What is Epicatechins?
Epicatechins are a class of bioactive compounds that belong to the family of flavonoids, which are polyphenolic substances naturally existing in various plant-based foods and beverages. Epicatechins are predominantly found in green tea, but they can also be derived from several fruits, beans, nuts, and cocoa.
These compounds are secondary metabolites instrumental in plant defense against external stressors. Forming part of the catechins, epicatechins are stereoisomers of catechin, with the major distinguishing feature being their different spatial structures. Their structural difference has a profound effect on their activity level, with epicatechins showing more significant biological activities compared to their catechin counterpart.
Scientific research has continually shed light on the health-promoting properties of epicatechins, inspiring the need for their systematic study and analysis. They exhibit various pharmacological activities, such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory effects, and cardiovascular and neuroprotective properties.
Studying epicatechins is imperative to our understanding of these health benefits and their potential therapeutic applications. Comprehensive analysis enables us to quantify their concentrations in different sources, understand their metabolic pathways, uncover their mechanisms of action, and optimize their use in health and nutrition. It is also a crucial part of food quality control and regulation for accurate labeling and consumer safety.
At Creative Proteomics, we employ our seasoned expertise and state-of-the-art resources to offer thorough analysis services, covering several directions and delivering reliable results necessary for advancing our collective knowledge on these precious compounds.
Specific Project Offered by Creative Proteomics in Epicatechins Analysis:
Identification and Quantification of Epicatechins: Using the cutting-edge technologies of High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), Mass Spectrometry (MS), and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), our team can accurately identify and quantify Epicatechins in any biological samples.
Toxicological Effect Analysis: Understanding how Epicatechins reacts in biological systems is critical for assessing their safety and efficacy. We provide comprehensive toxicologic analysis, integrating Metabolomics, Transcriptomics, and Proteomics for a complete understanding.
Metabolomic Analysis: We are capable of performing a comprehensive metabolomic analysis of Epicatechins, including essential characterization of their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) characteristics.
