Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service
Unlock the details behind your samples with Creative Proteomics' Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service. Whether you're ensuring product quality, exploring metabolic pathways, or developing new formulations, we deliver precise, reliable data that drives confident decisions.
- Comprehensive Coverage – Detect SFAs from C4:0 to C24:0 and key lipid derivatives.
- Ultra-Sensitive Detection – Quantify trace levels with LOQs as low as 0.2 ng/mL.
- Flexible Methodology – GC-FID, GC-MS, LC-MS/MS, and UHPLC-HRMS for diverse sample types.
- Tailored Solutions – Customized methods for challenging matrices and unique project needs.
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You'll Receive
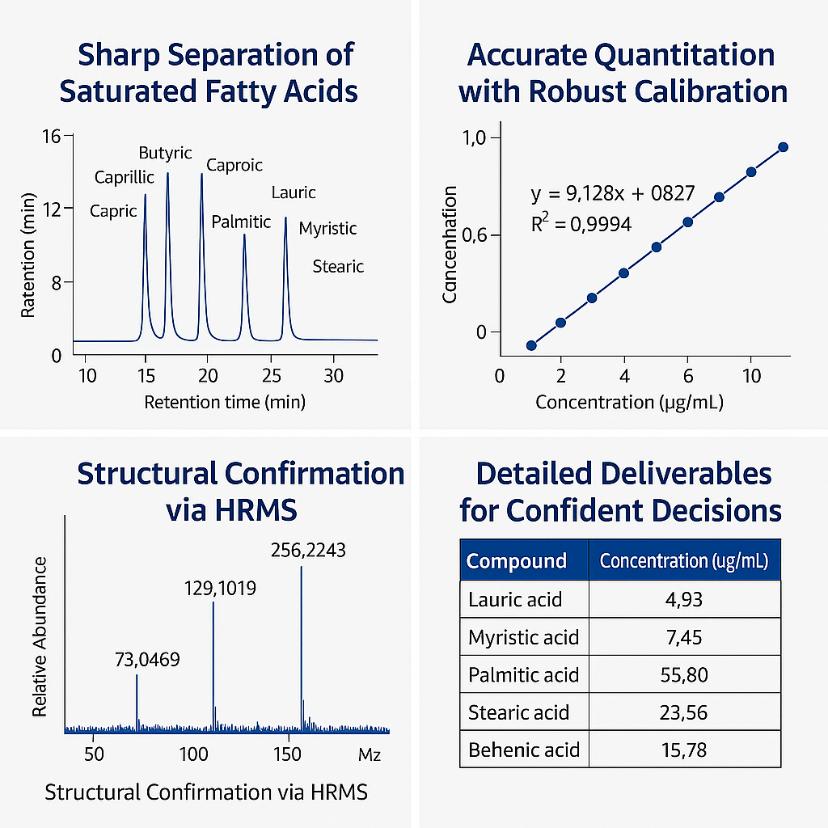
- Concentration data for each detected SFA, including LOQs and uncertainty values.
