Glycosylation, the process of attaching glycans to proteins or other organic molecules, is one of the most common post-translational modifications (PTMs). Glycans are highly branched carbohydrate structures, consisting of monosaccharide sugars, such as fucose, galactose, manose, sialic acid, and N-acetylglucosamine. Due to the complexity and diversity of composition and structure of glycans, and the site of glycan attachment, glycosylation may affect product stability, immunogenicity, serum clearance, pharmacokinetics, and anti-inflammatory activity. Therefore, glycosylation is a Critical Quality Attribute (CQA) that must be presented. Glycosylation analysis is critical step to ensure safety and potency of biopharmaceutical products during the process of drug discovery.
Creative Proteomics provides a high-quality and high-sensitivity glycosylation analysis to identify glycosylation sites, confirmation of peptide sequence, determination of glycan structure, and glycan mapping in accordance with relevant guidelines (ICH Q6B, PharmEu and USP<1047>). According to the complex nature of glycosylation structural characterization, our professional team will deploy different approaches to meet the requirements of every stage of drug discovery.
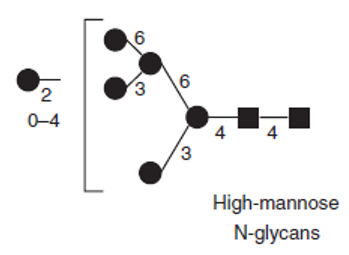
We Can Provide but Not Limited to:
- Glycosylation analysis
- Glycosylation sites identification
- Glycosylation linkage determination
- Glycan structure determination
- Glucose Unit (GU) values determination
Technology Platform of Glycosylation Analysis Service:
Creative Proteomics provides efficient and accurate glycosylation analysis services through different technologies based on different aspects of the glycan or glycoprotein structure, including enzymatic cleavage, mass spectrometry (MS), Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/ionization (MALDI)-MS, liquid chromatography systems, and so forth.
- Glycan release: Depending on the type of sample and sample volume, different methods will be used to release the attached N- or O-glycans.
- Glycosylation analysis: Purified N-glycan and O-glycan will be subjected to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS), Nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (Nano-ESI-MS-MS), gas chromatography (GC)-MS and linkage analysis. To determine the number of monomers in linear oligomers of glucose, Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC) will be applied to determine GU values. More optimized protocols will be applied to access different aspects of glycosylation.
N-glycan samples will be prepared in in-solution or in-gel deglycosylation. Then the PNGase F-released N-glycan will be purified by different method based on the approach used for deglycosylation and the interests of following studies. O-glycan will be release from the N-deglycosylated proteins/peptides by alkaline β-elimination. The N- and O-glycan can also be released by hydrazinolysis.
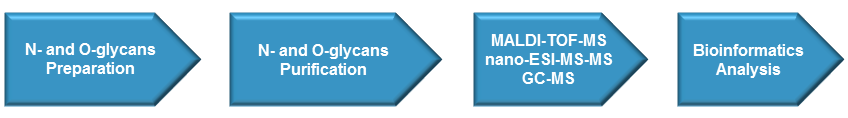
Advantages of Glycosylation Analysis Service:
- High sensitivity: glycosylation can be identified for low mass ones.
- Advanced equipment: MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry MALDI-8020, SHIMADZU.
- Optimized analysis platform: The current technology uses automatic chromatographic instruments designed for analysis, which can reduce the scale of analysis and greatly improve the flexibility and effectiveness of analysis.
- Rapid turnaround time: 5-7 days to provide comprehensive report.
- Customized service: Optimal buffers and protocols will be customized based on your project and sample type
Creative Proteomics's analytical scientists can provide complete analysis of glycosylation, as well as determination of GU values, glycosylation site, etc. Quick turnover, clear and concise written reports and protocols, and customized services to will be provided to help customers solve analytical and technical problems.
References
- Morelle W. and Michalski J.C. Analysis of protein glycosylation by mass spectrometry. Nature Protocols, volume 2, pages1585–1602(2007).
- Sola R.J. and Griebenow K. Effects of Glycosylation on the Stability of Protein Pharmaceuticals. J Pharm Sci. 2009 April; 98(4): 1223–1245.
- Wacker C., Berger C.N., Girard P., et al. Glycosylation profiles of therapeutic antibody pharmaceuticals. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 79 (2011) 503–507.






