Why Discovery Proteomics?
Rationale for proteome-scale, unbiased data in biomarker and drug discovery
Discovery proteomics is an unbiased, proteome-wide approach that identifies and quantifies thousands of proteins in a single experiment. Unlike targeted assays that measure a predefined set of proteins, discovery proteomics captures the full complexity of the proteome—revealing unexpected biomarkers, pathways, and therapeutic targets.
For biopharma and translational research teams, this means:
- Accelerated biomarker discovery – identify proteins that differentiate disease states, patient responses, or treatment outcomes.
- Support for drug discovery – uncover mechanisms of action, monitor protein degradation and stabilization, and detect on- and off-target effects.
- Deeper biological insight – integrate discovery proteomics with metabolomics, spatial proteomics, and chemical proteomics for a systems-level understanding.
- Better decisions earlier – use discovery data to prioritize candidates, design targeted assays, and reduce downstream attrition.
In short, discovery proteomics transforms large, complex biological questions into actionable data that supports biomarker discovery, drug discovery, and translational research.
Content Guide
- Why 4D Proteomics?
- What We Solve
- Why Creative Proteomics
- Discovery Proteomics Solutions
- Discovery → Targeted (How They Work Together)
- Workflow
- Platforms & Methods
- Sample Requirements
- Deliverables
What We Solve?
FDR-controlled cohort quantification, low-abundance detection, MOA elucidation, clinical translation

Low reproducibility in large cohorts
Missing values and batch effects undermine confidence. With DIA-based discovery proteomics and strict false discovery rate (FDR) control, we deliver consistent, high-quality data across studies.

Unclear drug mechanism of action
When small molecules or biologics show unexpected effects, our chemical proteomics, TPP/CETSA, and proteome-wide covalent ligand discovery approaches reveal true targets and off-targets.
Difficulty detecting low-abundance proteins
Many biomarkers are present at trace levels. Advanced workflows, including fractionation, 4D-DIA, and aptamer-based multiplexed proteomic technology, extend sensitivity and coverage.
Translating Biomarkers to the Clinic
Bridging discovery vs targeted proteomics, we guide the transition from broad screening to targeted panels (PRM/SRM/MRM), ensuring clinical readiness and reproducibility.

Complex biology requiring system-level insight
Multi-omics integration (proteomic and metabolomic approaches) and spatial proteomics provide a holistic view of disease pathways, protein localization, and treatment response.
Need for Faster, Scalable Analysis
Large-scale studies demand speed and scalability. With automation and high-throughput DIA workflows, we deliver robust discovery proteomics at scale—without compromising data quality.
Advantages of Our Discovery Proteomics
Comprehensive Protein Profiling
7,000–9,000 Proteins / Run
Profile thousands of proteins per experiment, enabling a broad and unbiased view of biological pathways and disease mechanisms.
Reliable Statistical Confidence
Protein-Level FDR ≤ 1%
Strict false discovery rate control guarantees accurate protein identification and robust conclusions.
Low Data Gaps
< 5% Missing Values
Maintain consistently low missing values across samples, ensuring reproducibility in large-scale studies.
High Quantitative Precision
CV < 15% Across Replicates
Achieve precise quantification suitable for differential expression analysis and biomarker discovery.
Scalable to Large Cohorts
Up to Hundreds of Samples / Study
Support biomarker discovery and translational projects with reproducible data quality across large clinical cohorts.
Multi-Omics Integration
Proteomics + Metabolomics + Spatial
Combine discovery proteomics with metabolomics, chemical proteomics, and spatial approaches for system-level insights.
Discovery Proteomics Services Tailored to Your Needs
Choosing the Right Approach: DIA and DDA
For discovery proteomics, Data-Independent Acquisition (DIA) is generally the preferred strategy because it offers deeper coverage, fewer missing values, and stronger reproducibility across large cohorts. Data-Dependent Acquisition (DDA) remains valuable in specific scenarios—such as building spectral libraries, ultra-deep analysis, or specialized PTM discovery. Our team recommends the most appropriate combination based on your project goals, sample type, and scale.
1) Unbiased DIA Discovery
- Best for: proteomics biomarker discovery, early drug discovery, cohort studies
- Typical samples: plasma/serum, CSF, saliva, tissue, cells
- Key outputs: proteome-wide differential analysis, pathway/network enrichment, ranked shortlists
- Quality metrics (typical): ~7,000–9,000 proteins/run (matrix-dependent), protein-level FDR ≤1%, missing values <5%, replicate CV <15%
- Upgrade path (optional): retrospective DIA-targeted extraction for shortlisted proteins; PRM/SRM/MRM if needed.
