What is Coumarin?
Coumarin is a natural aromatic organic compound with a distinctive sweet flavor. It is found in a wide variety of plants and is known for its many biological activities and chemical properties. The molecular structure of coumarin consists of a fusion of a benzene ring and an alpha-pyrone ring, resulting in a unique aromatic odor. This compound is widely used in areas such as medicine, agriculture and flavor production.
Coumarin Analysis at Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics is at the forefront of coumarin analysis, offering a range of tailored projects to meet the diverse needs of researchers. Our commitment to advancing scientific knowledge is exemplified through the following specialized services:
Coumarin Content Profiling
Our cutting-edge techniques allow for precise quantification of coumarin content in various plant samples. Through advanced analytical platforms, such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), we provide accurate and sensitive measurements of coumarin levels.
Identification of Coumarin Metabolites
We employ state-of-the-art metabolomics approaches to identify and characterize coumarin metabolites. By utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometers, such as the Thermo Scientific Q Exactive series, we can confidently determine the structures of coumarin-derived compounds.
Metabolic Pathway Analysis
Creative Proteomics excels in elucidating metabolic pathways involving coumarin and its derivatives. Our expertise extends to pathway mapping and flux analysis, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the connections between coumarin metabolism and lignin biosynthesis.
Coumarin Metabolomics Analysis Techniques
Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Series: This high-performance mass spectrometer offers exceptional resolution and sensitivity, enabling accurate mass measurements and precise isotopic pattern analysis.
Agilent 6550 iFunnel Q-TOF LC/MS: With its innovative ion funnel technology, this system provides rapid and accurate analysis of complex coumarin metabolite mixtures.
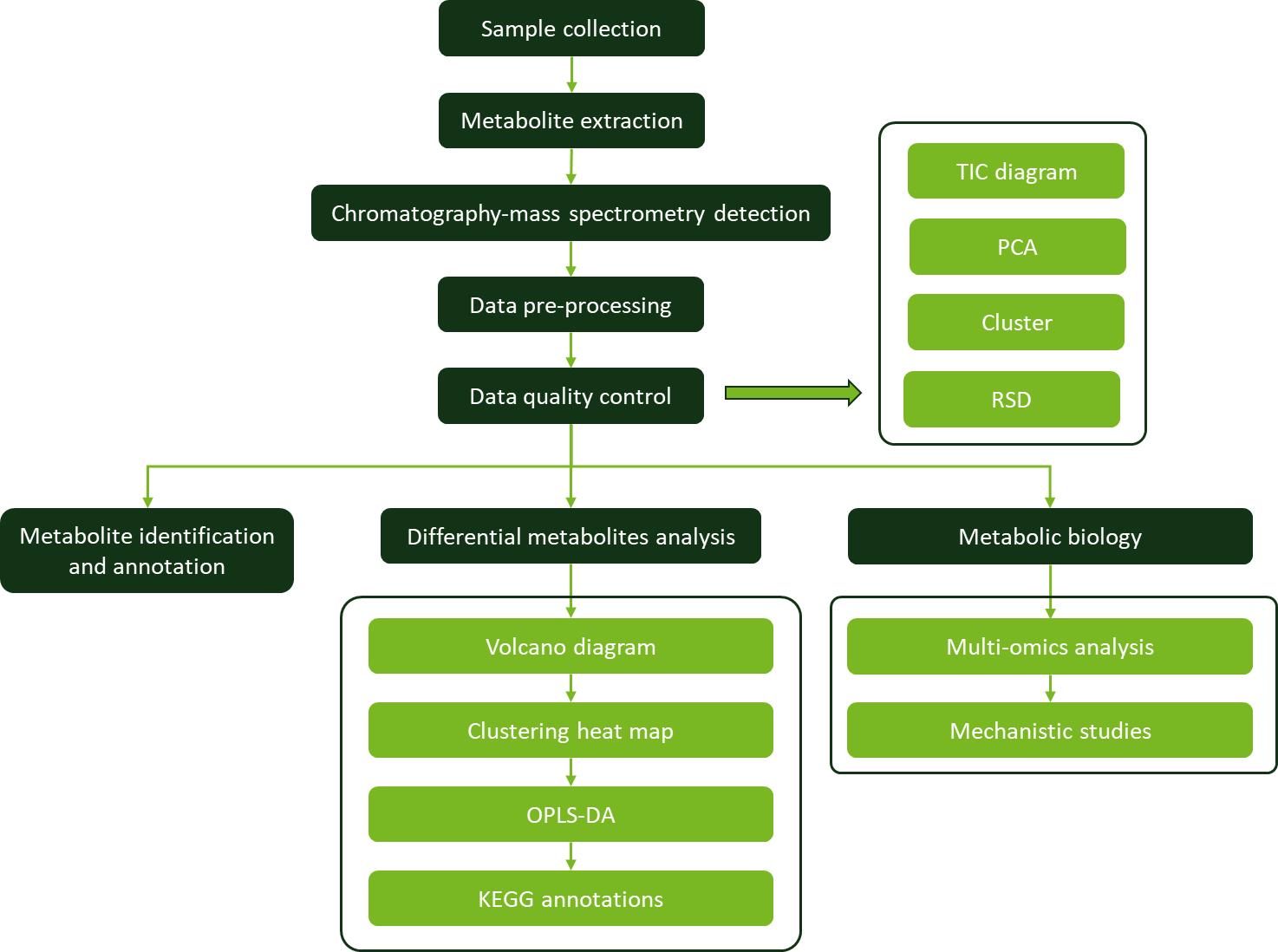 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Coumarin and Metabolites Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Types |
Coumarin and Metabolites |
| Coumarins and Derivatives |
Coumarin, Scopoletin, Umbelliferone, Aesculetin, 7-Hydroxycoumarin, Daphnetin, 4-Methylumbelliferone |
| Coumarin Acids and Esters |
Coumaric Acid, Ferulic Acid, Caffeic Acid, Ethyl Coumarate, Methyl Ferulate, Isopropyl Caffeate |
| Coumarin Lactones and Glycosides |
Coumarin Lactone, Esculin, Fraxin, Aesculin, Bergapten, Xanthotoxin |