Structural Elucidation: Our team boasts substantial experience in elucidating the structure of Epicatechins by utilizing advanced spectroscopic methods such as infrared spectroscopy (IR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV/VIS), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
Quality Control Analysis: We perform qualitative and quantitative determination of Epicatechins for quality control of raw materials and finished goods in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.
Epicatechins Analysis Techniques
We employ state-of-the-art, mass spectrometry-based techniques for Epicatechin analysis, leveraging high-end instruments like LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry) and UHPLC-QTOF-MS (Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled with Quadrupole Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry).
Utilizing these advanced technologies guarantees high sensitivity, reliability, and replicability in detecting various Epicatechins – even those present in minute quantities.
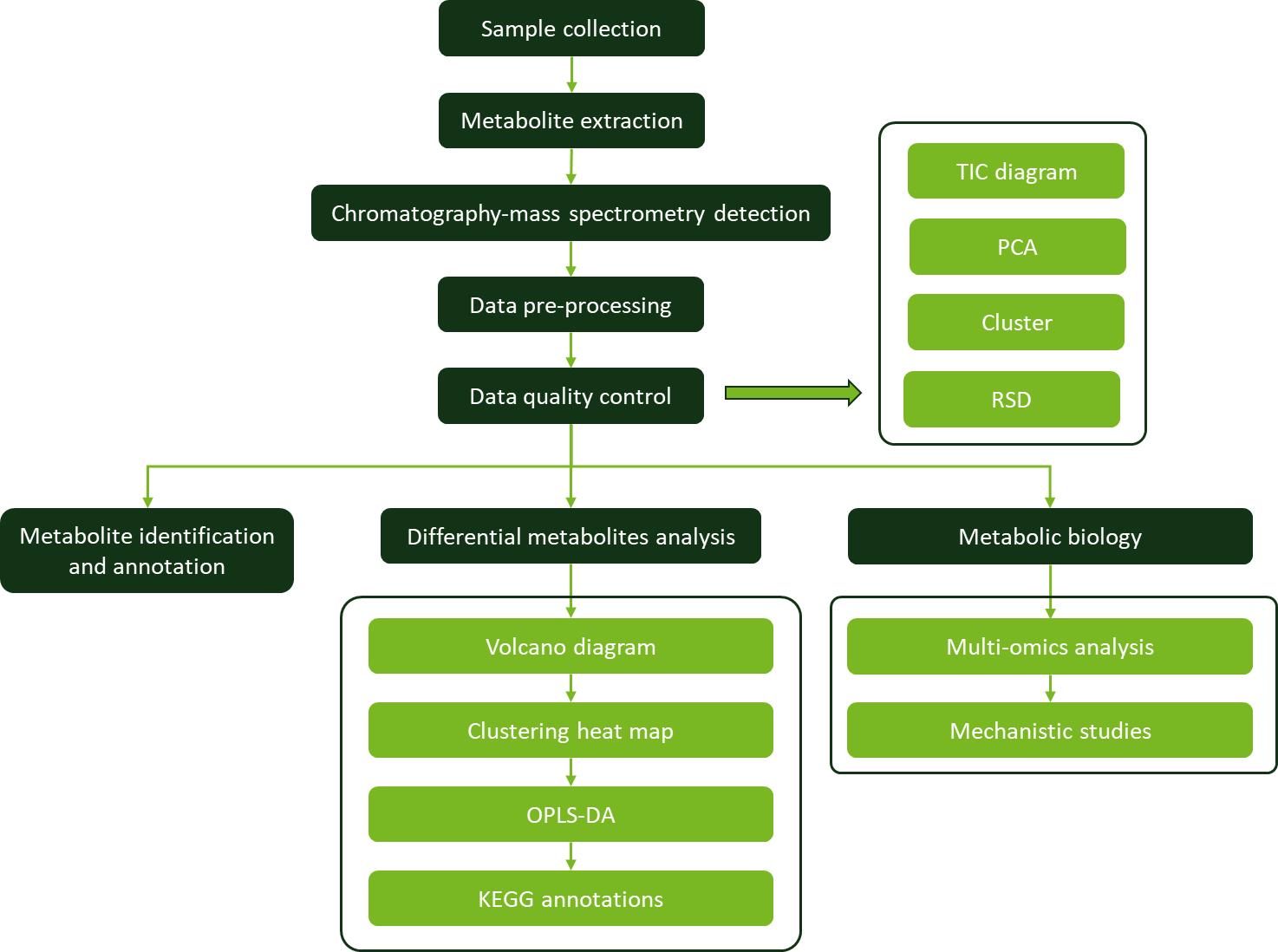 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
List of Epicatechins Analyzed (including but not limited to)
| Epicatechin |
Epicatechin gallate |
Epicatechin glucoside |
| Epicatechin gallate gallate |
Epicatechin gallate glucoside |
Proanthocyanidin B2 |
Sample Requirements for Epicatechins Assay
| Sample Type |
Sample Volume |
| Plant Extracts |
1-5 grams |
| Beverage Samples |
100-500 mL |
| Biological Fluids |
0.5-2 mL |
| Cocoa Products |
5-20 grams |
| Tea Leaves |
2-10 grams |
| Fruit Extracts |
1-5 grams |
Deliverables of Epicatechins Analysis
- A detailed experimental report.
- Review and interpretation of data.
- Raw and processed data files.
- Comprehensive consultation on result understanding and future works.
Case. Bioavailability of Dietary Epicatechin in Breast Milk
Background
Human breast milk (BM) is crucial for infant development, supplying essential nutrients and biologically active compounds. Despite accumulated knowledge about dietary polyphenols, little is known about their bioavailability in human BM, especially in free-living lactating women. This study focuses on understanding the presence and impact of epicatechin, a dietary polyphenol found in cocoa products, in the breast milk of lactating mothers.
Sample
Two sets of samples were collected. The preliminary experiment involved BM samples from two healthy lactating mothers after acute ingestion of dark chocolate (DCh). The population study included BM samples from 11 free-living breastfeeding women at different stages of lactation.
