Cholesterol Ester Analysis Service
Uncertain about lipid storage shifts or cholesterol ester composition?
Creative Proteomics delivers precise, matrix-ready cholesteryl ester profiling that reveals what's changing—and why—across your samples.
- Targeted & oxidized CE detection (LOQ ≤ 2 ng/mL)
- Matrix-matched calibration with internal standards
- Platform-ready data: TIC/XIC, calibration curves, PCA plots
- Custom workflows for serum, cells, tissues, oils, or cultures
Submit Your Request Now
×
What You Will Receive
- Raw Files – LC–MS/MS or HRAM data (.wiff / .raw / .mzML)
- Quant Tables – CE species with annotations and concentrations
- QC Summary – Calibration, ISTD recovery, batch QC results
- Visual Outputs – TIC/XIC plots, calibration curves, PCA, heatmaps
- What We Provide
- Advantages
- Technology Platform
- Sample Requirement
- Demo
- FAQs
What Are Cholesteryl Esters?
Cholesteryl esters are neutral lipids formed by the esterification of cholesterol with fatty acids. Stored primarily in lipid droplets and lipoproteins, they represent a major reservoir of both cholesterol and fatty acid chains, linking lipid storage with metabolic regulation. Their molecular composition—defined by fatty acid chain length and saturation—responds dynamically to enzymatic activity (such as ACAT1/ACAT2) and shifts in cellular state.
Profiling cholesteryl esters provides actionable insights into:
- Cholesterol metabolism and fatty acid utilization under different conditions
- Lipid droplet dynamics during cell culture, stress response, or nutrient shifts
- Lipid formulation stability and oxidative degradation
- Quality control in biological samples with lipid-rich content
Because they reflect both sterol and fatty acid pathways, cholesteryl esters serve as sensitive indicators of lipid remodeling, energy balance, and biochemical adaptation.
What Problems We Solve for Our Clients
Low-abundance cholesteryl ester quant in complex matrices: Signal-to-noise optimized chromatography and APCI-MRM to the cholesteryl cation (m/z 369.3) improves specificity over generic full-scan ESI.
Isobaric/co-eluting species: Sub-2 µm C18 and orthogonal SFC–MS options separate chain-length/unsaturation isobars; retention-time locks with isotopologues keep assignments stable.
Matrix effects & ion suppression: Isotope-dilution with deuterated CE standards and matrix-matched calibration minimize bias and drift.
Oxidation artifacts during prep: MTBE extraction with BHT antioxidant, low-light handling, and cold autosampler protect native CE profiles.
Throughput without quality loss: Pooled-QC every 10 injections, carryover checks, and real-time system suitability maintain data integrity across large batches.
Cholesteryl Ester Analysis Services Offered by Creative Proteomics
Targeted Quantification of Cholesteryl Ester Panel (Absolute & Relative)
- Absolute quant (calibration with isotopically labeled CE standards)
- Relative quant across extended CE coverage (C14–C24; 0–6 double bonds)
Oxidized Cholesteryl Esters (oxCE) Screening: Hydroperoxides/epoxides/oxo-CEs (semi-targeted HRAM with confirmatory PRM)
Total Cholesterol & CE/FC Ratio: Enzymatic or chemical saponification workflows for total sterol; CE vs free cholesterol (FC) reporting
Untargeted Lipidomics Context for CE: HRAM discovery with CE-focused curation; linkage to glycerolipids and sphingolipids
Full List of Detectable Cholesteryl Esters and Related Lipids