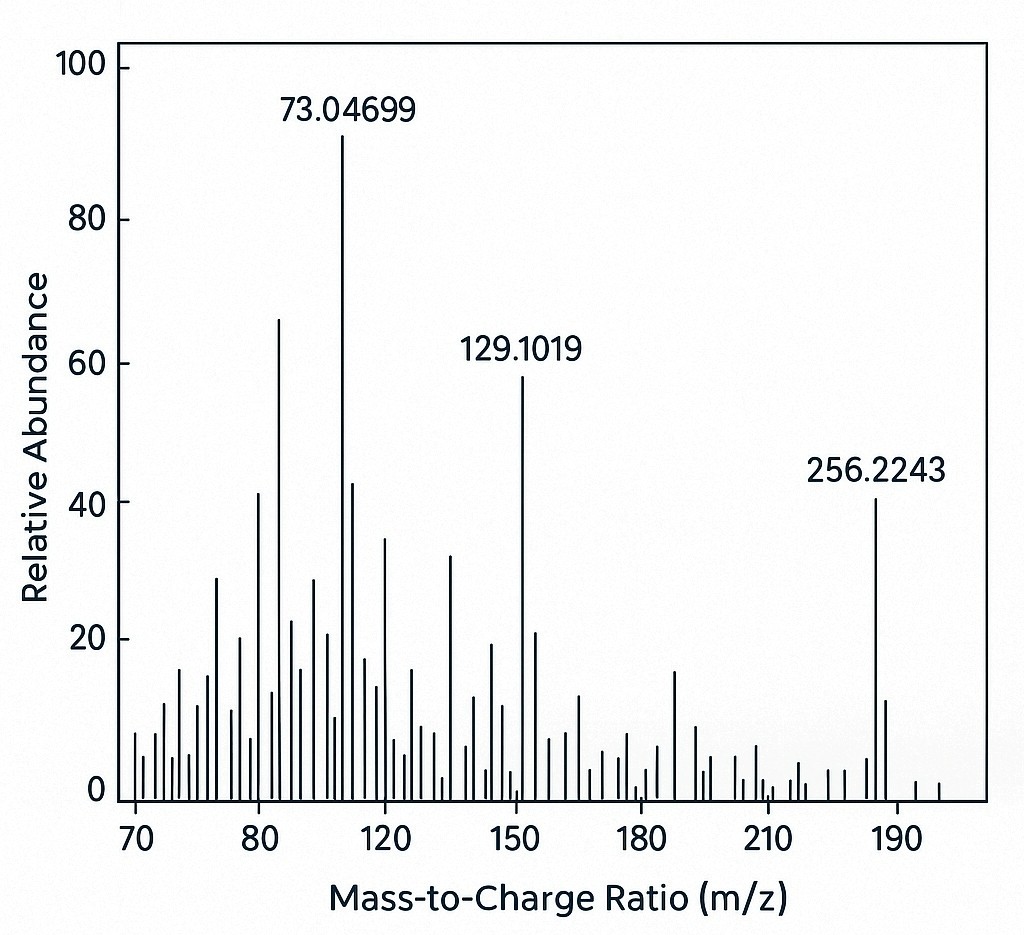
- Annotated chromatograms and high-resolution spectra for key analytes.
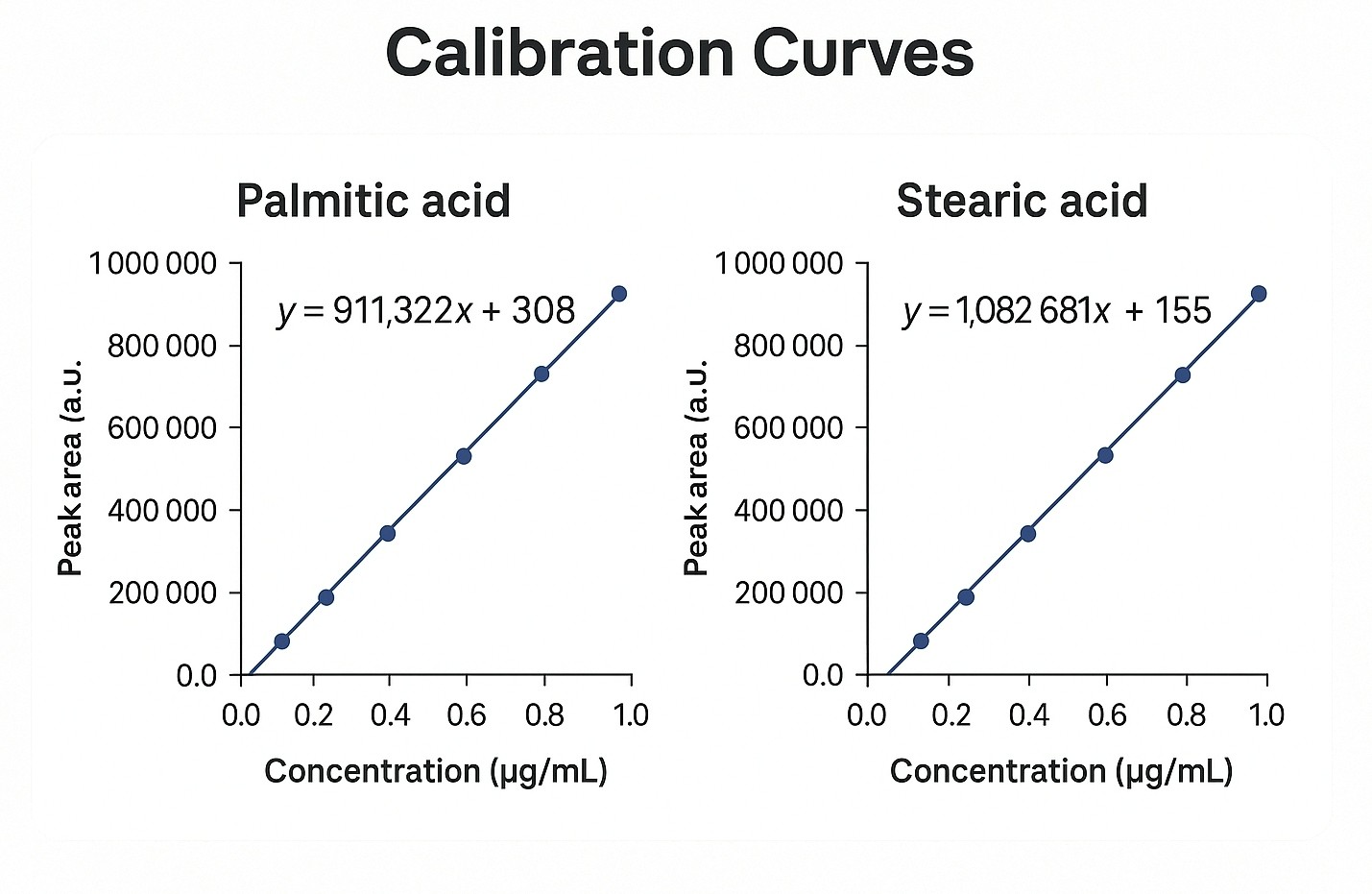
- Calibration curves and QC summaries ensuring data integrity.
- Customizable reporting formats tailored to research needs.
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- FAQ
What Are Saturated Fatty Acids (SFAs)?
Saturated fatty acids are straight-chain carboxylic acids with no carbon–carbon double bonds. From short-chain butyric acid (C4 :0) to very-long-chain lignoceric acid (C24 :0), SFAs are integral to membrane rigidity, energy storage, and signaling lipid pools. Quantitative shifts in SFA profiles influence food quality, metabolic research models, microbial fermentation yields, and plant-derived oil characteristics. Accurate, chain-length-resolved measurement is therefore a critical data point for R&D and quality programs alike.
Why Quantify SFAs? – Actionable Insights for Diverse Sectors
- Nutrition & Food Science: Validate label claims, optimize frying-oil life, and monitor hydrogenation side products.
- Metabolic & Pharmaceutical Research: Probe lipid remodeling in obesity, inflammation, and host–pathogen interaction studies.
- Agriculture & Breeding: Screen oilseed germplasm for desirable SFA/unsaturated ratios to boost shelf life without trans-fat formation.
- Industrial Biotechnology: Track SFA yields in engineered microbes or algal strains to guide bioprocess adjustments.
Each application demands absolute, isomer-resolved quantitation with tight precision—exactly what Creative Proteomics delivers.
Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Free Fatty Acid Profiling (GC-MS/FID): Converts SFAs to fatty acid methyl esters for precise quantitation. Suitable for biofluids, edible oils, and fermentation matrices, delivering absolute concentrations with external calibration.
- Intact Lipid Profiling (UHPLC-MS/MS): Maps saturated triglycerides, phospholipids, and sphingolipids with isomer-specific resolution. Supports lipidomic studies in tissues, cells, and functional food products.
- Acyl-CoA and Acyl-Carnitine Panels: Targets saturated acyl derivatives via LC-MS/MS with sub-picomole sensitivity. Ideal for exploring β-oxidation and lipid metabolism pathways in complex biological samples.
