Why Analyze Flavanols?
Flavanols, often referred to as flavan-3-ols, are part of the larger flavonoid family, polyphenolic compounds celebrated for their pronounced antioxidant properties. They are commonly found in various foods like tea, cocoa, grapes, apples, and some berries. Notably, the consumption of these flavanol-rich foods is associated with numerous health benefits, which are believed to be caused by the antioxidative, anti-inflammatory effects of flavanols, their influence on vascular function, among others, depending on their structure and amount consumed. Hence, the analysis of flavanol content in foods and other biological samples is crucial for nutritionists, biologists, and food technologists to understand more accurately their biological roles and potential health implications. This further aids the agri-food sector in quality control, product development, and supports the scientific community in experimental research and potentially, prophylactic strategies in healthcare.
The consumption of flavonoid-rich food and drinks (especially cocoa, tea, and apples) is linked to a reduced risk of several chronic diseases caused by oxidative stress, including cardiovascular diseases and certain cancer types. These enticing links necessitate comprehensive identification, quantification, and analysis of various flavonoids, including the sub-class flavanols. Creative Proteomics is committed to providing comprehensive and reliable flavanol analysis services.
Flavanols Analysis at Creative Proteomics
Flavanol Profiling: Comprehensive analysis of flavanols present in samples.
Quantitative Analysis: Measurement of flavanol concentrations for accurate quantification.
Identification of Flavanol Subtypes: Determination of specific flavanol subtypes within complex mixtures.
Metabolite Profiling: Profiling of flavanol metabolites in biological samples.
Bioavailability Studies: Assessment of the absorption and distribution of flavanols in biological systems.
Structural Elucidation: Determination of the chemical structure of flavanol compounds.
Method Development: Customized method development for flavanols analysis based on specific project requirements.
Flavanol Metabolism Analysis Techniques
Utilizing advanced analytical techniques, we are able to perform comprehensive flavanols analysis. Majorly, our techniques are based on mass spectrometry, which boasts sensitivity and accuracy for detecting flavanols.
- Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS): With high sensitivity, LC-MS/MS has been effectively used to analyze flavanols, such as catechin and epicatechin. Catechins are analyzed using Shimadzu Triple Quad 5500, while epicatechins are analyzed using Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS/MS): GC-MS/MS technique provides greater separation and is used for analyzing proanthocyanidins, another type of flavanols. We use Agilent 7890B GC system coupled with 5977A MSD for this purpose.
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): HPLC is another robust tool for the analysis of flavanols, providing high resolution and accuracy. HPLC devices such as Agilent 1260 Infinity and Waters e2695 are commonly utilized for flavanol analysis in our labs.
- Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS): We employ UPLC-MS/MS to provide ultra-fast and highly sensitive flavanol analysis. Equipment includes Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class and AB SCIEX Triple Quad 4500.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): NMR is used for structural elucidation of flavanols. Usually, we use Bruker Ascend™ 600 MHz spectrometers.
These instruments, associated with sophisticated enrichment methods, assure the accurate identification and quantification of flavanols in various samples. We continually invest in the latest technology to refine our detection capabilities, improving the precision, detection limits, and throughputs of flavanols analysis. With our rigorous analytical techniques, Creative Proteomics guarantees reliable and reproducible results that can meet your research needs and exceed expectations.
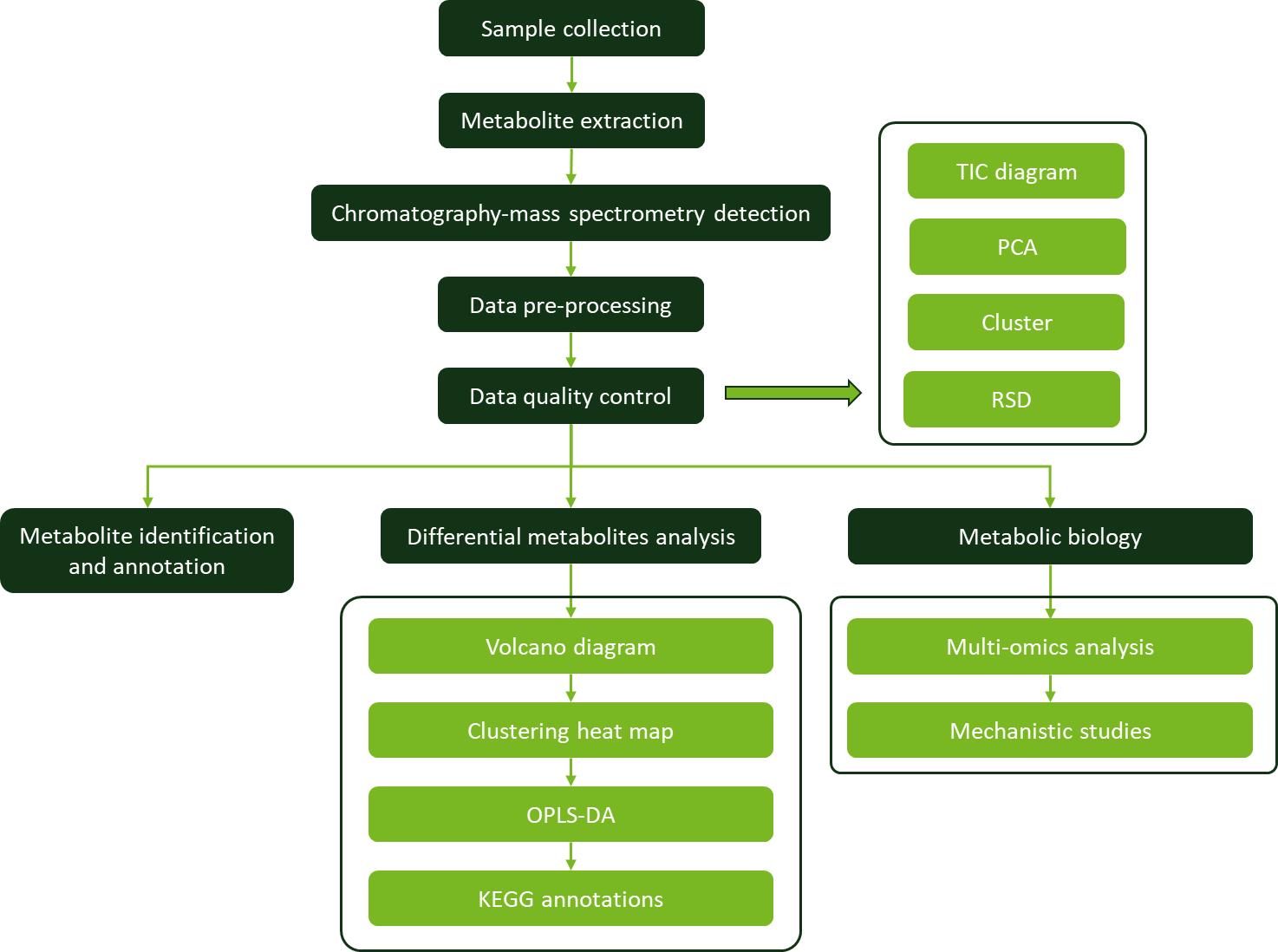 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Flavanols Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Apigenin |
Catechin |
Catechin 3-gallate |
Cyanidin |
Daidzein |
| Delphinidin |
Fisetin |
Gallocatechin |
Genistein |
Hesperetin |
| Isorhamnetin |
Kaempferol |
Luteolin |
Malvidin |
Morin |
| Myricetin |
Naringenin |
Pelargonidin |
Peonidin |
Proanthocyanidins |
| Quercetin |
Rutin |
|
|
|
Sample Requirements for Flavanols Metabolism Assay
| Sample Type |
Suggested Sample Amount |
| Plant Extracts |
50-100 mg |
| Tea Leaves |
5-10 g |
| Cocoa Products |
10-20 g |
| Red Wine |
5-10 mL |
| Fruits (e.g., Berries, Fruit Peels) |
20-50 g |
| Vegetables |
50-100 g |
| Nuts |
10-20 g |
| Grains/Cereals |
20-50 g |
| Flowers |
Variable |
| Biological Fluids (e.g., Plasma) |
0.5-1 mL |
| Tissues (e.g., Liver) |
20-50 mg |
| Dietary Supplements |
Variable |
Deliverables of Flavanols Analysis
After the successful completion of the analysis, you will receive:
- Experimental procedure
- Parameters of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
- MS raw data files
- Flavanol identification and quantitation results
- Bioinformatic analysis
Case. Comprehensive Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Peach Germplasms
Background:
Peach fruits are rich sources of polyphenolic compounds known for their health benefits. Understanding the variations in phenolic composition among different peach germplasms is crucial for breeding and exploiting antioxidant properties.
Sample:
Two consecutive growing seasons (2014 and 2015) of peach germplasms collected from the National Clonal Germplasm Repository of Peach Centers.
Technical Platform and Procedure:
Reagents and standards: Methanol, acetonitrile, formic acid, and various phenolic standards obtained from reputable sources.
Instrumentation: Utilization of Waters UPLC Xevo/TQ system with Acquity PDAeλ, Acquity UPLC® HSS T3 column, and other specialized equipment.
Plant materials: Collection from the National Clonal Germplasm Repository, with details on fruit harvesting and preparation.
Sample preparation: Extraction of peach fruit powder with 2% formic acid in methanol, followed by UPLC-PDA/ESI-MS analysis.
UPLC-PDA/ESI-MS analysis: Detailed conditions, including mass spectrometry and HPLC parameters.
Radical scavenging capacity (RSC): Evaluation using the DPPH assay and selection of appropriate antioxidant measurement methods.