| Class | Representative Analytes (examples) | Quant Type |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesteryl ester molecular species (chain length/unsaturation series) | Cholesteryl myristate (14:0), palmitate (16:0), palmitoleate (16:1), stearate (18:0), oleate (18:1), linoleate (18:2), linolenate (18:3), dihomo-γ-linolenate (20:3), arachidonate (20:4), eicosapentaenoate (20:5), adrenate (22:4), docosapentaenoate (22:5), docosahexaenoate (22:6), lignocerate (24:0), nervonate (24:1) | Absolute / Relative |
| Odd-chain cholesteryl esters | 15:0, 17:0, 17:1, 19:0, 21:0 | Relative (Absolute on request) |
| Very-long-chain cholesteryl esters | 26:0, 26:1 (matrix-dependent) | Relative |
| Trans-fatty-acid cholesteryl esters | Cholesteryl elaidate (18:1 trans), selected trans-PUFA esters (as applicable) | Relative |
| Oxidized cholesteryl esters—hydroperoxy/hydroxy/epoxy/keto families | Cholesteryl 9- and 13-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoate; 9- and 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoate; cholesteryl 5-/12-/15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoate; epoxy- and oxo-linoleate/arachidonate cholesteryl esters | Relative / Semi-quant |
| Nitrated-fatty-acid cholesteryl esters (optional) | Cholesteryl nitro-oleate (18:1-NO₂) and related species | Relative |
| Free cholesterol | Cholesterol | Absolute / Relative |
| Oxysterols (separate dedicated run) | 24S-hydroxycholesterol, 25-hydroxycholesterol, 27-hydroxycholesterol, 7-ketocholesterol, 7α-/7β-hydroxycholesterol | Relative |
| Stable-isotope tracer–derived cholesteryl esters | ^13C- or ^2H-labeled fatty-acid–derived cholesteryl esters | Enrichment ± Absolute |
| Isotopically labeled internal standards | Deuterated cholesteryl oleate-d7, cholesteryl palmitate-d31, and panel variants; ^13C-cholesterol for saponified runs | N/A |
Advantages of Our Cholesterol Ester Analysis Services
- Sensitivity: LOQ typically 0.5–2 ng/mL (plasma-like matrices) for abundant CE; ≤10 ng/mL for low-abundance PUFA-CEs.
- Linearity: ≥4 orders dynamic range, R² ≥ 0.995 with matrix-matched calibration.
- Precision: Pooled-QC CV ≤ 10% intra-batch; inter-batch ≤ 15% with retention-time locking.
- Mass accuracy (HRAM): ≤ 3 ppm; fragment ion for confirmation at m/z 369.3516 (cholesteryl cation).
- Carryover: < 0.1% with needle wash and diversion valves.
- Throughput: Up to 96 samples/day per platform (10–14 min gradient).
- Data completeness: >90% feature fill across batches with QC-driven signal correction.
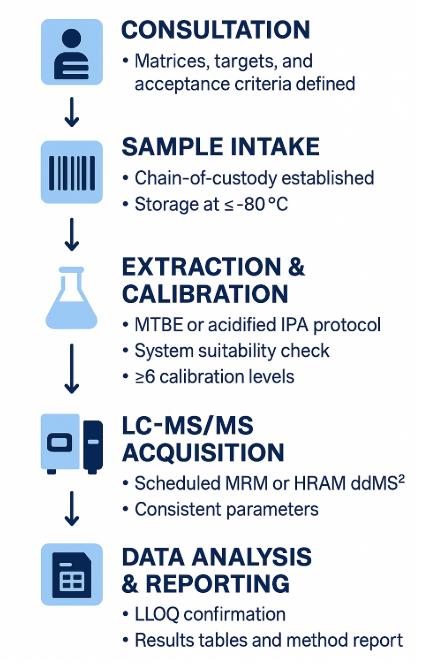
Workflow for Cholesterol Ester Analysis Service
1. Consult & Define Objectives — Matrix, target panel, quant type (absolute/relative), expected ranges.
2. Method Selection & Quotation — Choose APCI-MRM / HRAM / SFC and QC depth; finalize target list and calibration levels.
3. Sample Intake & Pre-QC — Receipt check, storage, and small-scale extraction test for recovery and matrix effects.
4. Extraction & ISTD Spiking — MTBE or hexane-based CE-preserving extraction with BHT; add deuterated CE ISTDs.
5. Chromatography & MS Acquisition — Gradient LC per above; scheduled MRM or HRAM PRM; pooled-QC every 10 samples.
6. Data Processing & QC Review — Calibration, RT/ion-ratio checks, blank/carryover review, drift correction if needed.
7. Reporting & Handover — Raw files, annotated tables, QC report, figures (TIC/XIC, calibration plots, heatmaps/PCA), and interpretation highlights.
