Ubiquitination analysis is a key biochemical technology for the development of new drugs and new targets. This method can be used to detect ubiquitinated proteins; determine the ubiquitination process of these proteins; identify specific sites where lysine residues are ubiquitinated; and also be used for quantitative analysis of ubiquitination protein.
As a reliable partner of biopharmaceutical companies, Innovative Proteomics aims to provide customers with protein ubiquitination-based modification analysis services. Ubiquitination modification is a post-translational modification of proteins, which provides a powerful means for cells to regulate various biological processes. We will provide you with ubiquitination analysis services based on protein ubiquitination modification.
We Can Provide but Not Limited to:
- Identify specific proteins that undergo ubiquitination
- Identify specific sites where specific proteins undergo ubiquitination
- Identify the specific lysine residues of ubiquitinated proteins
- Identify specific sites for ubiquitination modification to recognize lysine residues
- Detection of the protein that undergoes ubiquitination is the specific ligase that causes the protein to undergo ubiquitination modification
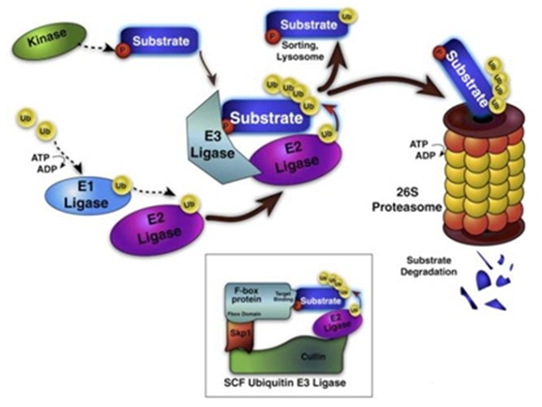
Diagrammatic process of ubiquitination (Qiu J et al. 2016).
The Working Method and Process of Ubiquitination Analysis:
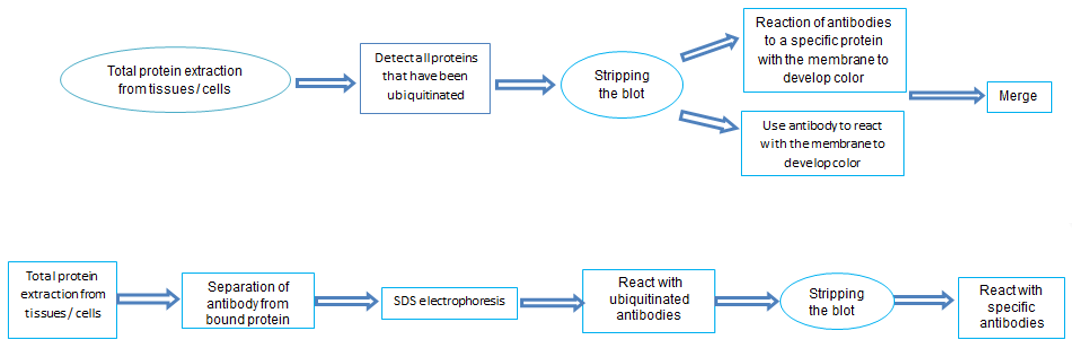
- WB+IP
It can be used for the detection of specific sites of specific proteins where ubiquitination occurs, specific lysine residues, specific sites of lysine residues, and specific ligases that cause ubiquitination modification of the protein.
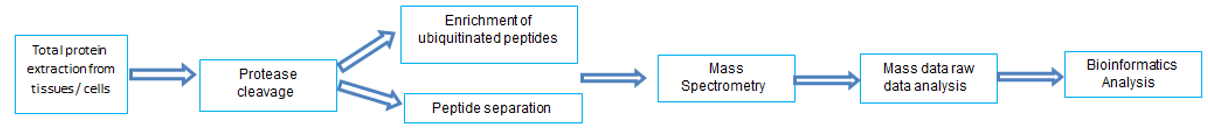
- LC-MS
LC-MS can identify ubiquitinated proteins, specific modification sites of lysine, enrich ubiquitinated peptides, quantitatively analyze ubiquitinated proteins and peptides, and analyze mass spectrometry.
Sample Requirements
- Plant tissue sample is not less than 400 mg
- Blood sample is at least 2 ml (plasma should be anticoagulated with EDTA)
- Serum 2 ml
- Urine 10 ml
- Animal tissue sample at least 2 g
- Cell sample is 1×108 cells
- Dry weight of yeast microorganism 400 mg
- Ordinary tissue and cell lysate can be used for protein extraction, the total amount of protein samples is 2-5 mg
Creative Proteomics' analytical scientists can provide customers with experimentally relevant mass spectrometry parameters, mass spectrometry images, raw data, and basic information for identifying ubiquitination sites. Provide a concise, concise written report to assist the customer in the ubiquitination analysis of related technical issues.
References
- Qiu J, et al. Ubiquitination independent of E1 and E2 enzymes by bacterial effectors. Nature, 2016.
- Udeshi, et al. Large-scale identification of ubiquitination sites by mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8:1950-1960.






