Chemical Cross-Llinking Mass Spectrometry Analysis Service
- Home
- Applications
- Biopharmaceutical Characterization Services
- Biopharmaceutical Purity Analysis Services
- Chemical Cross-Llinking Mass Spectrometry Analysis Service
Service Details
Chemical cross-linking mass spectrometry is a new developed method in recent years. It refers to the use of chemical cross-linking agents to combine proteins or protein complexes with sufficiently close spatial distances, and the cross-linking site is identified by mass spectrometry after the enzyme cuts into peptides, so as to obtain low-resolution structural information. Which helps infer the folding state of the protein in three-dimensional space and the approximate protein-protein interaction area. The use of chemical cross-linking to study proteins and protein complexes followed by MS identification of cross-linked peptides has been increasingly used. Proteins perform most of their functions in the form of protein complexes to control cell signaling, protein synthesis, folding and degradation, and many other important processes. Therefore, elucidating the composition and structure of such complexes has been a focus of research in the biopharmaceutical industry.
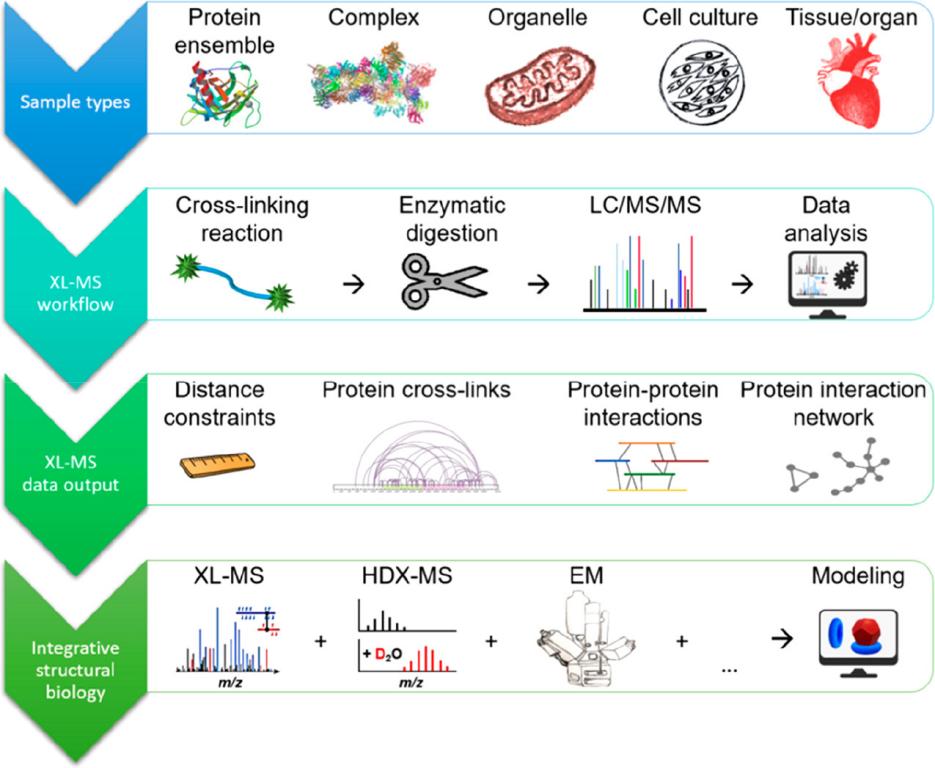 Fig.
1. Cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS) workflows allow the identification of cross-links in purified proteins,
cell culture, and intact tissue. (Piersimoni L, et al., 2022)
Fig.
1. Cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS) workflows allow the identification of cross-links in purified proteins,
cell culture, and intact tissue. (Piersimoni L, et al., 2022)
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been a key enabling technology for high-throughput and comprehensive protein identification and quantification at the proteome scale. In addition to these important contributions, MS can also be used to study the higher-order structures of biological macromolecules in a variety of ways. In one approach, intact proteins or protein complexes can be probed directly in a mass spectrometer. Alternatively, various forms of solution-phase chemistry are used to introduce modifications in intact proteins and localize these modifications at the peptide level by MS analysis for structural information.
Here, Cross-linked mass spectrometry (XL-MS) represents a powerful set of tools for defining protein-protein interactions (PPIs), and Creative Proteomics' scientists analyze protein-protein interactions using the following protocols conversion of non-covalent interactions within or between proteins in their native state into covalent bonds.
Our cross-linking mass spectrometry services are performed in a "bottom-up" approach, after the cross-linking reaction, the covalently linked proteins are digested enzymatically and the resulting peptide mixture is analyzed by LC-MS/MS (liquid chromatography method).
Our laboratory utilizes specialized XL-MS methods for in vitro and in vivo applications to determine the pathways and structures of difficult-to-define protein complexes. The combination of chemical cross-linking strategies can capture and identify not only stable proteins but also transient cross-linking residues. Identification of residues can provide interacting protein surface maps that can be used to:
Creative Proteomics is a reliable biopharmaceutical partner. Our professional team can provide high-quality chemical cross-llinking mass spectrometry analysis service for global customers. We will provide clear, comprehensive written reports, recommendations and agreements, as well as customized services to help clients solve analytical and technical problems. If you would like more information on a specific aspect of our services, please do not hesitate to contact us, we will be happy to answer any questions.
References
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.