What are Ellagitannins?
Ellagitannins, a subclass of hydrolyzable tannins, are biologically active polyphenolic compounds widely distributed mainly in various fruits such as pomegranates, raspberries, and strawberries, as well as nuts such as walnuts and oak-aged wines.
Hydrolysis of ellagitannins produces ellagic acid and other metabolites with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive properties. With the surging demand for plant-derived bioactive compounds, accurate analysis of ellagic tannins is essential for food science, agriculture and natural product development research.
At Creative Proteomics, we specialize in advanced ellagitannin analysis services that combine cutting-edge instrumentation, methodological rigor, and deep expertise to accelerate research and industrial workflows.
Ellagitannins Analysis Service by Creative Proteomics
Qualitative and quantitative analysis
- Accurate measurement of ellagitannins in plant-based foods, supplements and biological samples.
- Full Spectrum Identification and Quantification of Ellagitannins
- Identification of novel ellagitannin derivatives
Metabolite Identification
- Detection of ellagic acid, urolithins and other metabolites derived from the gut microbiota.
Metabolic pathway analysis
- Mapping of ellagitannin biosynthetic pathways
- Mapping of precursor-product relationships and enzyme interactions.
Isotope Tracking Studies
- Combined with mass spectrometry to track the binding of isotopically labeled compounds in metabolic pathways to determine metabolic rates and pathway activity.
Custom Assay Development
- Development and validation of customized ellagitannin quantification assays
- Optimization of extraction and sample preparation protocols for different sample matrices
- Optimization of protocols for novel matrices or low abundance targets
Data Interpretation and Report Generation
- Detailed, scientifically rigorous reports, including all relevant data, trends and analyses
- Assist in decision-making and further research
List of Ellagitannins -Related Metabolites (including but not limited to)
