O-Glycan Analysis Service
- Home
- Applications
- Proteomics Analysis Services
- Glycoproteomics Analysis Services
- O-Glycan Analysis Service
Service Details
Protein glycosylation is the most diverse and complex form of protein modification, greatly increasing protein heterogeneity to promote functional plasticity. Compared to N-linked glycosylation, the study of O-linked glycosylation is one of the most challenging post-translational modification analyses due to the structural complexity of added glycans and the technical challenges to unambiguously characterize them.
The process of O-linked glycosylation links different O-linked glycans to Ser and Thr residues, or the less common Tyr residues in the human proteome. Notablly, O-linked N-acetylgalactosamine (O-GalNAc) additions were the predominant type. Definitive characterization of O-linked glycoproteins requires quantitative analysis of O-linked glycosylation sites and their corresponding glycans. Unlike N-glycosylation, O-glycosylation is not governed by the presence of a linear consensus sequence in the amino acid chain, so O-glycosylation can't be predicted from linear amino acid sequences.
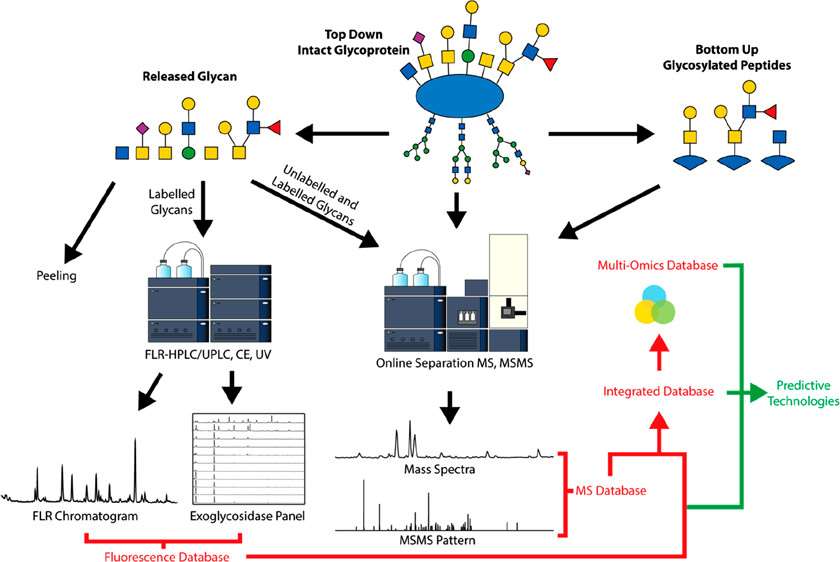 Fig. 1. Current Methods
for the Characterization of O-Glycans. (Wilkinson H, et al., 2020)
Fig. 1. Current Methods
for the Characterization of O-Glycans. (Wilkinson H, et al., 2020)
Liquid chromatography fluorescence analysis is only suitable for the analysis of unreduced labeled glycans, but both unreduced and unlabeled reduced glycans are suitable for mass spectrometry detection. Therefore, Creative Proteomics offers two commonly used MS techniques for the characterization of O-glycans, including matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) MS and electrospray ionization (ESI) MS.
At Creative Proteomics, our high-quality laboratory technicians analyze O-glycans by using MALDI-TOF MS or (ESI) MS. Permethylation of the O-glycan to transform all hydroxyl groups into methyl ethers and stabilizes sialic acids by methyl esterification of their carboxyl groups is necessary, which allows MALDI-TOF MS to analyze of all O-glycans in the positive mode.
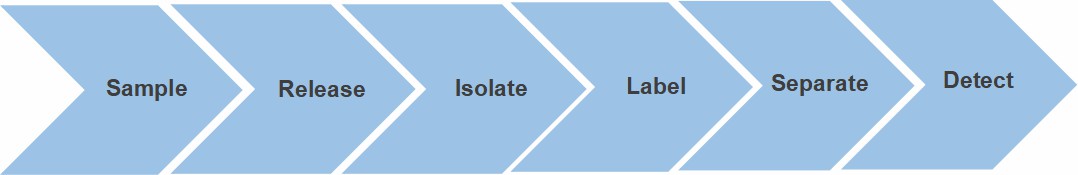 Fig. 2. Workflow for O-glycan profiling
service.
Fig. 2. Workflow for O-glycan profiling
service.
*Note: Creative Proteomics can also perform glycan studies at the glycopeptide or glycoprotein level, providing you with complete O-glycan characterization services for glycosylation.
ICH Q6B guidelines require comprehensive characterization of glycosylation of glycoproteins. With years of experience and an experienced scientific team, Creative Proteomics provides high-quality O-glycan analysis services. Additionally, we can provide fully custom project designs to meet any specific requirements. If you are interested, please contact us or send us an inquiry directly.
References
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.