2) Deep Discovery (Fractionation / 4D-DIA)
- Best for: complex matrices, low-abundance biology, comprehensive pathway coverage
- Typical samples: tissue, plasma/serum (depletion optional), organoids
- Key outputs: deeper coverage, enhanced low-abundance detection, refined candidate lists
- Quality metrics (typical): up to ~8,000–10,000 proteins/run (project-dependent), protein-level FDR ≤1%
- Upgrade path (optional): retrospective mining for verification; targeted panel lock-down if progressing
3) Chemical Discovery Proteomics (ABPP & Covalent Ligands)
- Best for: mechanism finding, on/off-target profiling, chemical proteomics in drug discovery
- Typical samples: cells, tissues, native lysates; electrophilic ligands, activity-based probes
- Key outputs: engagement maps, target liability flags, proteome-wide covalent ligand discovery in native biological systems
- Quality metrics (typical): FDR-controlled target lists with effect sizes; interference/RT checks
- Upgrade path (optional): retrospective DIA extraction on targets of interest; orthogonal validation or targeted assays
4) Thermal & Stability Discovery (TPP / Thermal Stability Proteomics; Proteostasis/Degraders)
- Applications: molecular glue research, protein stabilization studies, and discovery of degradation/stability effectors
- Sample Types: treated vs. control cells or tissues; time- and dose-response designs
- Key Outputs: proteome-wide stability and degradation profiles, substrate/effector hypotheses, pathway-level insights
- Quality Metrics: FDR-controlled hit lists; reproducible melt-curve or shift evidence
- Optional Upgrade: retrospective DIA verification of candidate substrates; targeted panels for follow-up
5) Spatial Discovery Proteomics
- Applications: subcellular localization, compartmental dynamics, and tumor microenvironment studies
- Sample Types: subcellular fractions, tissue regions, proximity-labeled samples
- Key Outputs: location-resolved proteome maps, differential localization profiles, pathway context analysis
- Quality Metrics: compartment marker QC, FDR-controlled identifications, cross-fraction missing-value control
- Optional Upgrade: retrospective DIA validation of localization-sensitive proteins; targeted assays for extended studies
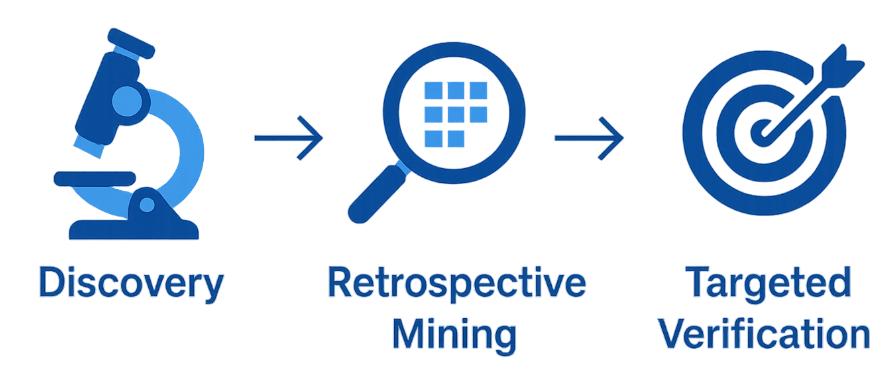
Discovery vs Targeted: How They Work Together
Discovery proteomics and targeted proteomics are two stages of one continuous workflow.
Discovery gives you the broad, unbiased proteome-wide map: thousands of proteins quantified, unexpected pathways uncovered, new biomarker and mechanism hypotheses generated.
From there, we use retrospective DIA re-mining to quickly validate shortlisted proteins directly within the same dataset—saving time and resources.
Once confidence is established, candidates can move seamlessly into targeted assays (PRM, SRM, MRM, or DIA-targeted extraction), which deliver precise, reproducible measurements across large cohorts or clinical-style studies.
This progression—Discovery → Retrospective Mining → Targeted—ensures that broad exploration leads naturally to focused, quantitative verification. It minimizes re-runs, accelerates timelines, and reduces risk, so your research advances with both breadth and precision.
