What are gallotannins?
Gallotannins are a class of hydrolyzable tannins consisting of gallic acid units esterified to a glucose core and are polyphenolic compounds widely distributed in plants.
Gallotannins are widely found in a variety of plant species, including oaks, grapes, and several species of myrtle, as well as some fruits, such as strawberries, and are valuable in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, food science, and cosmetics. They exhibit a variety of biological activities, including:
- Antioxidant effects (radical scavenging, metal chelation)
- Protein-binding properties (astringency in food/beverages)
- Antimicrobial and UV-protective roles (plant defense)
Creative Proteomics delivers gallotannins analysis services tailored to accelerate research and industrial workflows.
Gallotannins Analysis Service by Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics provides a wide range of specialized services for gallotannins analysis to ensure high-precision data back your research and development processes. Our service offerings include:
Identification and Quantification of Gallotannins
- We offer precise quantification of gallotannins in plant extracts, food products, and other biological samples using cutting-edge techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled with Mass Spectrometry (MS).
Metabolite Profiling of Gallotannins
- Analysis of gallotannin metabolites using advanced techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).
Metabolic Pathway Analysis
- Through our advanced data analytics and bioinformatics tools, we provide detailed metabolic pathway mapping of gallotannins in various plant species and biological systems, helping researchers understand their biochemical fate in the body or in vitro models.
Phytochemical Screening for Gallotannins and Other Polyphenols
- We conduct comprehensive screenings of plant samples to detect gallotannins and other related polyphenolic compounds, providing a holistic understanding of the plant's chemical profile.
Bioactivity Testing
- In addition to chemical analysis, we evaluate the bioactivity of gallotannins, including their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, using in vitro assay systems.