Technology Platform for Cholesterol Ester Analysis Service
UHPLC–APCI–MS/MS (Triple Quadrupole Quantification)
Instruments: SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+
Ionization: APCI in positive mode
Key Transition: [M+NH₄]⁺ → m/z 369.3 (cholesteryl cation)
Chromatography:
- Column: C18, 2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 µm
- Flow rate: 0.3 mL/min, Column temp: 55 °C
- Gradient: IPA/ACN-based, 10–14 min total runtime
LOD/LOQ: Down to 0.5–2 ng/mL (matrix-dependent)
High-Resolution LC–MS (HRAM Profiling & oxCE Screening)
Instrument: Thermo Q Exactive™ or Q Exactive HF
Resolution: 120,000 at m/z 200
Scan Modes: Full MS + PRM (targeted MS² to m/z 369.3516)
Use Case: Identification of oxidized species, confirmation of unknowns, extended profiling beyond MRM targets

SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)

Q Exactive™ HF-X (Figure from Thermo Scientifi)
Sample Requirements for Cholesterol Ester Analysis Service
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount | Container | Stabilization & Storage | Shipping | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum/Plasma | 50–100 µL | Low-bind microtube | 0.01% BHT optional; −80 °C | Dry ice | Avoid repeated freeze–thaw; no hemolysis |
| Cell Pellet | 1–5 × 10⁶ cells (or ≥10 mg wet) | Low-bind tube | Wash PBS (no serum); snap-freeze; −80 °C | Dry ice | Provide cell count and buffer details |
| Tissue | 10–30 mg | Cryovial | Snap-freeze; −80 °C | Dry ice | Homogenize cold; record region |
| Oils/Fats/Formulations | 50–100 mg or 50–100 µL | Amber vial | Inert atmosphere if possible; 4 °C/−20 °C | Cold pack/Dry ice | Indicate solvent/additives |
| Fermentation/Broth | 0.5–1 mL | Low-bind tube | Clarify if needed; −80 °C | Dry ice | Provide media composition |
| Purified Lipoproteins (optional) | 50–100 µL | Low-bind tube | −80 °C | Dry ice | Specify fraction (VLDL/LDL/HDL) |
Demo Results
FAQ of Cholesterol Ester Analysis Service
What insights can cholesteryl ester analysis provide in research or production systems?
Cholesteryl ester profiling reveals shifts in cholesterol storage, fatty acid availability, and lipid remodeling under changing biological or process conditions. It supports mechanism elucidation, formulation stability assessment, and product quality tracking across diverse matrices.
How is cholesteryl ester analysis different from total cholesterol or lipid panel testing?
Unlike general cholesterol or triglyceride assays, this analysis resolves individual cholesteryl ester species based on acyl chain composition, enabling high-resolution detection of subtle metabolic or compositional shifts.
Can this analysis detect oxidized or modified cholesteryl esters?
Yes. Oxidized derivatives such as hydroperoxides, epoxides, and oxo-cholesteryl esters can be detected and semi-quantified using high-resolution MS workflows with structure-specific fragmentation.
Is sample type a limitation for cholesteryl ester analysis?
No. The method supports diverse sample types including serum, plasma, cultured cells, tissue, fermentation media, oils, and lipid-based formulations. Extraction and detection are optimized per matrix to ensure accuracy and comparability.
How is quantification ensured across variable sample matrices?
Quantification is supported by isotopically labeled internal standards, matrix-matched calibration, and retention time locking. Data is QC-validated with strict intra- and inter-batch controls.
What if my sample contains low levels of cholesteryl esters or complex lipid backgrounds?
The method is sensitive to low ng/mL levels and employs APCI ionization to minimize suppression. Signal optimization and internal standard normalization enable confident detection in complex or lipid-rich samples.
Can I analyze both native and labeled cholesteryl esters?
Yes. The workflow supports tracer studies using 13C or 2H-labeled fatty acids and cholesterol to track esterification or lipid flux in dynamic systems.
Are oxidized cholesteryl esters stable during sample processing?
To minimize oxidation artifacts, samples are extracted with antioxidants under cold, light-protected conditions, and processed with validated timelines to preserve native species.
Does the method allow comparison between different treatment groups or timepoints?
Absolutely. Relative quantification and multivariate analysis (e.g., PCA, clustering) reveal sample group separation, lipid remodeling trends, and statistically relevant molecular changes.
Learn about other Q&A about proteomics technology.
Publications
Here are some of the lipidomics-related papers published by our clients:

- White matter lipid alterations during aging in the rhesus monkey brain. 2024.
- Characterization of Dnajc12 knockout mice, a model of hypodopaminergia. 2024.
- Annexin A2 modulates phospholipid membrane composition upstream of Arp2 to control angiogenic sprout initiation. 2023.
- Lipid Membrane Engineering for Biotechnology (Doctoral dissertation, Aston University). 2023.
- Summative and ultimate analysis of live leaves from southern US forest plants for use in fire modeling. 2020.