Step-by-Step Discovery Proteomics Workflow
Designed for Reliable, In-Depth Results
Clarify research objectives (biomarker discovery, mechanism exploration, translational profiling) and recommend the most suitable acquisition strategy—typically DIA for reproducibility, with DDA where deep exploration or library support is required.
Apply standardized, matrix-specific protocols with rigorous cleanup, internal standards, and QC to ensure reliable and reproducible data.
Use high-resolution LC–MS/MS (Orbitrap or TOF). DIA captures peptides comprehensively with minimal missing data; DDA may complement spectral libraries or PTM-focused analysis.
Identify and quantify thousands of proteins with advanced pipelines. Apply strict protein-level FDR (≤1%) and maintain <5% missing values for robust results.
Perform statistical testing and pathway/network enrichment. Re-mine DIA datasets to verify shortlisted proteins—no additional LC–MS run required.
Provide raw and processed data, QC metrics, and publication-ready visuals. When needed, develop targeted assays (PRM, SRM, MRM, or DIA-targeted extraction) for precise validation in larger studies.
- Library-free workflows → start projects even without existing spectral libraries.
- Low-input precision → high-quality results from minimal sample amounts.
- Fast turnaround → speed up your research timelines.
- Expert support → guidance from data analysis to next steps.
What Makes Our Discovery Proteomics Service Stand Out?
Orbitrap Exploris 480 / Q Exactive HF-X (Thermo Scientific)
- Resolution: up to 240,000 @ m/z 200
- Mass accuracy: < 2 ppm
- Scan speed: up to 40 Hz
- Widely applied for DIA & DDA
timsTOF Pro 2 (Bruker Daltonics)
- TIMS with high-speed fragmentation for 4D proteomics
- 100 Hz MS/MS acquisition rate
- Dynamic range: 5–6 orders
- Excellent for low-abundance detection

TripleTOF 6600+ (SCIEX)
- Resolution: ~35,000
- Mass accuracy: < 5 ppm
- Fast duty cycle for SWATH-DIA
- Suitable for large-scale biomarker studies
- Proteome coverage: 7,000–10,000 proteins/run
- Dynamic range: 5–6 orders of magnitude
- Protein-level FDR: ≤1%
- Quantitative precision: CV < 15%
- Mass accuracy: <1–2 ppm
Discovery Proteomics: Sample Requirements and Preparation

Storage and Shipping Tips
- Store all samples at –80°C unless otherwise noted.
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- Ship samples on dry ice for long-distance transport.
- Include a detailed sample manifest with every shipment.
| Sample Type | Minimum Amount | Storage & Transport | Notes / Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | 1–5 million cells | Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice | Snap-freeze pellets; avoid repeated freeze–thaw |
| Tissues | 20–50 mg wet weight | Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice | Collect fresh, snap-freeze immediately |
| Plasma / Serum | 50–100 µL | Store at −80 °C; EDTA tubes preferred | Avoid hemolysis; aliquot to reduce freeze–thaw |
| CSF / Saliva / Urine | 100–200 µL | Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice | Clarify compatibility in advance |
| FFPE Sections | 5–10 sections (5–10 µm) | Room temperature (with precautions) | Older FFPE may yield lower proteome coverage |
| Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) | Equivalent to ≥100 µg protein | Store at −80 °C; ship on dry ice | Consult for optimized isolation method |
Not sure whether your samples meet the requirements?
Contact us — we're happy to help design the best strategy for your discovery proteomics study.
