Respiratory Quinones Analysis
Get defensible, isoprenologue-resolved respiratory quinone profiles—fast. We quantify UQ/MK/DMK/RQ distributions to index aerobic/anaerobic electron flow and fingerprint microbial communities across complex matrices.
- What you get: Quantitative UQ/MK ratios, full isoprenologue panels, hydrogenation states (H₂/H₄), and DMK/RQ detection
- Where it works: Activated sludge, digestates, soils/sediments, cultures, biofilms, fermentation broths, food/feed, and environmental waters
- Why it's trusted: UHPLC-APCI/APPI-MS/MS femtomole-level sensitivity; orthogonal DAD (270/326 nm) and qTOF confirmation; rigorous QC with internal standards and matrix spikes.
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You Will Receive
- Raw Data Files: LC–MS/MS spectra, chromatograms (vendor format + mzML)
- Quantitative Tables: UQ, MK, DMK, RQ isoprenologues with absolute/relative abundance
- Redox Index Outputs: UQ:MK ratios, hydrogenation-state profiles
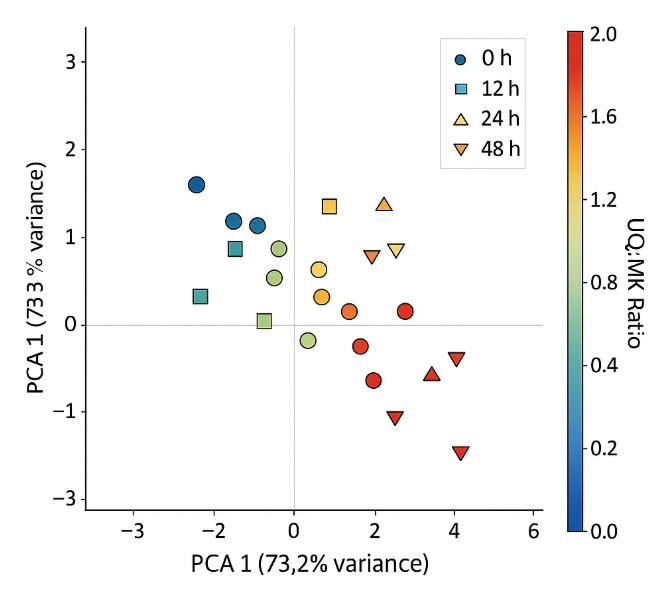
- Statistical Visuals: Heatmaps, PCA plots, clustering outputs
- Comprehensive Report: Methods, QC metrics, interpretive summary with actionable insights
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- FAQs
What Are Respiratory Quinones?
Respiratory quinones—primarily ubiquinones (UQs), menaquinones (MKs), demethylmenaquinones (DMKs), and rhodoquinones (RQs)—are membrane-bound lipid cofactors that mediate electron transport in prokaryotic and eukaryotic respiration. Their structural variations, including isoprenoid chain length (e.g., MK-7 vs MK-9) and hydrogenation state (e.g., MK-8(H₂)), reflect the organism's metabolic adaptation to oxygen tension and terminal electron acceptors.
Analyzing respiratory quinones provides a functional readout of microbial redox state and a chemotaxonomic fingerprint of microbial community structure. For instance:
- UQ-rich profiles are associated with aerobic or facultative aerobic respiration, often seen in Proteobacteria.
- MK-dominated profiles correlate with anaerobic or microaerophilic conditions, common in Actinobacteria and Firmicutes.
- Shifts in the UQ:MK ratio, or the appearance of DMK/RQ species, can signal transitions in redox environment, electron acceptor availability, or community succession.
Compared to DNA or protein-based approaches, quinone profiling is metabolically integrative and redox-resolved, capturing only viable and metabolically active cells.
Respiratory quinone analysis connects community composition with metabolic function—a critical insight for systems where microbial activity determines performance, stability, or safety.
Respiratory Quinones Analysis Services Offered by Creative Proteomics
- Quantitative Profiling of Ubiquinones (UQ-n) and Menaquinones (MK-n)
LC–MS/MS-based quantification of key isoprenologues (e.g., UQ-8, UQ-10, MK-7, MK-9) across a wide range of biological and environmental matrices. - Detection of Alternative Quinones: DMK-n and RQ-n
Sensitive detection of demethylmenaquinones and rhodoquinones associated with nitrate-respiring and anaerobic microbial populations. - Hydrogenation-State Analysis (e.g., MK-8(H₂), MK-10(H₄))
Resolution and quantification of reduced vs. oxidized menaquinones to capture redox-adaptive responses. - Extended Isoprenologue Mapping (UQ-6 to UQ-11, MK-4 to MK-13)
Comprehensive chain-length coverage to support microbial community fingerprinting and metabolic state assessment. - Optional High-Resolution qTOF-MS/MS Confirmation
Structural verification of unknown or co-eluting quinone species via exact mass and MS² fragmentation patterns.
