Recently most of biopharmaceutical products approved are protein drugs, such as hormones, monoclonal antibody and receptor. Their synthesis is affected by many parameters, which can lead to a change in the three-dimensional structure and impact on quality, safety and efficacy, and can lead to clinical consequences ultimately. As a result, the physical and chemical nature of biosimilar is a challenging task for both industry and regulators. Protein biosimilars are also protein drugs. In order to obtain regulatory approval, protein biosimilars also need to pass strict physical and chemical characteristics analysis to ensure the comparability of biological similar products and original products.
What Are Physicochemical Properties
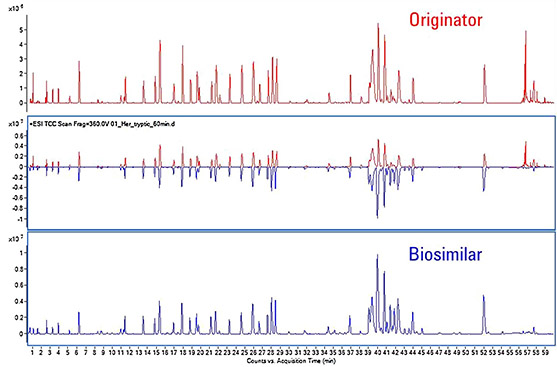
Figure 1. The mapping chromatograms of originator and biosimilar of tryptic peptide (Parr M K., 2016)
The physicochemical properties of proteins refer to the physical and chemical properties of proteins. Only when the environment is suitable for the physicochemical properties of protein can it remain alive and play its role. So, for protein drugs, it is very important to study their physical and chemical properties to treat some diseases clinically and to develop new drugs. Studies on the physicochemical properties of protein biosimilars are as important as that of generic protein drugs, which is an essential indicator of the market acceptance of protein biosimilars. Some of the physicochemical properties of proteins are similar to those of amino acids, such as amphoteric ionization, isoelectric point, color reaction, salt reaction, etc, while some of them are different from amino acids, such as high molecular weight, colloid property, denaturation, etc. According to these physical and chemical properties, various methods and technologies need to be used for research, and Creative Proteomics can provide these methods and technical services.
Physicochemical Properties Analysis at Creative Proteomics
- Molecular Weight (MW) & Size
The molecular weight and size of a complete molecule are the first physical parameters to be analyzed, as it defines a biological identity and identifies the original structure. The determination of molecular weight of protein biosimilars requires the application of state-of-the-art mass spectrometers with high resolution and quality accuracy, such as electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). In addition, gel electrophoresis and size exclusion chromatography-hplc (SEC-HPLC) are also widely used, providing information on the molecular weight of the compound. Creative Proteomics can provide these technologies to meet your requirements.
- Extinction Coefficient (EC)
Extinction coefficient is the absorption value of the measured solution to light. The higher the concentration of the measured solution, the darker the color of the solution after color rendering, and the greater the absorption of light. The concentration of protein is crucial to the efficacy of protein drugs, while the extinction coefficient of protein is the precondition for accurate determination of protein solution concentration by the ultraviolet absorption method. We can provide alkaline hydrolysis, nitrogen quantitative, spectral and Edelhoch methods to measure the extinction coefficient of protein biosimilars.
- Electrophoretic Patterns
Electrophoresis is a phenomenon in which charged particles or molecules move in an electric field. Electrophoresis is very useful in the study of proteins and can show some of the physical and chemical properties of proteins. For example, gel electrophoresis technology is used to determine the molecular weight of protein; Isosteric focusing electrophoresis is for the determination of protein isoelectric point, 2D electrophoresis separates proteins according to their molecular weight and isoelectric point; capillary electrophoresis is widely applied in amino acids, peptides, proteins, ion, enantiomer analysis and many other ions material analysis. Creative Proteomics can provide these analyses according to your needs.
- Liquid Chromatographic Patterns
The separation mechanism of liquid chromatography is based on the different affinity of the components in the mixture in the two phases, such as distribution coefficient and adsorption capacity. According to the adsorption capacity, it can be divided into adsorption chromatography, allocation chromatography, ion exchange chromatography and gel permeation chromatography. Therefore, liquid chromatography can be used to study the size, charge, hydrophobicity, affinity, etc. According to the different physicochemical properties of protein biosimilars, different chromatograms can be used for analysis.
- Spectroscopic Profiles
Spectrum is divided into UV-visible spectrum, fluorescence spectrum and infrared spectrum, which are used to study the spectral information of various drugs. In different environments, the conformation of proteins is different due to different factors such as different groups or molecular vibration frequencies. These conformations can be analyzed by means of spectra. In addition, the spectra of proteins are different with different concentrations.
Our Advantages
- At Creative Proteomics, the technical methods, such as mass spectrometry, chromatography and electrophoresis, are provided by a professional team, which can guarantee the smooth progress of the experiment.
- The detection of different physicochemical properties of protein biosimilars requires different experimental techniques, and we can help you choose the optimal technique to detect your physicochemical properties of drugs, thus saving your financial and material resources.
- You can contact us at any time. We will help you solve the problem in a timely manner.
Based on the various techniques and methods, we can determine the physicochemical properties of protein biosimilars to help you with the production of your protein biosimilars.
Reference
- Parr M K, Montacir O; etc. Physicochemical characterization of biopharmaceuticals. Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biomedical Analysis, 2016, 130:366-389.