Technical Platform and Procedure
Preliminary Experiment: Acute DCh ingestion by lactating mothers, BM collection, and subsequent analysis of epicatechin metabolites. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) used for sample preparation, followed by ultra performance liquid chromatography−tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC−MS/MS) analysis. Calibration curves constructed for quantification.
Population Study: Dietary assessment using food frequency questionnaires (FFQ) and 24-hour dietary recalls (24 h DR). Epicatechin metabolite analysis in BM samples using a similar methodology as the preliminary experiment. Correlation analysis between dietary intake and epicatechin metabolites.
Results
Epicatechin Metabolites in BM after Acute DCh Ingestion: DCh intake led to the identification of host and microbial-derived epicatechin metabolites in BM, persisting up to 12 hours post-ingestion. The cumulative excretion of host metabolites accounted for a small percentage of the ingested epicatechin.
Epicatechin in BM of Free-Living Lactating Women: Among free-living lactating women, DCh was a significant source of flavan-3-ols. The detected host metabolites were sporadic, while the microbial metabolite DHPV-Sulf-2 was consistently found. Dietary data correlated with DHPV-Sulf-2 levels in BM.
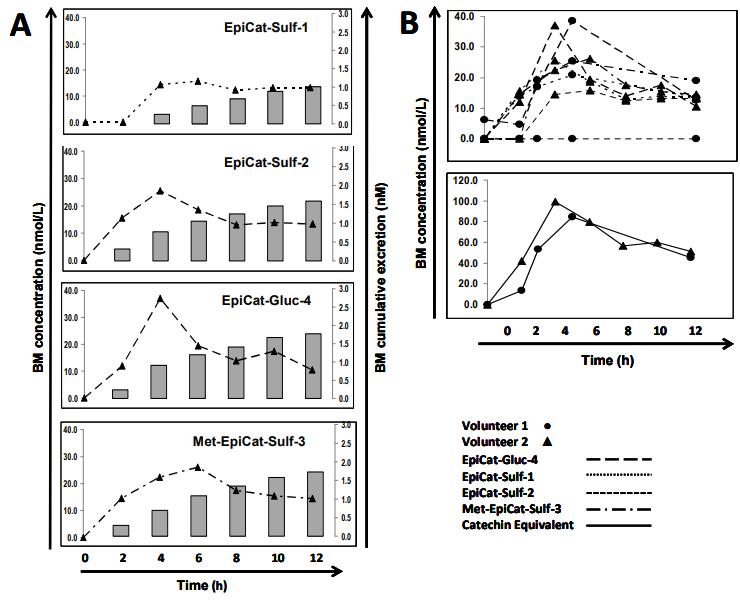 12 hr postprandial host epicatechin metabolites in breast milk (BM): (A) metabolite concentrations (lines) vs. their cumulative excretion (bars) in BM of Volunteer 2; (B) kinetics of detected metabolites in BM of both volunteers.
12 hr postprandial host epicatechin metabolites in breast milk (BM): (A) metabolite concentrations (lines) vs. their cumulative excretion (bars) in BM of Volunteer 2; (B) kinetics of detected metabolites in BM of both volunteers.
Reference
- Khymenets, Olha, et al. "Dietary epicatechin is available to breastfed infants through human breast milk in the form of host and microbial metabolites." Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 64.26 (2016): 5354-5360.


 Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service
Workflow for Plant Metabolomics Service 12 hr postprandial host epicatechin metabolites in breast milk (BM): (A) metabolite concentrations (lines) vs. their cumulative excretion (bars) in BM of Volunteer 2; (B) kinetics of detected metabolites in BM of both volunteers.
12 hr postprandial host epicatechin metabolites in breast milk (BM): (A) metabolite concentrations (lines) vs. their cumulative excretion (bars) in BM of Volunteer 2; (B) kinetics of detected metabolites in BM of both volunteers.