What You'll Receive from Our Discovery Proteomics Service
Data, insights, and publication-ready results for your research
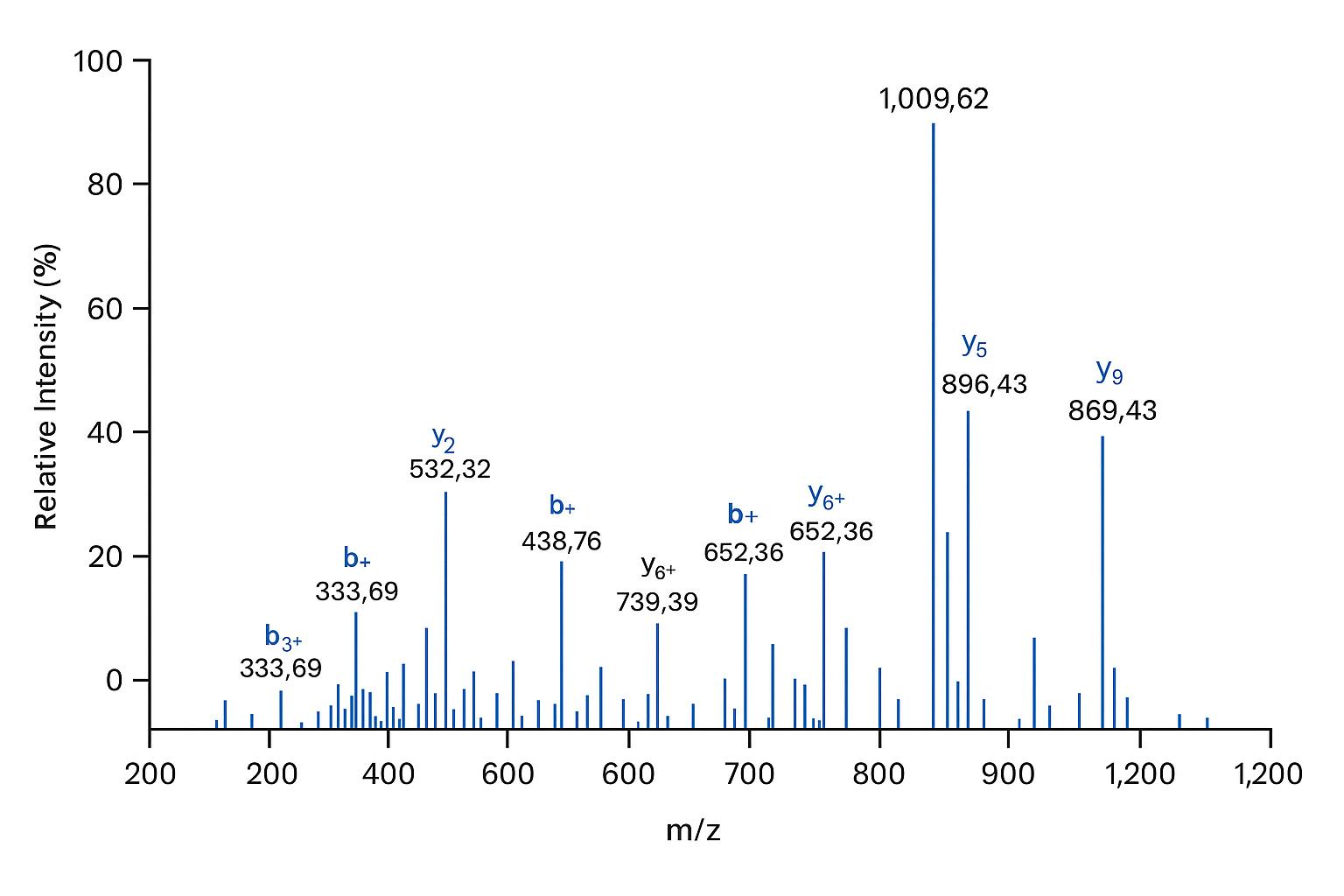
Representative LC–MS/MS spectrum showing peptide fragmentation patterns, demonstrating high-resolution detection and reliable protein identification.
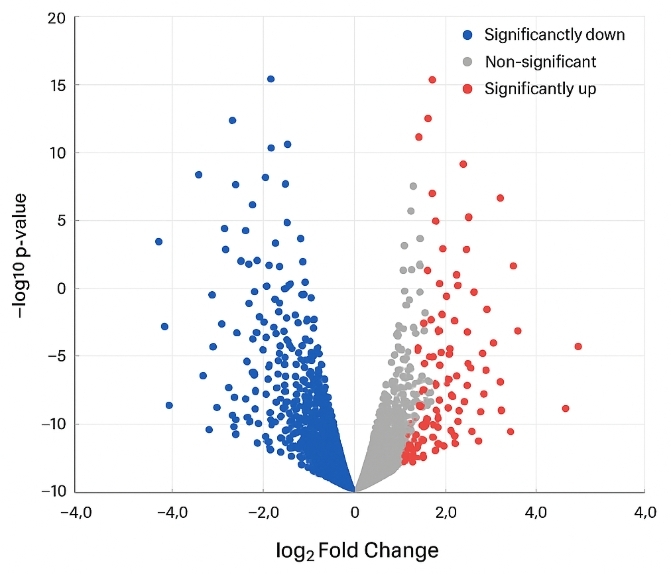
Volcano plot displaying significantly upregulated and downregulated proteins, highlighting candidate biomarkers identified in discovery proteomics.