Results
- Quantification of 10 main phenolic compounds, including anthocyanins, flavanols, phenolic acids, and flavonols.
- Variability in polyphenol content between 2014 and 2015.
- Identification of key polyphenols: CGLU, CAT, B1, NCHA, and CHA.
- Anthocyanins (CGLU) predominant in red-fleshed peaches.
- Flavanols (CAT, ECAT, B1) show significant variations among germplasms.
- Phenolic acids (NCHA, CHA) contribute significantly to antioxidant capacity.
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reveals correlations and discrimination among germplasms based on phenolic components.
- Implications for breeding: Red-fleshed peaches with high anthocyanins and phenolic acids recommended for active substance extraction.
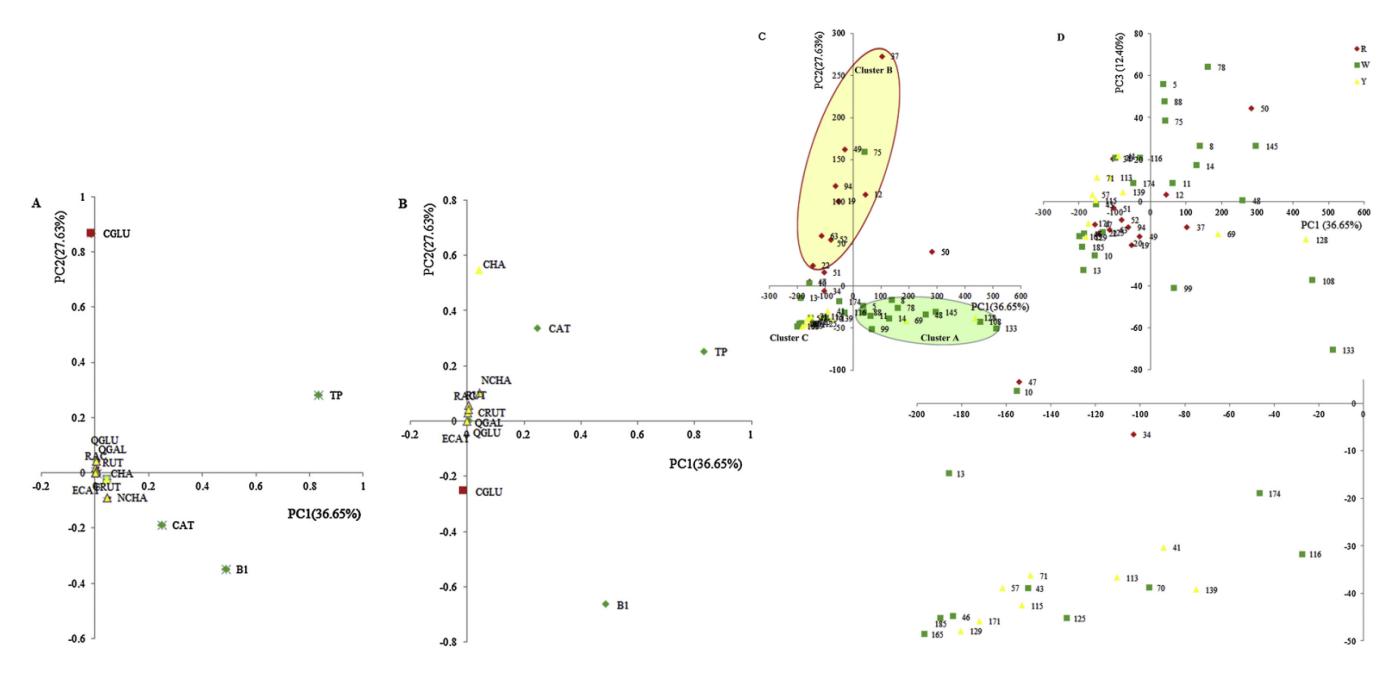 Discrimination of 44 germplasms in 2015 by PCA performed on fruit quality traits (CGLU, CRUT, CAT, ECAT, B1, NCHA, CHA, QGAL, QGLU, RUT, TP, RSC).
Discrimination of 44 germplasms in 2015 by PCA performed on fruit quality traits (CGLU, CRUT, CAT, ECAT, B1, NCHA, CHA, QGAL, QGLU, RUT, TP, RSC).
Reference
- Ding, Tiyu, et al. "Evaluation of phenolic components (anthocyanins, flavanols, phenolic acids, and flavonols) and their antioxidant properties of peach fruits." Scientia Horticulturae 268 (2020): 109365.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service Discrimination of 44 germplasms in 2015 by PCA performed on fruit quality traits (CGLU, CRUT, CAT, ECAT, B1, NCHA, CHA, QGAL, QGLU, RUT, TP, RSC).
Discrimination of 44 germplasms in 2015 by PCA performed on fruit quality traits (CGLU, CRUT, CAT, ECAT, B1, NCHA, CHA, QGAL, QGLU, RUT, TP, RSC).