Respiratory Quinones Analyte Panel
| Class | Representative Compounds | Alias | [M+H]+ (Exact Mass) | Detection Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquinones (UQ) | UQ-5, UQ-6, UQ-7, UQ-8, UQ-9, UQ-10, UQ-11, UQ-12 | Coenzyme Q | UQ-8: 724.6 UQ-10: 880.7 UQ-12: 992.8 | APCI-MS/MS + DAD 270 nm |
| Menaquinones (MK) | MK-4, MK-5, MK-6, MK-7, MK-8, MK-9, MK-10, MK-11, MK-12, MK-13 | Vitamin K₂ | MK-7: 648.6 MK-9: 776.7 MK-13: 920.8 | APCI-MS/MS + DAD 326 nm |
| Hydrogenated MKs | MK-7(H₂), MK-8(H₂), MK-9(H₂), MK-10(H₂), MK-8(H₄), MK-9(H₄) | – | MK-9(H₂): 778.7 MK-9(H₄): 780.7 | APPI-MS/MS preferred; qTOF optional |
| Demethylmenaquinones (DMK) | DMK-6, DMK-7, DMK-8, DMK-9, DMK-10 | – | DMK-7: 706.6 DMK-8: 734.6 DMK-10: 790.7 | APCI or APPI-MS/MS |
| Rhodoquinones (RQ) | RQ-7, RQ-9, RQ-10 | – | RQ-9: 800.7 RQ-10: 884.7 | qTOF-MS/MS recommended |
| Other Quinones | Plastoquinone-9, Phylloquinone (K₁), 1,4-Naphthoquinone derivatives | – | PQ-9: 749.6 Phylloquinone: 451.6 | qTOF-MS or exclusion filtering |
Advantages of Our Respiratory Quinones Analysis Services
- Sensitivity: femtomole-level MS/MS detection demonstrated for UQ and MK classes; APPI typically ~3× more sensitive than APCI in benchmark studies (LLOD ≈ 1–2 fmol/µL for UQ-6/MK-4).
- Selectivity: dual confirmation (SRM + DAD 270/326 nm) with optional qTOF MS for ambiguous peaks.
- Quant rigor: calibration R² ≥ 0.995; intra-run CV ≤ 8%, inter-run CV ≤ 12% (matrix-dependent); spike-recovery 85–110%; carryover < 0.1%; RT tolerance ± 0.05 min.
- Trace-sample capability: SFE-LC enables profiling from milligram-level biomass while minimizing solvent consumption (AGREE greenness score reported 0.66 in recent work).
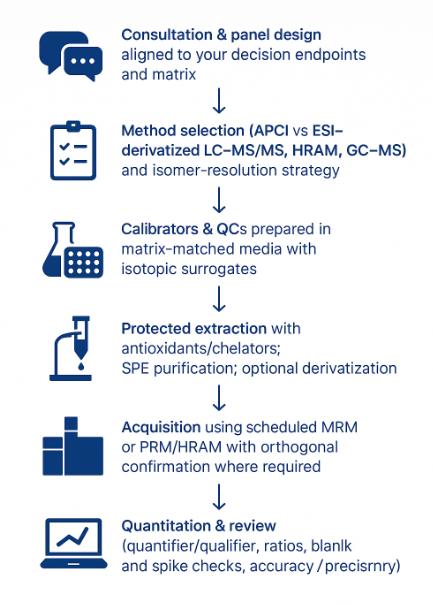
Workflow for Respiratory Quinones Analysis Service
- Consultation & panel design — define matrices, target classes (UQ/MK/DMK/RQ), expected ranges, and need for hydrogenation-state tracking.
- Extraction — CHCl₃:MeOH extraction with silica SPE cleanup or greener SFE-LC with in-line trapping for trace samples.
- UHPLC run — RP-18 separation; dual detection (SRM + DAD 270/326 nm); optional APPI for ultra-low-level targets.