| Coumarin Ketones and Alcohols |
Dihydrocoumarin, 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin, Daphnoretin, Isoscopoletin, 6-Hydroxy-7-methoxycoumarin, 6-Hydroxy-8-methoxycoumarin |
Sample Requirements for Coumarin Assay
| Sample Types |
Minimum Sample Size |
| Plant Samples |
Roots, stems and leaves, floral parts, fruits/seeds, rhizomes, buds/tender leaves, tissue sections, pollen, bark, trunk/wood, resin/gum, resin acids, seedlings/young plants, rhizosphere soil, root exudates. |
50 mg - 1 g |
Applications of Coumarin Metabolomics Analysis
Unlocking Lignin Dynamics
Lignin, a complex polymer found in plant cell walls, plays a crucial role in plant structure and function. Coumarin's structural similarities to certain lignin precursors suggest its potential involvement in lignin biosynthesis and degradation pathways. Our analysis provides a deep dive into these intricate processes, shedding light on lignin dynamics and contributing to the understanding of plant growth and development.
Tailored Insights for Research
Researchers across various domains, from plant physiology to pharmaceuticals, require precise insights into coumarin metabolism. By offering comprehensive coumarin analysis, we enable scientists to unravel its metabolic pathways, identify key intermediates, and investigate its role in various biological systems. Our services provide a valuable resource for researchers seeking to advance their understanding of coumarin-related processes.
Advancing Agricultural Applications
In agriculture, coumarins have been implicated in plant defense mechanisms against pathogens and pests. By analyzing coumarin content and metabolism, we contribute to the development of strategies for enhancing plant resistance and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. Our analytical offerings facilitate the exploration of novel avenues for crop protection and improvement.
Fostering Drug Discovery
Coumarin-derived compounds exhibit a wide range of bioactivities, making them attractive candidates for drug discovery and development. Through our analysis, we aid researchers in identifying potential therapeutic compounds, guiding the search for new drugs that harness coumarin's natural properties. Our services accelerate the discovery of valuable pharmaceutical agents.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Understanding the interactions between plants and their environment is vital for assessing ecological impacts and plant stress responses. By delving into coumarin metabolism, we contribute to environmental science by providing insights into how plants interact with their surroundings. This knowledge aids in evaluating ecosystem health and resilience.
