More than 100 years ago, Tswett, a Russian botanist, poured petroleum ether extract of plant pigment into an upright glass tube filled with calcium carbonate, and then added petroleum ether to let the mixture flow free. As a result, the components in the pigment separated from each other to form bands of various colors. Tswett used the Greek words chroma (color) and graphos (spectrum) to describe his experimental method, which is now known as Chromatography.
The principle of chromatography: When each component dissolved in the mobile phase passes through the stationary phase, the size and strength of each component's interaction with the stationary phase (adsorption, distribution, exclusion, affinity) are different. Therefore, the residence time of these components in the stationary phase is different, flowing out from the stationary phase at different times one after another. The essence of chromatography is a method of separation and analysis. Liquid chromatography (LC) refers to when liquid is used as the mobile phase.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is based on classic liquid chromatography. Using a high-pressure infusion system, this method pumps mobile phases, such as single solvents with different polarities or mixed solvents and buffers in different proportions, into a chromatographic column equipped with extremely fine particles and a high-efficiency stationary phase. After the components in the column are separated, they enter the detector to be analyzed.
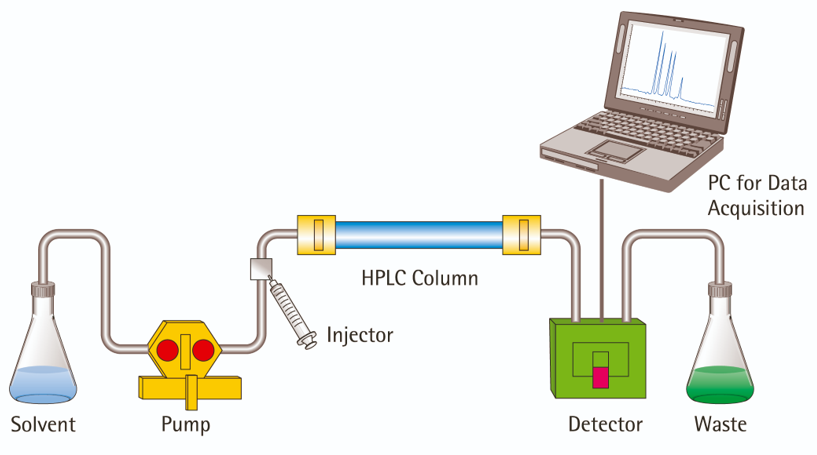
HPLC is an important branch of chromatography with a wide range of applications, and it is not limited by the volatility and thermal stability of the analytical object. Almost all compounds including high boiling point, polar, ionic compounds, and macromolecular substances can be analyzed and determined by HPLC.
HPLC can make up for the shortcomings of gas chromatography. Among the currently known organic compounds, about 20% can be analyzed by gas chromatography, and 80% needs to be analyzed by HPLC. HPLC has the characteristics of high separation efficiency, fast analysis speed, good detection sensitivity, and can analyze and separate thermally unstable physiologically active substances with high boiling points and cannot be vaporized. It has become an important separation analysis technique that can be applied in chemistry, medicine, industry, agronomy, commodity inspection, and legal inspection.
Creative Proteomics has extensive experience and can provide you with HPLC Analysis Service for purification analysis.