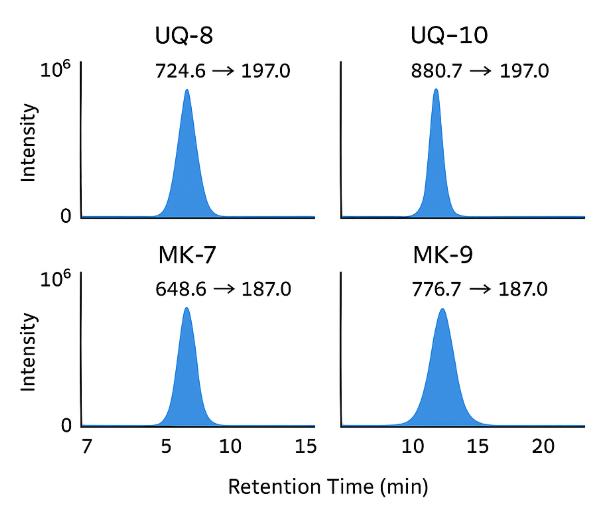
- Quantification & ID — isotope-labeled or class-matched IS, ENIU-indexed retention alignment, MRM library (e.g., 880.7→197.0 for UQ-10), qTOF confirmation as needed.
- QC gates — blanks, bracketing QCs, matrix spikes; acceptance by linearity, precision, recovery, RT window, and ion-ratio match.
- Reporting — UQ/MK ratio, full isoprenologue table with hydrogenation states, ENIU plots, PCA/heatmap option, and method/QC appendix.
Technology Platform for Respiratory Quinones Analysis Service
UHPLC–APCI/APPI–MS/MS (Triple Quadrupole)
Instruments: Thermo TSQ Altis, Agilent 6495C, SCIEX QTRAP 6500+
Ion Source:
- APCI (Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization) – standard for UQ and MK
- APPI (Photoionization) – recommended for low-abundance hydrogenated MKs
Detection Mode: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM)
- UQ-10 → m/z 880.7 → 197.0
- MK-9 → m/z 776.7 → 187.0
LOD/LOQ: Down to 1–5 fmol on-column, depending on analyte and matrix
Chromatography:
- RP-18 column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 µm)
- Methanol/IPA-based mobile phase, flow rate 0.2–0.3 mL/min
- Column oven: 35–40 °C
Internal Standards: Class-specific or isotope-labeled quinones
UHPLC–DAD (Diode Array Detector)
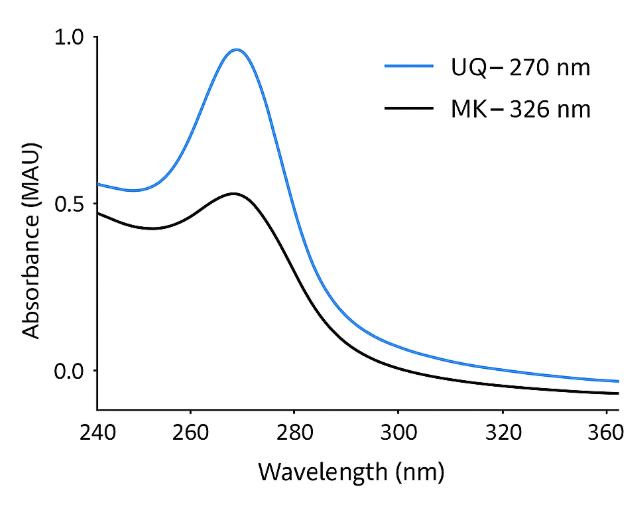
Wavelengths:
- 270 nm for ubiquinones
- 326 nm for menaquinones and demethylmenaquinones
Use Case: UV absorbance confirmation of class identity and purity; supports peak verification in complex matrices

Agilent 6495C Triple Quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)

TSQ Altis Triple Quadrupole MS (Figure from Thermo Scientific)

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)
Sample Requirements for Respiratory Quinones Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount | Container | Storage & Shipping | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass / Sludge / Digestate | ≥ 0.5 g wet (or ≥ 50 mg lyophilized) | 2 mL amber vial or cryovial | Freeze (–20 °C or lower); ship on dry ice; avoid light | For trace-level analysis, ≥ 10 mg lyophilized sample may suffice (SFE-LC applicable) |
| Pure Microbial Culture (Pellet) | Pellet from ≥ 10⁸ cells or ≥ 20 mg dry mass | Cryovial, amber vial | Freeze immediately; avoid repeated freeze-thaw | Optional: add 0.01% BHT for antioxidant protection |
| Soil / Sediment | ≥ 1 g (air-dried or frozen) | Whirl-Pak bag or amber glass jar | Frozen preferred; store in dark | Remove stones/debris; document moisture content if possible |
| Fermentation Broth / Water | ≥ 10 mL | Amber HDPE bottle or glass vial | Cold (4 °C); ship with ice packs or freeze | Biomass can be filtered upon arrival if needed |
| Food / Feed Material | ≥ 2 g homogenized | Amber container | Cold or frozen; minimize air exposure | Please note fat content and provide sample description |
Demo Results
Use Cases for Respiratory Quinone Analysis
Anaerobic Digestion & Wastewater Monitoring
Track UQ/MK ratios and isoprenologue shifts to assess redox stability, detect early process drift, and guide microbial performance optimization.
