- Service Details
- Demo
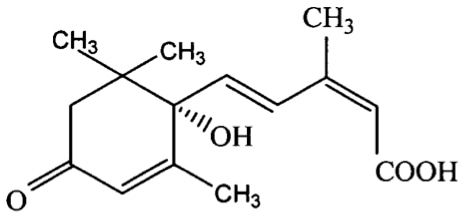
There is a wide variety of plant hormones, among which abscisic acid (ABA) is so named due to its higher concentration in senescent or shedding organs, along with auxins, cytokinins, ethylene, and gibberellins, collectively referred to as the 'five classes of plant hormones.' Natural ABA exists as enantiomers, with the biologically active form being the S-ABA, a right-handed isomer.
The Biosynthesis of Abscisic Acid
The biosynthesis of abscisic acid (ABA) can be broadly categorized into indirect pathways (in higher plants) and direct pathways (in fungi). In the former, it commences with 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) and undergoes a complex series of steps to synthesize the crucial intermediate β-carotene, which then, through a sequence of oxidations, epoxidations, and isomerizations, leads to the pivotal intermediate xanthoxin. Subsequently, xanthoxin undergoes two oxidative steps mediated by xanthoxin dehydrogenase and abscisic aldehyde oxygenase, resulting in the production of ABA. In contrast to higher plants, fungi generally utilize farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) as the starting material for ABA synthesis, albeit with species-specific variations. Here, we briefly outline the pathway for ABA synthesis in gray mold fungus as an illustrative example. Initially, FPP undergoes cyclization to form α-sesquiphellandrene under enzymatic action, followed by two oxidative steps to yield 1',4'-ABA-diol, which is ultimately converted into ABA through the action of a short-chain dehydrogenase.
The Functions and Applications of Abscisic Acid
Abscisic acid (ABA) primarily functions to induce dormancy in plant buds and inhibit their sprouting. Another notable physiological role is its rapid closure of stomata, a response observed when plant leaves experience an increase in ABA content, particularly during drought conditions. When ABA levels rise, stomata close, reducing transpiration, while watering decreases ABA levels, allowing stomata to reopen. This reversible and swift regulation of stomatal aperture by ABA contributes to its role in transpiration control.
Furthermore, ABA inhibits the growth of nutrient organs, promotes aging in organs such as leaves, and triggers the shedding of cotton bolls, among other effects. Given its pivotal role in regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses, the judicious use of ABA holds significant importance for enhancing crop yield, production, and improving crop varieties. Currently, numerous commercial ABA products are available, playing a crucial role in modern agricultural production.
Beyond its applications in agriculture, ABA finds utility in the human body, exerting broad regulatory effects on the immune system, cardiovascular cells, stem cells, and diabetes, among others. The emergence of practical ABA formulations in the market is expected to yield substantial economic and societal benefits.
 (Nguyen, C.H et al,. Genes 2023)
(Nguyen, C.H et al,. Genes 2023)
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Abscisic Acid
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is an ideal method for analyzing plant endogenous hormones. Apart from ethylene, all other endogenous hormones can be determined using LC-MS. Creative Proteomics offers a precise and efficient plant hormone testing service employing LC-MS to accurately measure changes in abscisic acid levels in plant samples. We have established a mature testing platform, selecting optimized methods for endogenous hormone extraction and purification, mobile phases, chromatographic columns, and detectors. This platform not only yields highly precise results but also enables simultaneous measurement of various endogenous hormones.
Platform
AB Sciex QTrap 6500 LC-MS/MS;
Detection Mode: Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM);
Ion Source: Electrospray Ionization (ESI) in both positive and negative ionization modes.
Key Advantages
Exceptional Sensitivity: This method allows precise quantification of plant hormone levels even at low concentrations, elucidating their functions in plant physiological processes.
Outstanding Selectivity: Employing chromatographic separation and mass spectrometry detection, it ensures precise analysis of diverse plant hormones while mitigating interference from other compounds.
Superior Resolution: It effectively separates and quantifies intricate blends of plant hormones, delivering precise outcomes.
Concurrent Detection of Multiple Plant Hormones: By means of meticulous optimization, it enables the simultaneous measurement of multiple plant hormones, enriching our insight into the intricate plant hormone network.
Sample Types
Plant tissues (recommended ≥1.0 g/sample, not less than 0.5 g minimum), fungal liquid cultures (≥50 ml/sample); Storage: Rapidly freeze samples in liquid nitrogen and store at -80°C; Transport: Ship samples on dry ice.
 Total Ion Chromatogram (TIC) Plot
Total Ion Chromatogram (TIC) Plot
References
- Hemberg, T. Significance of Growth-Inhibiting Substances and Auxins for the Rest-Period of the Potato Tuber. Physiology Plant,1949, 2, 24–36.
- Li, J.;Wu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Gong, Z. 2017. Abscisic acid. In: Li J, Li C, Smith SM, eds. Hormone Metabolism and Signaling in Plants. Academic Press, 161–202.
- BOOZ V, CHRISTIANSEN CB, KUHRE RE, SALTIEL MY, SOCIALI G, SCHALTENBERG N, FISCHER AW, HEEREN J, ZOCCHI E, HOLST JJ, BRUZZONE S. Abscisic acid stimulates the release of insulin and of GLP-1 in the rat perfused pancreas and intestine. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 2019, 35(2): e3102.
- GURI AJ, HONTECILLAS R, BASSAGANYA- RIERA J. Abscisic acid ameliorates experimental IBD by downregulating cellular adhesion molecule expression and suppressing immune cell infiltration. Clinical Nutrition, 2010, 29(6): 824-831
- Nguyen, C.H.; Yan, D.; Nambara, E. Persistence of Abscisic Acid Analogs in Plants: Chemical Control of Plant Growth and Physiology. Genes 2023, 14, 1078.