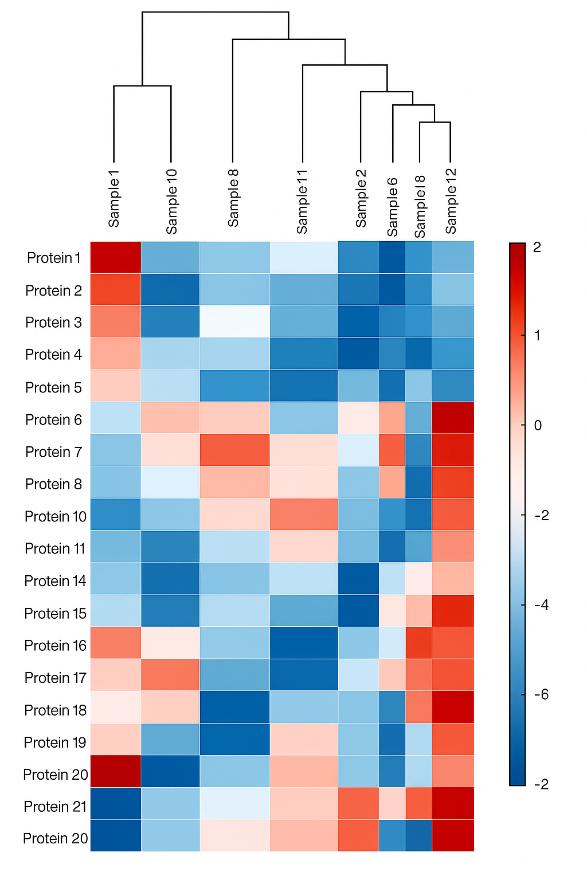
Heatmap with hierarchical clustering of proteins and samples, visualizing expression patterns and group-specific clusters.
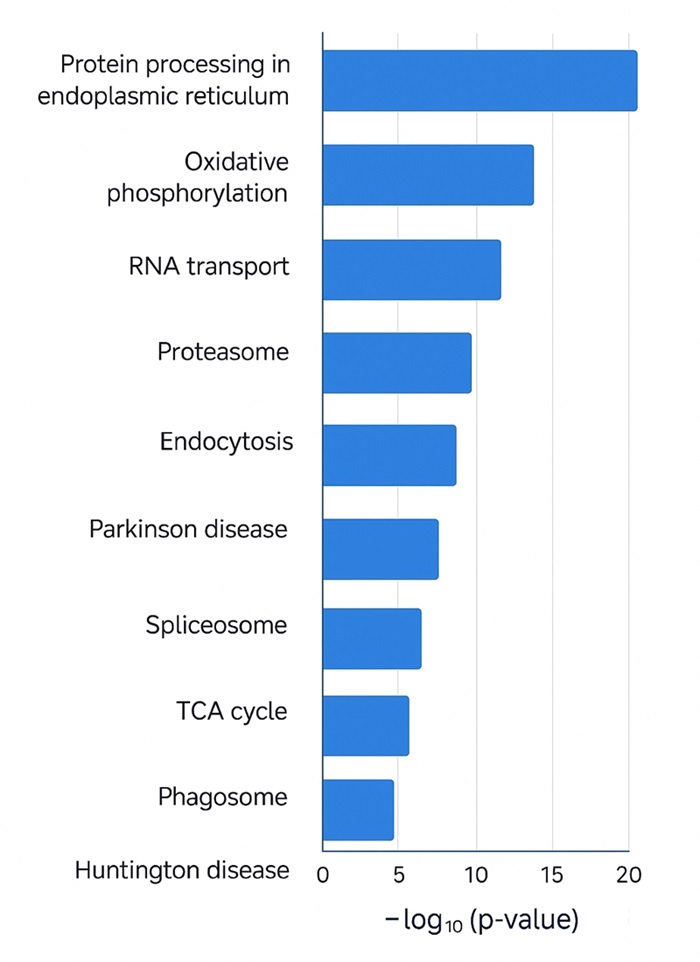
Pathway enrichment analysis illustrating biological pathways significantly associated with differentially expressed proteins.