| Ellagitannins |
Key Metabolites |
Pathway-Specific Markers |
Detection Limit (ng/mL) |
| Punicalagin |
Ellagic acid |
Gallic acid |
0.5 |
| Pedunculagin |
Urolithin A |
Glucuronide conjugates |
0.8 |
| Casuarictin |
Urolithin B |
Quercetin derivatives |
1.2 |
| Sanguiin H-6 |
Methyl-ellagic acid |
Shikimate pathway intermediates |
0.7 |
Techniques and Instrumentation for Ellagitannins Analysis
Bruker 400 MHz NMR spectrometer (Figure from Bruker)
Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Agilent 6495C Triple quadrupole (Figure from Agilent)
Mass-Based 1290 Infinity II Preparative LC/MSD System (Figure from Agilent)
Workflow for Ellagitannins Analysis Service
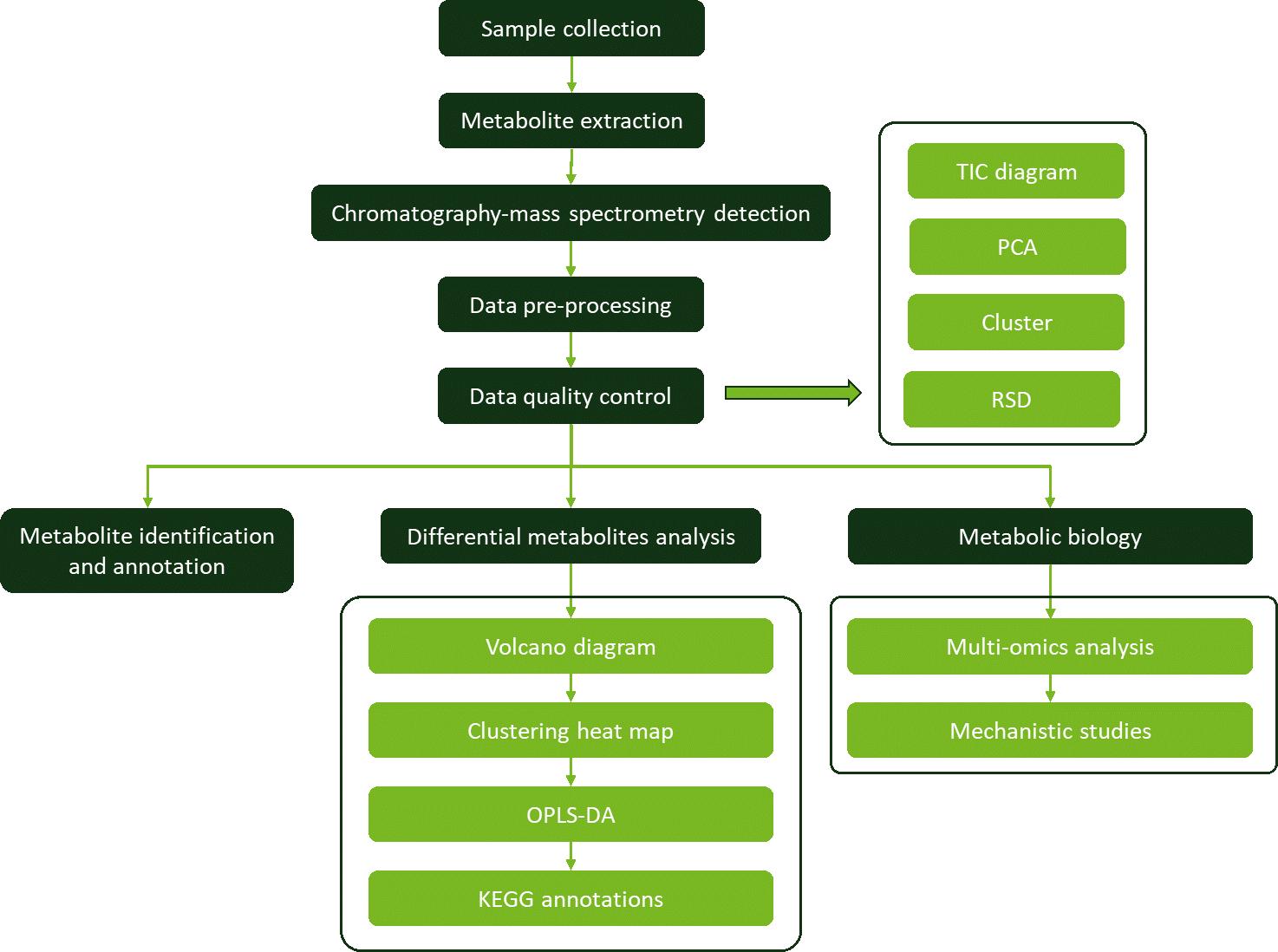
Why Choose Us?
- High sensitivity and precision: Detection limits down to the picomolar level and high resolution mass spectrometry to ensure isomer differentiation.
- Multi-platform integration: Combine HPLC, QTOF-MS and NMR for cross-validated results.
- Comprehensive metabolic profiling: Our service not only detects ellagitannins compounds, but also provides a detailed understanding of the entire metabolic pathway of their derivatives and end products.
- Low sample consumption: Analyze samples as small as 10 µL or 5 mg (dry weight).
- Dynamic range: Quantify compounds from 0.5 ng/mL to 100 µg/mL without dilution.
- Proprietary database: Access to our curated library of over 200 ellagitannin spectra.
- Speed and efficiency: Our state-of-the-art systems enable rapid processing and quick turnaround without compromising quality.
- Comprehensive after-sales service: full interpretation of final reports, free technical advice and data review services.
- Customized solutions: We understand that every research project is unique, so we offer tailored analytical programs to meet your specific needs.
- Expert guidance: With more than 20 years of experience in the field, our team of biologists provides invaluable insights and advice to ensure that your studies are robust and scientifically sound.
Applications of Ellagitannins Analysis
|