- Stable Isotope Tracer Studies: Tracks incorporation of ^13C-labeled SFAs into lipid pools to analyze biosynthetic pathways. Enables dynamic flux analysis for metabolic research and bioprocess development.
- Custom Method Development: Tailors workflows to unique sample types or regulatory standards. Includes method optimization for challenging matrices like cosmetics, environmental samples, and plant extracts.
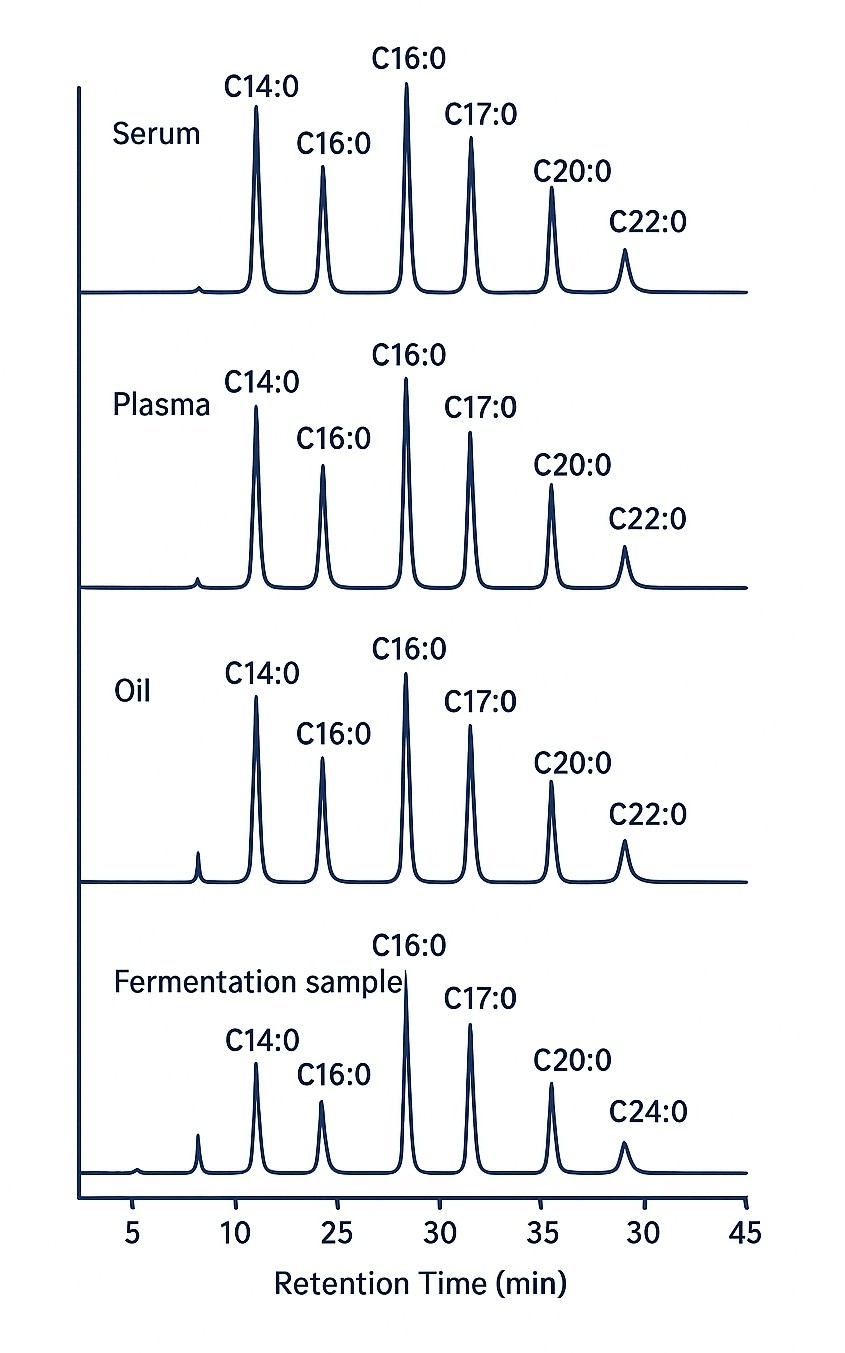
Target Coverage – Detected SFAs & Related Analytes
| Carbon Chain | Common Name | Formula | LOQ† (ng mL⁻¹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C4:0 | Butyric acid | C₄H₈O₂ | 0.5 |
| C6:0 | Caproic acid | C₆H₁₂O₂ | 0.4 |
| C8:0 | Caprylic acid | C₈H₁₆O₂ | 0.3 |
| C10:0 | Capric acid | C₁₀H₂₀O₂ | 0.3 |
| C12:0 | Lauric acid | C₁₂H₂₄O₂ | 0.2 |
| C14:0 | Myristic acid | C₁₄H₂₈O₂ | 0.2 |
| C15:0 | Pentadecanoic | C₁₅H₃₀O₂ | 0.2 |
| C16:0 | Palmitic acid | C₁₆H₃₂O₂ | 0.2 |
| C17:0 | Margaric acid | C₁₇H₃₄O₂ | 0.2 |
| C18:0 | Stearic acid | C₁₈H₃₆O₂ | 0.2 |
| C20:0 | Arachidic acid | C₂₀H₄₀O₂ | 0.3 |
| C22:0 | Behenic acid | C₂₂H₄₄O₂ | 0.4 |
| C24:0 | Lignoceric acid | C₂₄H₄₈O₂ | 0.5 |
†Limit of quantitation determined with GC-EI-MS using deuterated internal standards.
Related detectable species: chain-matched acyl-CoAs, acyl-carnitines, saturated di-/triacylglycerols, lysophospholipids, ceramides, and wax esters.
Advantages of Saturated Fatty Acids Assay
- Sensitivity: LOQ down to 0.2 ng mL⁻¹ for medium-chain SFAs; signal-to-noise > 10 at 0.1 ng injection.
- Dynamic Range: Linear quantitation across 10⁵-fold concentration span (R² ≥ 0.999).
- Precision: Intra- and inter-batch coefficient of variation ≤ 5 % based on seven replicates.
- Accuracy: Spike-recovery of NIST-certified reference materials 92 ± 4 %.
- Throughput: Autosampler workflow accommodates > 120 samples per sequence without recalibration drift.
- Data Integrity: Every batch includes procedural blanks, matrix spikes, and isotopic QC standards for traceability.
Workflow for Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service