Data Package
- Raw LC–MS/MS files
- Processed identification and quantification tables (peptide & protein levels)
Quality Control Report
- Instrument performance and run-level QC
- Protein-level FDR reporting and missing-value statistics
Bioinformatics & Insights
- Differential expression analysis
- Pathway and network enrichment results
- Ranked candidate proteins/biomarkers with interpretation
Publication-Ready Outputs
- Figures: volcano plots, PCA, heatmaps, pathway diagrams
- Final comprehensive PDF report
- Optional: targeted assay design (PRM, SRM, MRM, DIA re-mining) for validation
Success Stories with Discovery Proteomics
Discovery + Targeted Proteomics Define a Prognostic Signature in Oral Cancer
Journal: Nature Communications · Published: 2018
Study Scope
Researchers combined discovery proteomics (on FFPE tumor regions) with targeted verification to uncover prognostic protein signatures in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The study analyzed:
- Histology-guided laser microdissection of invasive tumor front (ITF) vs. inner tumor (neoplastic islands & stroma) for discovery proteomics
- Discovery phase identified region-specific proteins and candidates with clinicopathological associations
- Two independent cohorts for verification: 125-patient IHC cohort and 40-patient saliva SRM-MS cohort
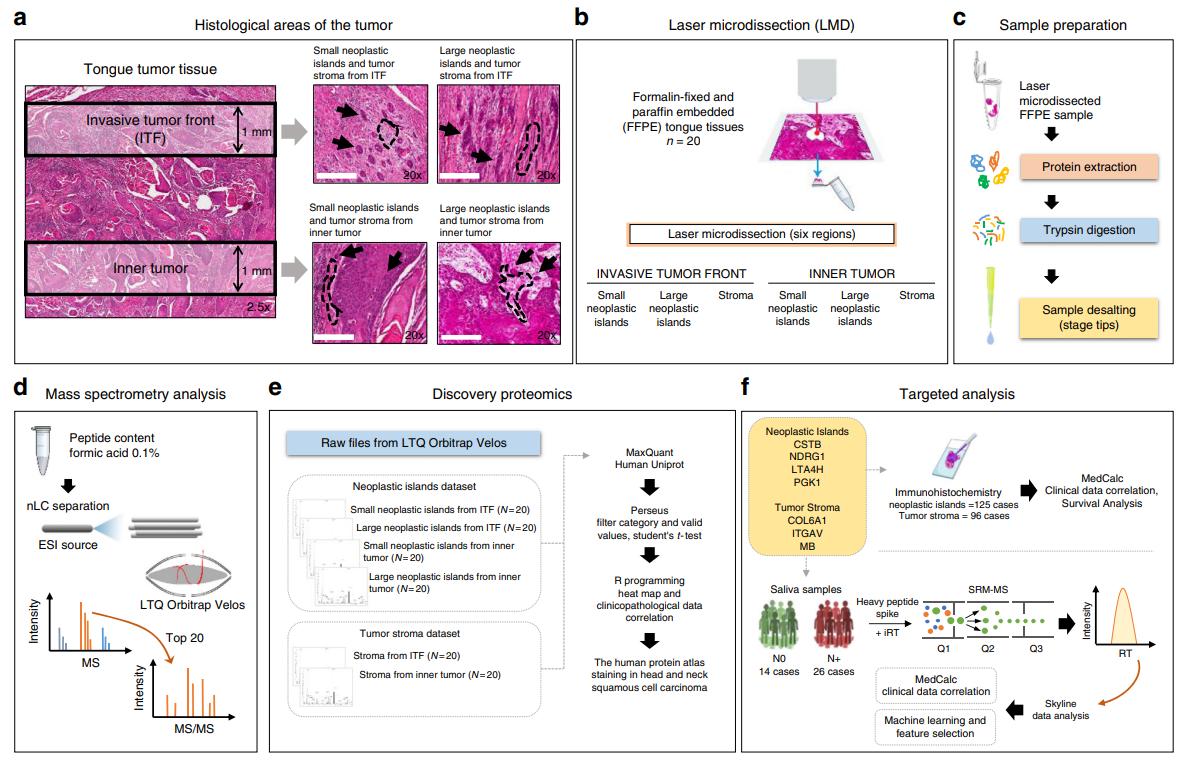 Experimental design.
Experimental design.
Proteomic Coverage and Data Quality
- Quantified 2,049 proteins in neoplastic islands (ITF vs. inner); after stringent filtering, 799 proteins retained for analysis
- Quantified 1,733 proteins in tumor stroma; 704 proteins retained after filtering
- Unsupervised clustering captured biologically meaningful separation between ITF and inner tumor regions, reflecting tumor heterogeneity and robust measurement design
These results support the stability and biological specificity of the discovery proteomics dataset.
