The primary structure of protein molecules such as polypeptides (10-50AA), recombinant proteins, nanobodies (15kDa), monoclonal antibodies (150kDa), and polyclonal antibodies is the core of their biological functions. Therefore, accurate and rapid analysis of protein complete sequence facilitate functional studies of unknown proteins. Direct sequencing of existing antibody products in the market is a shortcut to develop antibody drugs, antibody diagnostic reagents and other antibody products; the primary sequence of the antibody can be obtained by monoclonal antibody sequencing, which can be used as a basis for antibody affinity improvement and antibody humanization to develop antibody drugs; the accurate primary structure information of the original drug is the basis and prerequisite for antibody generic drug development.
Spectrometry-based de novo sequencing
Compared with traditional database search methods and Edman degradation, mass spectrometry-based de novo sequencing allows direct analyze protein sequences without any protein or DNA database information.
We offer the service for the complete de novo sequencing of mAb and other proteins. The service is based on the proprietary protein sequencing technology that we developed over many years. Currently, our standard procedure combines top-down and bottom-up mass spectrometry techniques to ensure the correctness of each amino acid and sequence accuracy of whole antibodies, includingN-terminal and C-terminal modifications and N-linked glycans, which can compensate for the shortcomings of traditional protein identification methods for unknown protein sequences and mutation analysis.

Monoclonal Antibody De novo Sequencing Service Workflow
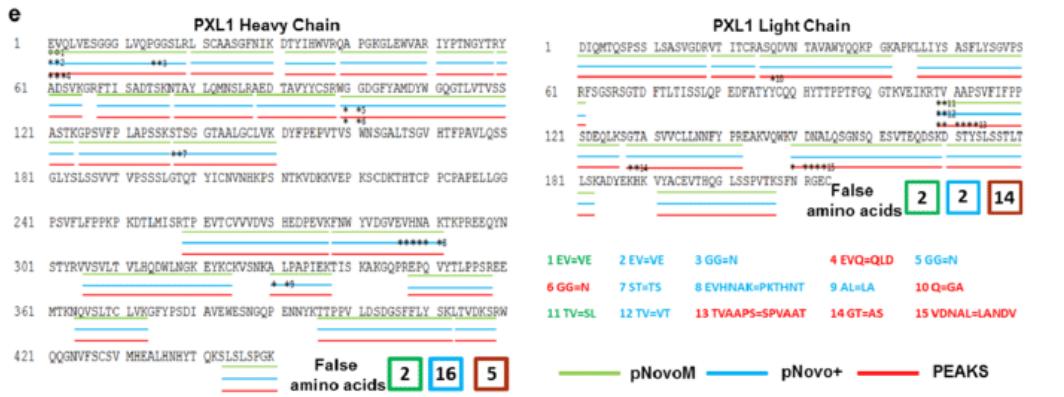
1. Full sequence coverage of monoclonal antibody light and heavy chain peptides
In the process of determining the antibody sequence, we will select 5 different proteases for digestion. We guarantee a result with a 100% sequencing coverage of the entire light and heavy chains of the antibody molecule, a better than 99.5% accuracy and distinct assignment of Leu/Ile residues.
Monoclonal Antibody De novo Sequencing
2. Advanced data processing algorithms
For de novo sequencing, the key issue is not mass spectrometer ( many different types of MS can do the job) but the bioinformatics software. We have 10+ proprietary software toolsused in our sequencing process.
3. High resolution and high sensitivity
We will use high resolution and high sensitivity Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer in the sequencing process; compared with older generation mass spectrometers (e.g. Obitrap Elite, Q Exactive, etc.), Lumos improves the speed of mass spectrometry scanning while ensuring the accuracy of peptide molecular weight.
4. Multiple subtypes and different types of antibodies can be sequenced
The technology platform we established is not affected by small groups (such as FITC, Biotin). Although larger protein groups make sequencing difficult, they can still be successfully sequenced if the protein concentration is high.
5. Rigorous sequence prediction and rigorous sequence validation
For the sequencing results, we will first predict the sequence and indicate the CDR region of the antibody (as shown in the figure below); at the same time, we will also create a new database based on the determined sequence, and analyze the collected mass spectrometry data again using the Sequence Confirmation mode.
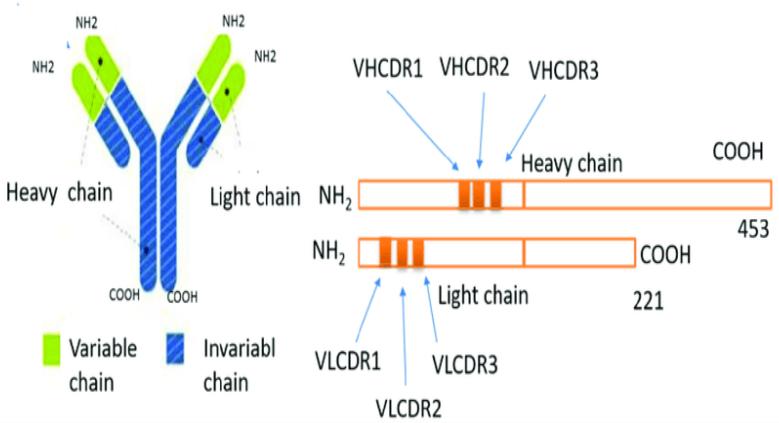
The Complementarity-determining regions
Procedure
The complete mAb de novo sequencing is often a very complex process, involving more than ten different proteolytic digestions, several steps of chemical derivatizations, NanoLC-ESI-MS/MS data acquisition, bioinformatics analysis with more than a dozen proprietary softwares, the manual spectra assignment, etc. In general the process contains the following steps:
1). Proteolytic digestion and chemical derivatization.
2). LCMS data acquisition.
3). Database search and peptide de novo sequencing.
4). Draft sequencing assembling.
5). Sequence gap filling.
6). Sequence error screening.
7). I/L determination.
8). Sequence validation.
Our mAb de novo sequencing technology can also apply to other proteins. However, changes in the process is often needed based on the nature of the protein.
Sample requirement:
Since more than ten different proteolytic reactions are carried out in the sequencing process, we prefer to have > 1mg mAb protein for each project, although ~500ug mAb sample is acceptable. A better than 90% purity is required.
The main concern about the quality of a sample is immunoglobin contamination since there is no easy way to separate contaminating antibodies from the mAb of interest, and there is not easy to determine if a peptide from contaminating peptides or from the mAb of interest. The major source of such a contamination is the serum in cell culture media.
Report
1. Experimental steps
2. Relevant mass spectrometry parameters
3. Mass Spectrogram
4. Raw data
5. Peptide sequence information
References
- RS Baradie et al. Can Pharmacological Inhibitors and Antibodies Against m CRP Suppress Interactions with Platelets and Leukocytes-Dampening Inflammation after Stroke. 2019
- Hao Yang et al. Precision De Novo Peptide Sequencing Using Mirror Proteases of Ac-LysargiNase and Trypsin for Large-scale Proteomics. 2018