1. Project Consultation
- Discuss study objectives, target fatty acids, matrices, and detection limits.
- Recommend optimal analytical methods and instruments based on sample type.
2. Sale Receipt & Logging
- Check sample integrity, document conditions upon arrival.
- Assign unique IDs and log into secure tracking system.
3. Sample Preparation
- Derivatization to fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) for GC analyses, or direct extraction for LC-MS/MS.
- Internal standards added for accurate quantification.
4. Instrumental Analysis
- GC-FID or GC-MS for FAME profiling with chain-length resolution.
- LC-MS/MS for targeted detection of acyl derivatives in complex matrices.
5. Data Processing & Quality Control
- Integration of chromatographic peaks or MRM transitions.
- Review calibration curves, blanks, spikes, and replicate results for precision and accuracy.
6. Reporting & Deliverables
- Provide concentration tables, annotated chromatograms, raw data files.
- Include method details, detection limits, and optional statistical summaries

Technology Platform for Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service
Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detection (GC-FID)
- Instrument: Agilent 7890B GC System
- Column: DB-23 or equivalent, 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm
- Temperature Program: 50–250°C
- Detection Limit: ~0.02 µg/mL
- Ideal for profiling saturated fatty acids after derivatization to fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), widely applied in oils, food products, and biological samples for high-throughput quantitation.
 Agilent 7890B (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 7890B (Figure from Agilent)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
- Instrument: Agilent 7890B GC coupled with 5977A MS
- Mode: Selected Ion Monitoring (SIM) for enhanced specificity
- Detection Limit: ~0.01 µg/mL
- Suitable for confirming identities and detecting trace levels of saturated fatty acids across diverse matrices, delivering high selectivity even in complex samples.
 Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
- Instrument: Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole
- Operating Mode: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM)
- Detection Limit: As low as ~0.5 fg on column under optimized conditions
- Excellent for direct analysis of saturated fatty acid derivatives such as acyl-CoAs and acyl-carnitines without derivatization, providing high sensitivity and selectivity in plasma, cosmetics, and challenging biological matrices.
 Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS)
- Instrument: Thermo Orbitrap Exploris 480 MS
- Resolution: Up to 120,000 (FWHM) at m/z 200
- Mass Accuracy: ±2 ppm with lock-mass calibration
- Ideal for untargeted profiling of intact saturated lipids, providing structural elucidation and differentiation of isomeric species in complex biological and food matrices.
 Orbitrap Exploris 480 MS (Figure from Thermo)
Orbitrap Exploris 480 MS (Figure from Thermo)
Sample Requirements for Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount Required | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Serum / Plasma | ≥ 50 µL | Store at –80°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| Tissue Homogenate | ≥ 20 mg | Fresh-frozen preferred; provide homogenization details if available |
| Cell Pellets | ≥ 1 × 10⁶ cells | Wash with PBS; store pellet at –80°C |
| Microbial Cultures | ≥ 1 mL broth or ≥ 20 mg pellet | Pellet preferred for higher analyte concentration |
| Edible Oils / Food Products | ≥ 100 mg or ≥ 100 µL | Store sealed, protected from light and heat |
| Fermentation Broths | ≥ 1 mL | Clarify if broth contains oil layers or emulsions |
| Cosmetic Formulations | ≥ 50 mg | Indicate presence of surfactants or complex matrices |
Demo Results
FAQ of Saturated Fatty Acids Analysis Service
Can your assay differentiate between endogenous and exogenous saturated fatty acids in tracer studies?
Yes. We offer stable isotope tracing protocols (e.g., ^13C-labeled substrates) that allow clear discrimination between endogenous pools and exogenously administered saturated fatty acids via mass shifts in MS spectra.
Is it possible to quantify minor SFAs present at very low abundance in complex matrices?
Absolutely. Using GC-MS in SIM mode or LC-MS/MS in MRM mode, we routinely detect SFAs down to low ng/mL or even sub-ng/mL levels, depending on the chain length and matrix background.
Do you provide data interpretation services beyond raw quantitation?
Yes. We offer optional statistical analysis, lipid class distribution summaries, and visualization tools like heatmaps or PCA plots to support biological interpretation of your SFA profiles.
Can you analyze SFAs in non-traditional matrices like cosmetics, environmental samples, or engineered microbial oils?
Yes. We routinely handle complex matrices, developing custom extraction and cleanup protocols tailored to challenging sample types to ensure accurate quantitation.
How do you ensure method reproducibility across different batches or projects?
We implement rigorous QC including calibration checks, spiked recovery experiments, and inter-batch replicates. Our typical relative standard deviation (RSD) for SFA quantitation is ≤ 5%.
Can you identify and quantify odd-chain saturated fatty acids?
Yes. Our method covers odd-chain SFAs like C15:0 and C17:0, which are increasingly studied as biomarkers for certain dietary or metabolic conditions.
Is the method suitable for both qualitative and quantitative analysis?
Indeed. We can perform qualitative profiling to identify which SFAs are present, or full quantitation with calibration curves and precise concentration reporting, depending on your project's goals.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Publications
Here are some of lipidomics-related papers published by our clients:

- White matter lipid alterations during aging in the rhesus monkey brain. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-024-01353-3
- Characterization of Dnajc12 knockout mice, a model of hypodopaminergia. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.06.602343
- Evidence for phosphate-dependent control of symbiont cell division in the model anemone Exaiptasia diaphana. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01059-24
- The olfactory receptor Olfr78 promotes differentiation of enterochromaffin cells in the mouse colon. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44319-023-00013-5
- Annexin A2 modulates phospholipid membrane composition upstream of Arp2 to control angiogenic sprout initiation. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202201088R
- Lipid Membrane Engineering for Biotechnology. 2023. https://doi.org/10.48780/publications.aston.ac.uk.00046663