Custom Assay Development
- Development and validation of customized gallotannins quantification assays
- Optimization of extraction and sample preparation protocols for diverse sample matrices
Data Interpretation and Report Generation
- Detailed, scientifically rigorous reports, including all relevant data, trends and analyses
- Assist in decision-making and further research
List of Gallotannins -Related Metabolites (including but not limited to)
| Compound |
Metabolite Class |
Detection Method |
| Monogalloyl glucose |
Simple Gallotannin |
UHPLC-MS/MS, HPLC-DAD |
| Digalloyl glucose |
Oligomeric Gallotannin |
HRMS (Orbitrap/Q-TOF) |
| Trigalloyl glucose |
Oligomeric Gallotannin |
LC-ESI-MS/MS |
| Pentagalloyl glucose (PGG) |
Key bioactive Gallotannin |
Triple Quadrupole MS |
| Gallic acid |
Hydrolysis product |
GC-MS, HPLC-UV |
| Ellagic acid |
Oxidative metabolite |
UPLC-QTOF-MS |
| Pyrogallol |
Microbial degradation product |
GC-MS, HPLC-ECD |
Techniques and Instrumentation for Cembrene Analysis
SCIEX Triple Quad™ 6500+ (Figure from Sciex)
7890B Gas Chromatograph (Figure from Agilent)
Mass-Based 1290 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System (Figure from Agilent)
ISQ™ EC Single Quadrupole MS (Figure from Thermo Scientific)
Agilent 6495C Triple quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Workflow for Gallotannins Analysis Service
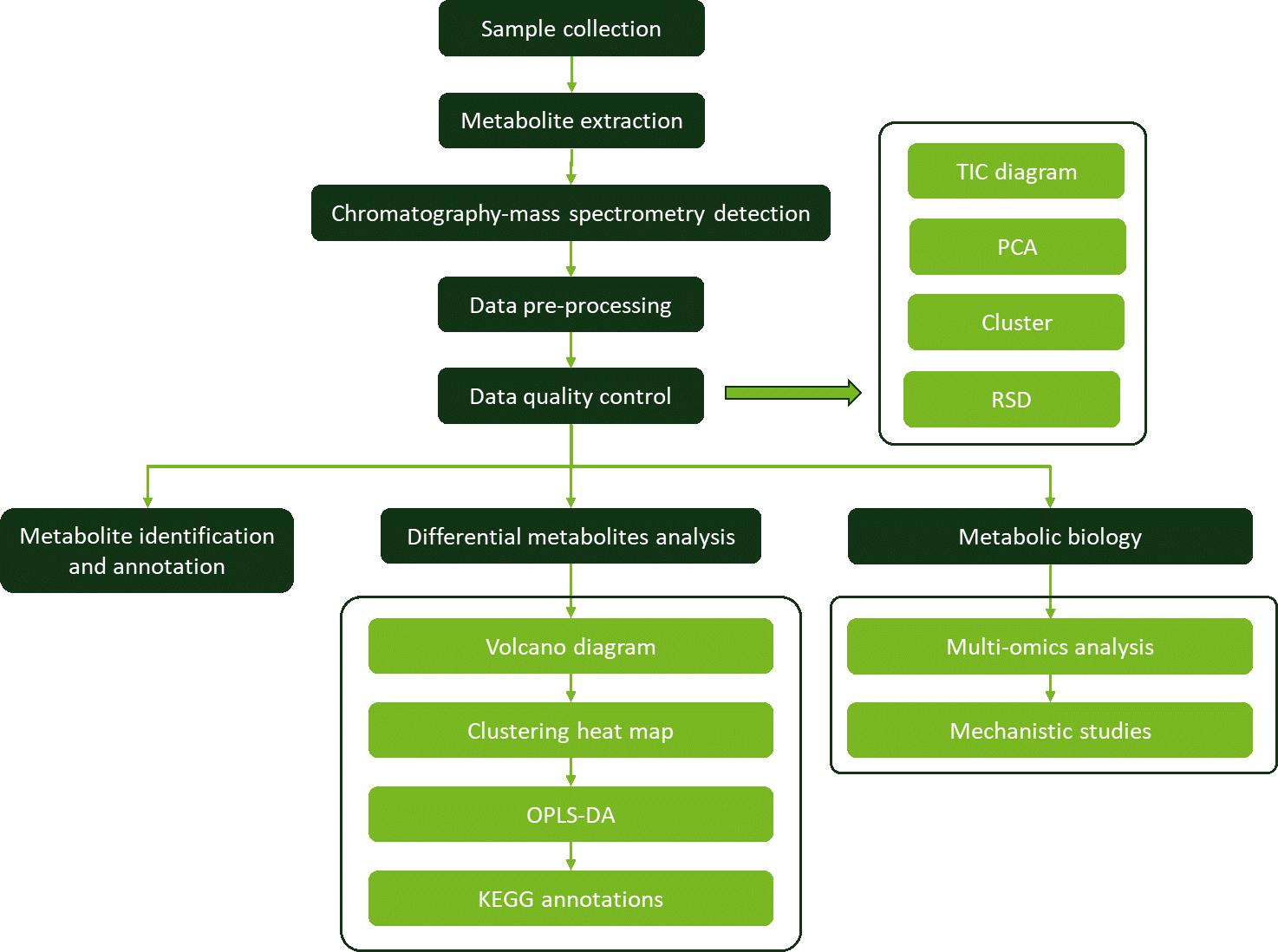
Why Choose Us?
Our gallotannins analysis service provides several compelling advantages that ensure you receive high-quality, reliable, and accurate results:
- High Sensitivity and Selectivity: Detection limits as low as 0.1 ng/mL for trace gallotannins.
- Comprehensive Data Reporting: Detailed metabolite identification, fragmentation patterns and pathway maps.
- Customized Method Development: Tailored protocols for unique matrices (plant extracts, fermentation broths, etc.).
- Comprehensive portfolio of services: Our comprehensive portfolio of services, ranging from identification and quantification of gallotannins to bioactivity screening, ensures a comprehensive overview of the gallotannins in your samples.
- Comprehensive analyses: 12 analyses, 22 graphical displays.
Applications of Gallotannins Analysis
|