Fermentation Process Control
Monitor respiratory quinone dynamics to evaluate oxygenation, phase transitions, and microbial adaptation under varying culture conditions.
Environmental Redox Mapping
Profile MK chain-length and hydrogenation states to resolve vertical or spatial redox gradients in soils, sediments, or aquatic systems.
Microbial Product Validation
Authenticate strain identity, metabolic activity, and redox integrity in probiotics, feed additives, and engineered consortia.
Bioelectrochemical System Profiling
Characterize electron transport modes in microbial fuel cells or MESs by detecting MK/RQ patterns and hydrogenated species.
Industrial Strain Authentication
Use strain-specific quinone profiles for batch consistency checks and contamination screening in fermentation and probiotic production.
FAQ of Respiratory Quinones Analysis
How is this different from DNA-based community profiling (e.g., 16S or metagenomics)?
DNA tells you who is present; quinone profiling tells you who is actively respiring and under what electron-acceptor conditions—capturing only viable, metabolically active cells with redox specificity.
Do I need a large biomass input?
No. Our method accommodates low-input samples (≥10 mg dry weight), especially when SFE-LC or optimized extraction is applied. Trace-level profiling is routine for concentrated microbial matrices.
How do you ensure quinones aren't oxidized or lost during handling?
We apply light-protected sampling, cold-chain logistics, and rapid organic extraction with silica cleanup. Antioxidants (e.g., BHT) can be added if needed, and carryover is minimized by validated wash protocols.
When should I request UQ vs MK vs DMK/RQ panels?
UQ profiles suit aerobic/facultative systems, MK/DMK are markers for anaerobic/nitrate respiration, and RQ is selected when fumarate-based respiration is suspected. Mixed panels help track redox transitions.
Can reduced MKs (e.g., MK-8(H₂)) be distinguished from oxidized forms?
Yes. We resolve hydrogenation states via optimized ion source selection (APPI preferred) and MRM transitions, allowing clear separation of MK-n, MK-n(H₂), and MK-n(H₄) species.
What if unknown or co-eluting peaks appear in my sample?
We apply ENIU-based retention indexing, fragment screening, and optional qTOF-MS/MS to confirm structure or flag as tentative. UV–DAD spectra at 270/326 nm provide orthogonal validation.
Which ionization mode is best for my targets: APCI or APPI?
APCI is standard for most UQ and MK; APPI enhances detection of long-chain, low-abundance, or hydrogenated MKs. We recommend mode based on analyte class and matrix complexity.
Can I compare results across batches or locations?
Yes. All runs are standardized with internal standards, ENIU-indexed retention alignment, and harmonized transitions to ensure inter-study and inter-site comparability.
What QC measures are in place to ensure data reliability?
Each batch includes method blanks, bracketing QCs, matrix spikes, and ion ratio matching. We apply strict thresholds for linearity (R² ≥ 0.995), RT tolerance (±0.05 min), and CV (≤12%).
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Publications
Here are some of the lipidomics-related papers published by our clients:

- A human iPSC-derived hepatocyte screen identifies compounds that inhibit production of Apolipoprotein B. 2023.
- The activity of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in T cells tunes the gut microenvironment to sustain autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. 2023.
- Lipid droplet-associated lncRNA LIPTER preserves cardiac lipid metabolism. 2023.
- Inflammation primes the kidney for recovery by activating AZIN1 A-to-I editing. 2023.
- Anti-inflammatory activity of black soldier fly oil associated with modulation of TLR signaling: A metabolomic approach. 2023.
- Non-invasive elevation of circulating corticosterone increases the rejection of foreign eggs in female American robins (Turdus migratorius). 2022.
- Untargeted metabolomics reveal sex-specific and non-specific redox-modulating metabolites in kidneys following binge drinking. 2023.