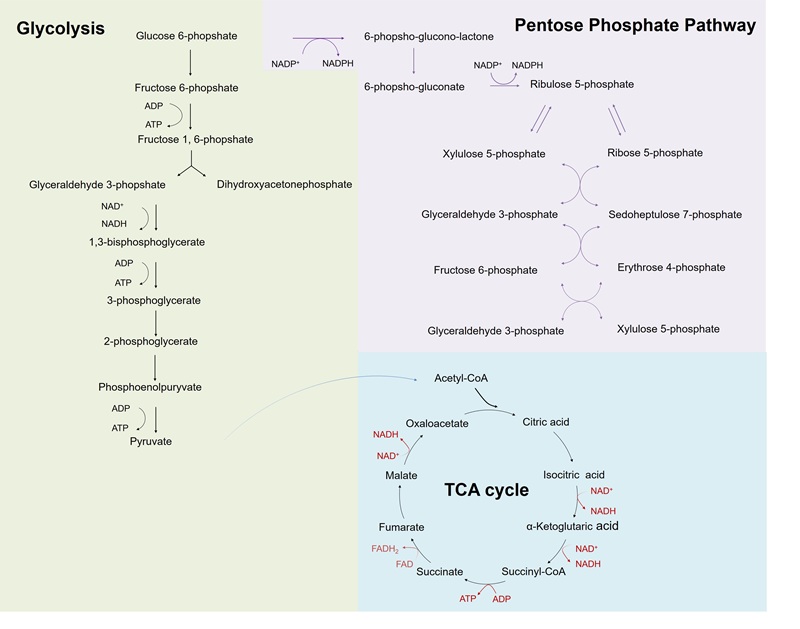 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the main processes of central carbon metabolism
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the main processes of central carbon metabolism
What We Can Do for Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis?
To determine the concentrations of multiple metabolites, LC-MS/MS is used for central carbon metabolism analysis. The current panels we provide are listed below. Have specific metabolite requirements? Our panels can be fully customized based on your unique needs, simply submit a request.
| Glycolysis Pathway Metabolites Quantified in This Service | |
|---|---|
| Glucose | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) |
| Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) | 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (1,3-BPG)/2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) |
| Fructose-6-phosphate (F6P) | 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) |
| Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F1,6BP) | 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) |
| Fructose-1-phosphate | Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) | Pyruvate |
| TCA Cycle Analysis in This Service | ||
|---|---|---|
| Acetyl-CoA | α-Ketoglutaric acid | ADP |
| AMP | ATP | cAMP |
| Citric acid | DL-α-OH-glutaric acid | Erythrose-4-P |
| Fumaric acid | GDP | GTP |
| Glycolic acid | Isocitric acid | Lactic acid |
| Malic acid | Malonyl-CoA | Succinyl-CoA |
| Mannose-6-P | NAD+ | NADH |
| NADP+ | NADPH | Oxaloacetate |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) | Pyruvic acid | Ribose-5-P |
| Ribulose-5P | Sedoheptulose-7P | Succinic acid |
| UDP-glucose | UDP | |
| Pentose Phosphate Pathway Metabolites Quantified in This Service | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fructose-6-phosphate | Glucose | Glucose-6-phosphate |
| NADP | NADPH | Ribulose-5-phosphate |
| Ribose-5-phosphate | 6-phosphogluconate | Gluconic acid-6P |
| Sedoheptulose-7P | Ribulose-bisP | Erythrose-4P |
| Xylulose-5P | ||
Instruments for Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis

How Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis Work?