|
Agricultural Research
Optimize crop breeding for ellagitannin-rich varieties
|
|

|
Food & Beverage Development
Validate functional ingredient stability in products
|
|

|
Cosmeceuticals
Screen plant extracts for antioxidant efficacy
|
|

|
Pharmacological Research
Investigating the bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of ellagitannins and their metabolites in various biological systems.
|
Sample Requirements for Ellagitannins Analysis Assay
| Sample Type |
Required Quantity |
Preparation |
| Plant Extracts |
10-50 mg |
Freeze-dried or liquid extract |
| Urine |
1-5 mL |
Fresh sample, stored at -20°C |
| Blood Plasma |
1-3 mL |
Collected in EDTA tubes |
| Tissue (e.g., liver) |
50-100 mg |
Fresh or frozen tissue |
| Supplement Products |
10-20 mg |
Crushed or powdered form |
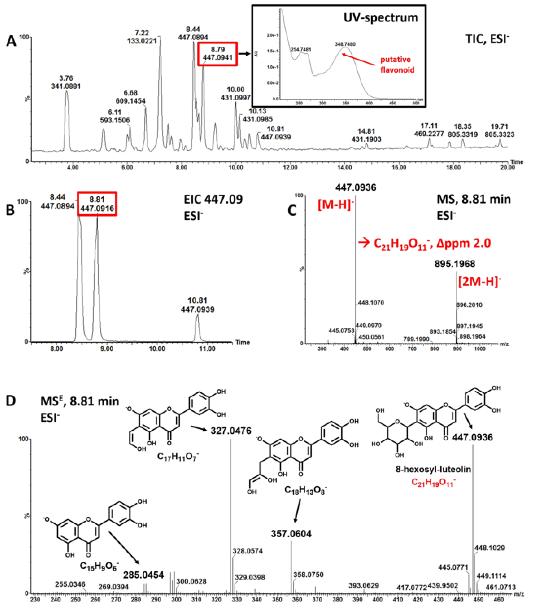 Putative identification of polyphenolic compounds from LC-MS measurements. (Figure from Anat Yaskolka Meir et al., 2014)
Putative identification of polyphenolic compounds from LC-MS measurements. (Figure from Anat Yaskolka Meir et al., 2014)
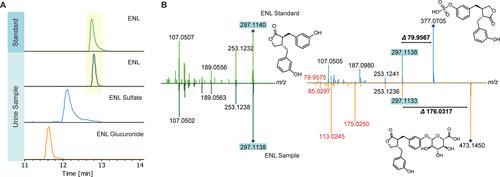 Structure validation of enterolactone (ENL) and its phase II modifications. (Figure from Ioanna Tsiara et al., 2025)
Structure validation of enterolactone (ENL) and its phase II modifications. (Figure from Ioanna Tsiara et al., 2025)
Case. Punicalagin attenuates hyperuricemia via restoring hyperuricemia-induced renal and intestinal dysfunctions
Background:
- Punicalagin(PU) is the most abundant ellagitannin in pomegranate rind and is characterized by high levels of hydroxylation. PU has been shown to have a variety of biological functions including anti-inflammatory and regulation of glycolipid metabolism.
- Uric acid (UA) excretion is impaired in 90% of cases of hyperuricemia. The two main organs responsible for UA excretion are the kidneys (70%) and the intestines (30%). However, the efficacy of PUs in the treatment of hyperuricemia and the deeper mechanisms of action remain unclear.
- Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of Punicalagin in hyperuricemic mice and the mechanism of action of Punicalagin in reducing UA.
Samples:
- The male Kunming mice (18-22 g)
Technical methods procedure:
- Establishment of a mouse model of hyperuricemia
- Fecal samples were obtained the day before mouse autopsy for 16S rRNA sequencing analysis.
- After autopsy, mouse kidneys are homogenized with a methanol solution containing 2-chloro-L-phenylalanine and the supernatant is collected.
- To the supernatant was added pyridine solution of methoxylamine hydrochloride, dried under vacuum and methoxylated.
- The resulting samples were then analyzed for metabolites using GC/MS.
Results:
- PU significantly reduced the serum uric acid level in hyperuricemic mice and significantly improved the renal and intestinal injury induced by hyperuricemia.
- PU improved the expression of uric acid transporter proteins in the kidney and intestine of hyperuricemic mice by regulating the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.
- PU improves renal glucose metabolism disorders induced by hyperuricemia in mice.
- PU has the effect of restoring the homeostasis of intestinal flora in hyperuricemic mice, and can improve the intestinal inflammation and injury caused by hyperuricemia.
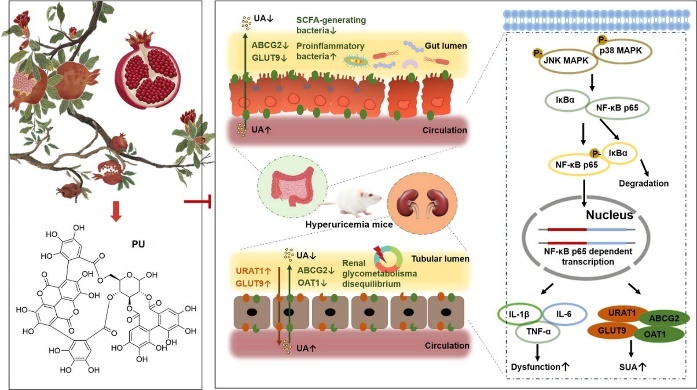 Mechanism of action of punicalagin in ameliorating hyperuricemia. (Figure from Qing-qing Han et al., 2025)
Mechanism of action of punicalagin in ameliorating hyperuricemia. (Figure from Qing-qing Han et al., 2025)
Reference
- Qing-qing Han, et al. Punicalagin attenuates hyperuricemia via restoring hyperuricemia-induced renal and intestinal dysfunctions, Journal of Advanced Research, 69(2025), pp. 449-461, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.029.










 Putative identification of polyphenolic compounds from LC-MS measurements. (Figure from Anat Yaskolka Meir et al., 2014)
Putative identification of polyphenolic compounds from LC-MS measurements. (Figure from Anat Yaskolka Meir et al., 2014) Structure validation of enterolactone (ENL) and its phase II modifications. (Figure from Ioanna Tsiara et al., 2025)
Structure validation of enterolactone (ENL) and its phase II modifications. (Figure from Ioanna Tsiara et al., 2025) Mechanism of action of punicalagin in ameliorating hyperuricemia. (Figure from Qing-qing Han et al., 2025)
Mechanism of action of punicalagin in ameliorating hyperuricemia. (Figure from Qing-qing Han et al., 2025)