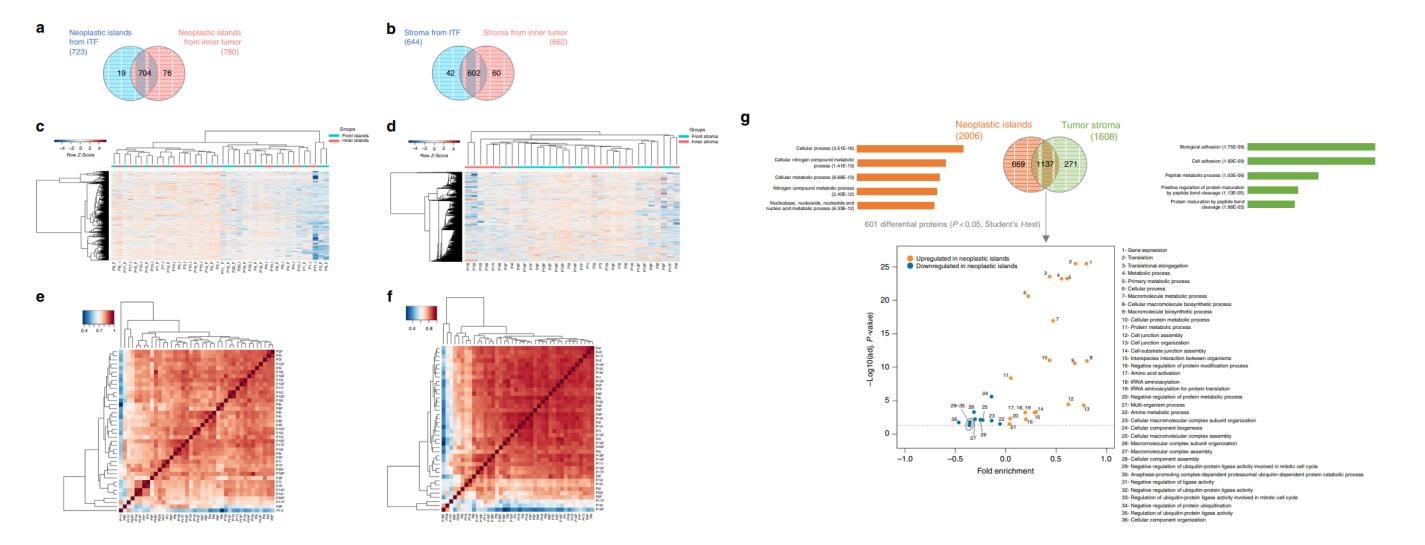 Quantitative proteome analysis indicates spatially distinct protein signatures.
Quantitative proteome analysis indicates spatially distinct protein signatures.
Biological Insights
The study revealed:
- Distinct protein expression between ITF vs. inner tumor in both neoplastic islands and stroma, with 32 and 101 significant differentials respectively (t-tests, p<0.05)
- Candidate markers (e.g., LTA4H, COL6A1, ITGAV, CSTB, NDRG1, PGK1) linked to clinicopathological features and tumor microenvironment biology
- In independent cohorts, IHC and SRM-MS verified prognostic signatures; peptide-level signatures outperformed protein-level ones in cross-validation analyses
These findings illustrate how discovery proteomics can reveal spatially resolved, prognostic biology and translate to noninvasive biofluids.
Technical Highlights
- Discovery proteomics on microdissected FFPE regions with label-free quantification; downstream IHC and SRM-MS for targeted validation
- Statistical filtering and multiple QC steps (e.g., exclusion lists, valid-value thresholds) to ensure confident identifications
- Machine-learning evaluation of signature performance (ROC/AUC; cross-validation) on targeted data
Why It Matters
This study demonstrates how discovery proteomics can:
- Pinpoint region-specific tumor biology from FFPE tissues and bridge to targeted verification
- Produce prognostic signatures validated in independent patient cohorts (tissue and saliva)
- Offer a repeatable blueprint for translating discovery findings into clinical decision support tools
Reference
Carnielli, Carolina Moretto, et al. "Combining discovery and targeted proteomics reveals a prognostic signature in oral cancer." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 3598.