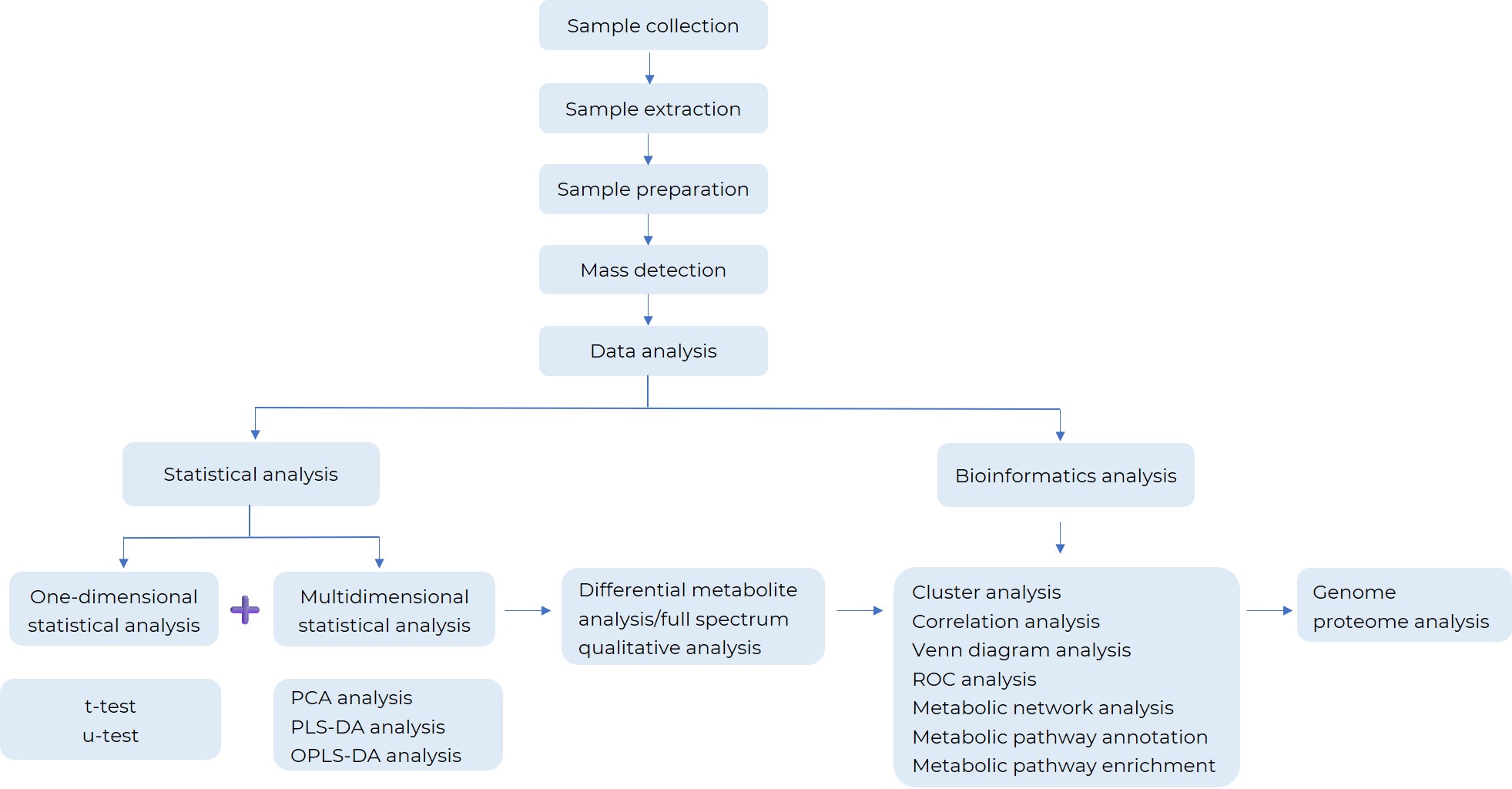
What Are the Applications of Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis?
Cancer Biology
Tumor Development and Progression: Exploring how oncogenes (e.g., Myc, RAS) and tumor suppressor genes (e.g., p53) reprogram metabolic networks to meet the rapid proliferation of cancer cells, which require biomacromolecule precursors (nucleic acids, lipids, proteins) and energy.
Immunometabolism
Cancer Immunotherapy: Investigating how nutrient competition (e.g., glucose and amino acid deprivation) in the tumor microenvironment leads to T cell exhaustion, and exploring ways to enhance the efficacy of CAR-T cells or immune checkpoint inhibitors through metabolic intervention.