|
Food & Beverage Industry
Quality control of tannin-rich products (wine, tea, nuts).
|
|

|
Nutraceutical Development
In the development of functional foods or dietary supplements containing
|
|

|
Phytochemical Profiling
To map the chemical composition of medicinal plants, food products, and herbal supplements.
|
|

|
Environmental Science
To study the role of gallotannins in plant defense mechanisms, ecological interactions, and soil biochemistry.
|
Sample Requirements for Gallotannins Analysis Assay
| Sample Types |
Minimum Quantity |
Storage & Shipping |
| Plant extracts |
50 mg (dry weight) |
-20°C, avoid light |
| Fermentation broth |
5 mL |
Frozen, ship on dry ice |
| Food/beverage samples |
10 g (liquid/solid) |
Refrigerated, preservative-free |
| Serum/plasma |
200 µL |
-80°C, no repeated freeze-thaw |
| Cell culture lysate |
1 mL |
Snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen |
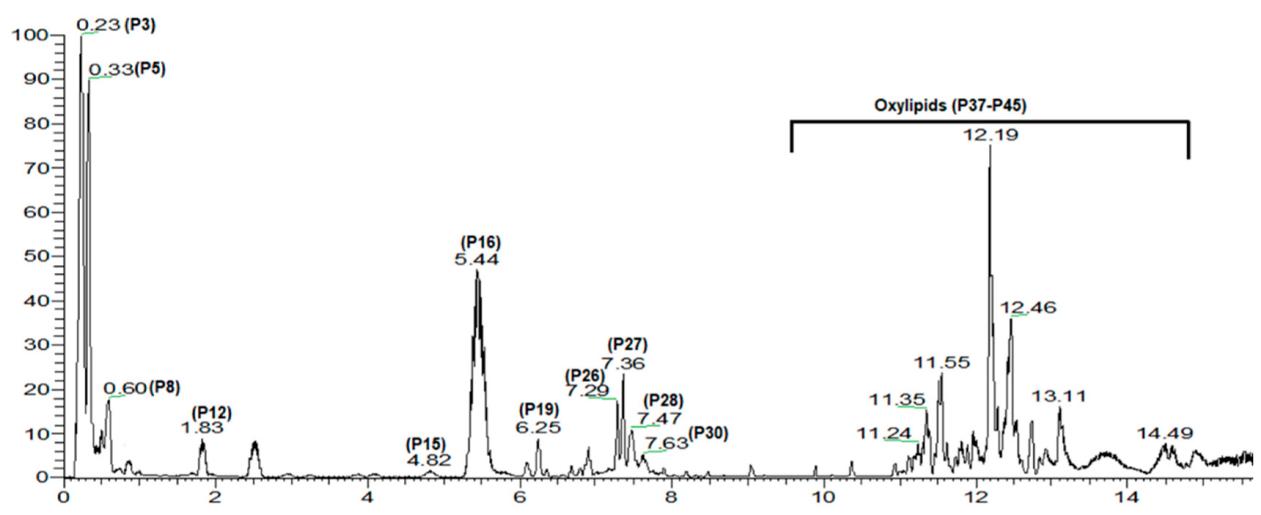 UPLC/MS total ion chromatogram (TIC) chromatogram of mango fruit methanol extract detected in negative ion mode. (Figure from Mohamed A. Farag et al., 2022)
UPLC/MS total ion chromatogram (TIC) chromatogram of mango fruit methanol extract detected in negative ion mode. (Figure from Mohamed A. Farag et al., 2022)
 LC-MS/MS base peak intensity (BPI) profiles of the phenolic and polyhydroxy compounds of samples. (Figure from Fenglin Gu et al., 2018)
LC-MS/MS base peak intensity (BPI) profiles of the phenolic and polyhydroxy compounds of samples. (Figure from Fenglin Gu et al., 2018)
Case. Comprehensive comparison on the chemical metabolites and taste evaluation of tea after roasting using untargeted and pseudotargeted metabolomics
Background:
- The flavor components of tea are mainly non-volatile compounds such as tea polyphenols, caffeine and some amino acids (L-theanine).
- Roasting is one of the very important procedures in tea processing, after high temperature roasting, the flavor and chemical composition of tea leaves have undergone significant changes.
- Therefore, the aim of this study was to synthesize and compare the chemical profiles and taste changes during tea roasting based on liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis and a combined strategy of non-targeted and targeted metabolomics methods.
Samples:
- A total of 8 samples of roasted and non-roasted teas were obtained, including 4 roasted teas: Large-leaf yellow tea (RT1), Feng huang dan cong (RT2), Strong flavor Tie guanyin (RT3), Da hongpao (RT4); and 4 non-roasted teas: Huo shan huang ya (NRT1), Jun shan yin zhen (NRT2), Lu shan yun wu (NRT3), and Gu zhang mao jian (NRT4).
- Six biological replicates of each tea species
Technical methods procedure:
- A 100 mg tea sample was extracted twice with 4 mL of water in a 90 °C water bath for 15 min. The extract was centrifuged for 5 min and all the supernatants were combined to obtain the tea extract.
- Non-targeted metabolomics analysis of tea leaf extracts.
- Targeted metabolomics analysis of taste compounds on tea extracts.
Results:
- The content of main galloylated and simple catechins, caffeine and theobromine in roasted were significantly lower than non-roasted teas.
- Targeted taste-compounds metabolomics revealed that (–)-epigallocatechin gallate, kaempferol-glucose-rhamnose-glucose and (–)-epicatechin gallate were main contributors tightly correlated to astringent intensity.
- Flavonol glycosides including kaempferol-glucose, quercetin-glucose, kaempferol-glucose-rhamnose-glucose, and quercetin-glucose-rhamnose-glucose in roasted teas were also significantly less than non-roasted teas.
 The metabolomics and multivariate analysis for roasted and non-roasted teas by LC-MS. (Figure from Zongde Jiang et al., 2018)
The metabolomics and multivariate analysis for roasted and non-roasted teas by LC-MS. (Figure from Zongde Jiang et al., 2018)
Reference
- Jie Xia, et al. Comprehensive comparison on the chemical metabolites and taste evaluation of tea after roasting using untargeted and pseudotargeted metabolomics. Food Science and Human Wellness, 11(3) (2022), pp 606-617, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.017.












 UPLC/MS total ion chromatogram (TIC) chromatogram of mango fruit methanol extract detected in negative ion mode. (Figure from Mohamed A. Farag et al., 2022)
UPLC/MS total ion chromatogram (TIC) chromatogram of mango fruit methanol extract detected in negative ion mode. (Figure from Mohamed A. Farag et al., 2022) LC-MS/MS base peak intensity (BPI) profiles of the phenolic and polyhydroxy compounds of samples. (Figure from Fenglin Gu et al., 2018)
LC-MS/MS base peak intensity (BPI) profiles of the phenolic and polyhydroxy compounds of samples. (Figure from Fenglin Gu et al., 2018) The metabolomics and multivariate analysis for roasted and non-roasted teas by LC-MS. (Figure from Zongde Jiang et al., 2018)
The metabolomics and multivariate analysis for roasted and non-roasted teas by LC-MS. (Figure from Zongde Jiang et al., 2018)