Case 1. Comprehensive Method for Quantification and Identification of Coumarins and Furanocoumarins in Citrus Peel Extracts
Background:
The study aimed to develop a comprehensive method for the identification and quantification of coumarins and furanocoumarins in citrus peel extracts. These compounds are of interest due to their potential phototoxic and toxic effects, particularly in relation to the consumption of citrus fruits and juices.
Samples:
Six different citrus varieties were analyzed in the study, including 'Washington Navel' sweet orange, 'Eureka' lemon, 'Duncan' grapefruit, 'Castagnaro' bergamot, 'Chandler' pummelo, and 'Commune' clementine. Peel samples from these varieties were collected and used for analysis.
Methods:
Calibration and Linearity: Calibration curves were established using seven calibration solutions spanning a concentration range of 1 to 30 μM for each compound. The linear correlation coefficients (r2 > 0.99) demonstrated the method's linearity and ability to quantify the target compounds accurately.
Detection and Quantification Limits: Limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were determined based on signal-to-noise ratios for each compound in lemon peel extracts. The method exhibited low LOD and LOQ values for most compounds, indicating high sensitivity.
Specificity and Matrix Effect: Specificity was assessed by spiking lemon peel extracts with known compounds. The method demonstrated no significant matrix effect, ensuring accurate compound identification and quantification.
Precision and Accuracy: Repeatability and intermediate precision were evaluated by analyzing the same fruit's peel extracts on different days. The method displayed good repeatability and intermediate precision for most compounds, showcasing its reliability. Accuracy was confirmed by spiking tomato leaf extracts with target compounds, yielding results close to the expected concentration.
Robustness: The method's robustness was tested by varying column oven temperature and flow rate. The results indicated consistent performance and robustness across different conditions.
Optimization of UPLC Separation: A solvent gradient-based UPLC separation method efficiently separated compounds with the same m/z ratio. This method allowed for rapid analysis and facilitated subsequent mass spectrometry detection.
Optimization of MS Detection: Mass spectrometry detection in single ion monitoring (SIM) mode enhanced selectivity and sensitivity. Optimal voltages were applied to improve signal intensity and resolution.
Results
The study successfully identified and quantified coumarins and furanocoumarins in the peel extracts of six citrus varieties. Different varieties exhibited varying profiles and concentrations of these compounds. 'Bergamot' peel contained the highest total furanocoumarin content, and the method provided insights into the potential toxicity implications of consuming different citrus varieties based on their quantitative results.
In conclusion, the study developed a robust and efficient method for the analysis of coumarins and furanocoumarins in citrus peel extracts, contributing to our understanding of the chemical composition of different citrus varieties and their potential health implications.
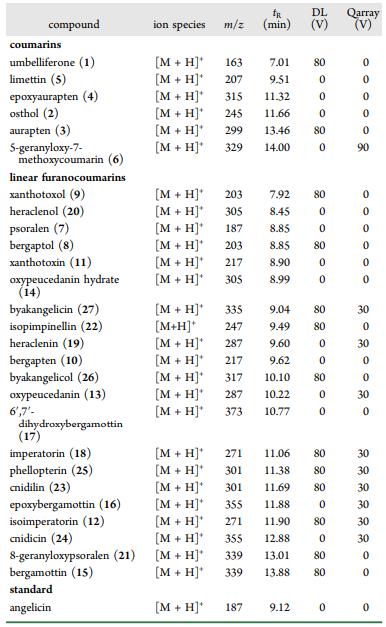 Analyzed Molecules and Their Characteristics: Ion Species, Mass/Charge Ratio (m/z), Retention Time (tR), Desolvation Line Voltage (DL), and Qarray Voltage
Analyzed Molecules and Their Characteristics: Ion Species, Mass/Charge Ratio (m/z), Retention Time (tR), Desolvation Line Voltage (DL), and Qarray Voltage
Reference
- Dugrand, Audray, et al. "Coumarin and furanocoumarin quantitation in citrus peel via ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS)." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 61.45 (2013): 10677-10684.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service Analyzed Molecules and Their Characteristics: Ion Species, Mass/Charge Ratio (m/z), Retention Time (tR), Desolvation Line Voltage (DL), and Qarray Voltage
Analyzed Molecules and Their Characteristics: Ion Species, Mass/Charge Ratio (m/z), Retention Time (tR), Desolvation Line Voltage (DL), and Qarray Voltage