Metabolic Diseases
Type 2 diabetes: Study how glucose metabolism (glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, TCA cycle) in the liver, muscle and adipose tissue is disturbed during insulin resistance.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Alzheimer's Disease: Investigating the role of impaired glucose utilization in the brain (known as "type 3 diabetes"), mitochondrial dysfunction, and TCA cycle impairment in Aβ and Tau protein pathology.
Developmental Biology and Stem Cell Biology
Tissue and Organ Development: Explore how metabolic pathways change dynamically during embryonic development to provide energy and material needs at different stages.
The Sample Requirements of Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis
| Sample type | Minimum amount |
|---|---|
| Animal and clinical tissue samples | 100 mg |
| Blood samples (serum, plasma and whole blood) | 100 µL |
| DBS | 100 µL |
| Urine samples | 1 mL |
| Stool and intestinal contents | 100 mg |
| Body fluid samples (cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, etc.) | 200 µL |
| Plant tissue samples (roots, stems, leaves flowers and fruits, etc.) | 200 mg |
| Cells and microbial organisms | 2×107 |
| Culture media and fermentation broth | 500 µL |
Our Advantages on Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis
- Extensive database coverage
80 analytes in the three major pathways of tricarboxylic acid cycle, glycolysis, and pentose phosphate pathway.
- High sensitivity and accurate quantitation
LC-MS/MS technology enables precise quantification of dozens of metabolites, even in extremely small sample volumes (such as small amounts of cells or tissues), with reliable and reproducible data. ng/mL level can be performed.
- Bioinformatics interpretation
We transform your raw data into intuitive biological conclusions through advanced statistical analyses (such as multivariate analysis PCA/PLS-DA), pathway mapping, and flux analysis models.
- Professional support and service
Our service throughout the entire process, from experimental design to sample processing and after-sales technical support.
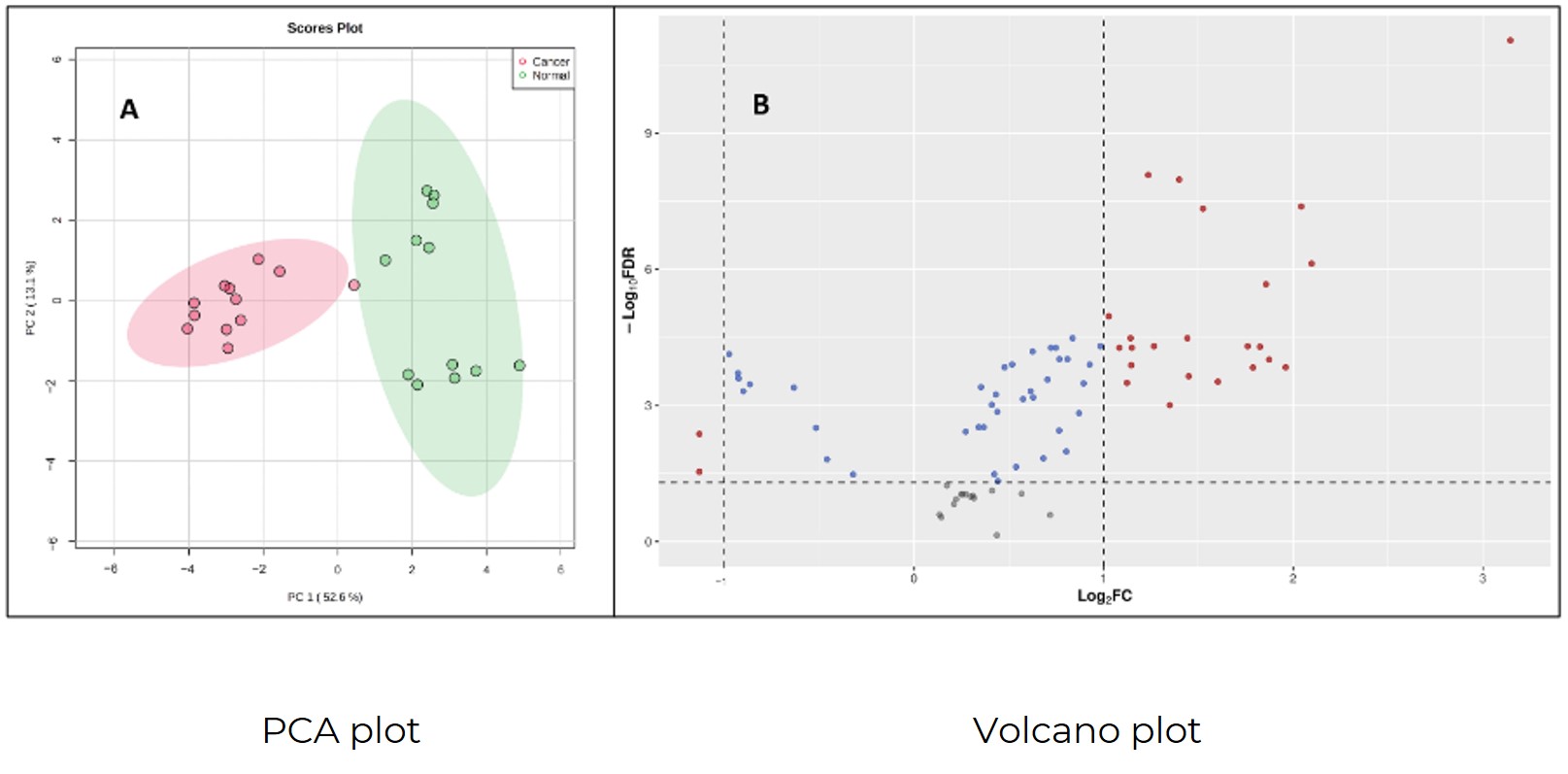
Demo for Central Carbon Metabolism Analysis
Figures come from (Jain SK. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. 28;25(11):5901)
FAQs
How does central carbon metabolism analysis work?
