Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) is an analytical technique used in the development and quality control of protein drugs. From medium optimization, clone screening, formulation stability research and purification process monitoring, to protein characterization, related impurity detection, protein structure identification and protein drug product quality control, CE is required in all aspects of protein drug development. For example, for protein purity determination, sodium dodecyl sulfate-capillary gel electrophoresis (CE-SDS) is better compared to SDS-PAGE. To determine protein isoelectric point, capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF) is more accurate than the traditional gel strip method. For the characterization of glycosylation heterogeneity of glycoprotein drugs, CE can achieve high-resolution analysis.
In the pharmacopeias of various countries, the detection methods of CE technology for protein drugs are also continuously enriched and developed. The earliest protein drug detection method in pharmacopeia is the determination of the sugar isomer of erythropoietin (EPO). The difference in glycoprotein isomers is small, and it is difficult to separate and quantify multiple isomers in EPO with traditional analysis methods. The European Pharmacopeia and the United States Pharmacopeia have designated the CE method as the standard for the analysis of EPO isomers and the separation and quantification of various glycosylated isomers in EPO products. In addition, CE is also used in the detection standards for related impurities of growth hormone.
Capillary electrophoresis in the analysis of monoclonal antibody drugs
- Analysis of purity and size heterogeneity of monoclonal antibody drugs
Using SDS-PAGE for purity analysis of monoclonal antibody drugs, in terms of resolution, quantitative accuracy, and automation can no longer meet the requirements of biopharmaceutical research and development and quality control. The CE-SDS method is based on the separation of protein molecular weight differences and is used for the purity analysis of reduced and non-reduced monoclonal antibody drugs. CE-SDS eliminates complicated manual operations, makes quantification more accurate, and has higher resolution. It can separate and accurately quantify non-glycosylated heavy chains in the reduction mode.
Different capillary lengths can be used to realize purity analysis in high-resolution mode and fast mode. The CE-SDS method in high-resolution mode provides the highest resolution, and the CE-SDS method in fast mode provides shorter washing and separation times, which improves the throughput of analysis.
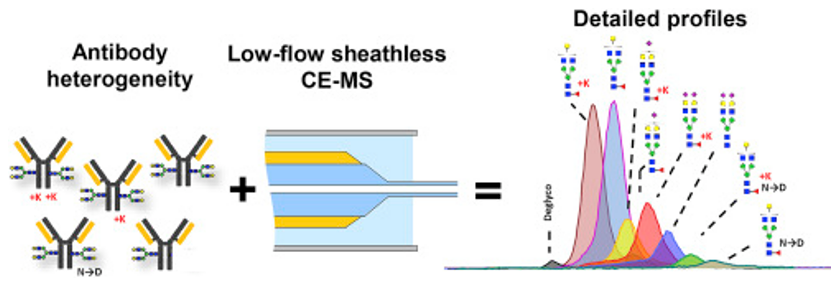
Antibody homogeneity analysis (Haselberg et al., 2018)
- Determination of isoelectric point of monoclonal antibody drugs and analysis of charge heterogeneity
The post-translational modifications such as glycosylation, deamidation, isomerization, and oxidation on the monoclonal antibody drug will cause changes in the surface charge and cause the charge heterogeneity of the monoclonal antibody. Each variant has a different isoelectric point. The isoelectric point separation function of CIEF can be used for high-resolution separation and quantification of monoclonal antibody drug variants, and separate 0.03 pI variants.
- Glycosyl heterogeneity analysis of monoclonal antibody drugs
In glycoprotein drugs such as monoclonal antibodies, the type and order of glycosyl groups can cause glycosyl heterogeneity. The glycosylation modification of monoclonal antibody drugs has a great impact on their safety and efficacy. Therefore, the quality control of glycosyl heterogeneity is very important. The advantages of CE for glycosyl analysis are high resolution and fast speed. Not only can the difference in a sugar group be distinguished, but the sugar group isomers of the same molecular weight can also be separated.
Application of capillary electrophoresis in the analysis of recombinant protein drugs
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) is a highly glycosylated protein drug. The heterogeneity of glycosylation leads to the existence of multiple variants. The capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) method can be used to separate and quantify EPO variants. This has become the standard method for the analysis of EPO variants in the European Pharmacopoeia. In addition, the CIEF method can also achieve the high-resolution separation of various variants in EPO. Not only the same number of variants and quantitative information can be obtained by the CZE method, but also the precise isoelectric point value of each variant can be provided.
Reference
- Haselberg, R. and De Vijlder, T., et al. (2018). Heterogeneity assessment of antibody-derived therapeutics at the intact and middle-up level by low-flow sheathless capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Analytica chimica acta, 1044, 181-190.