Central carbon metabolism analysis mainly studies metabolic activities in cells through metabolic flux analysis (MFA) technology. Among them, 13C-metabolic flux analysis (13C-MFA) is a commonly used method, which tracks the isotopic distribution of metabolites by labeling substrates (such as [1,2-¹³C] glucose) to estimate metabolic flux. With LC-MS/MS, metabolic fluxes can be quantified, pathway activities can be determined, as well as the contribution of different carbon sources to metabolic fluxes.
What are the advantages of LC-MS/MS for central carbon metabolism analysis?
In metabolite quantification, LC-MS/MS provides high sensitivity, accuracy, and selectivity. Through comprehensive analysis, a wide range of carbon metabolism metabolites can be detected, enabling us to understand metabolic pathways, metabolic fluxes, and how genetic or environmental factors influence cell metabolism.
What are the challenges of central carbon metabolism analysis testing in practical applications?
The challenges include the separation and detection of metabolites, stability, quantitative and qualitative analysis, and the complexity of metabolic flux analysis.
Recommended biological replicates?
To ensure the reliability of experimental results, more biological sample replicates are required.
Learn about other Q&A about other technologies.
Central Carbon Metabolism Case Study
Publications
Here are some publications in Metabolomics research from our clients:

- Effects of Aronia melanocarpa juice-powder on hindgut function and performance in post-weaned pigs. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2024.106196
- A comprehensive biochemical characterization of settlement stage leptocephalus larvae of bonefish (Albula vulpes). 2021. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.14846
- The activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in T cells tunes the gut microenvironment to sustain autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002000
- Insect derived extra oral GH32 plays a role in susceptibility of wheat to Hessian fly. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81481-4
- Physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic insights of three extremophyte woody species living in the multi-stress environment of the Atacama Desert. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04484-1
Reference
- Jain SK.; et al. An optimized method for LC-MS-based quantification of endogenous organic acids: metabolic perturbations in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. 28;25(11):5901.