Creative Proteomics Team — Proteomics & PTM Research Unit, Creative Proteomics. We specialize in PTM-focused mass spectrometry for translational biomarker work, with hands-on experience in immunoenrichment workflows and Orbitrap PRM quantitation for CSF/plasma. Our group supports targeted assay validation and SIL-based calibration for site-specific phosphorylation studies.
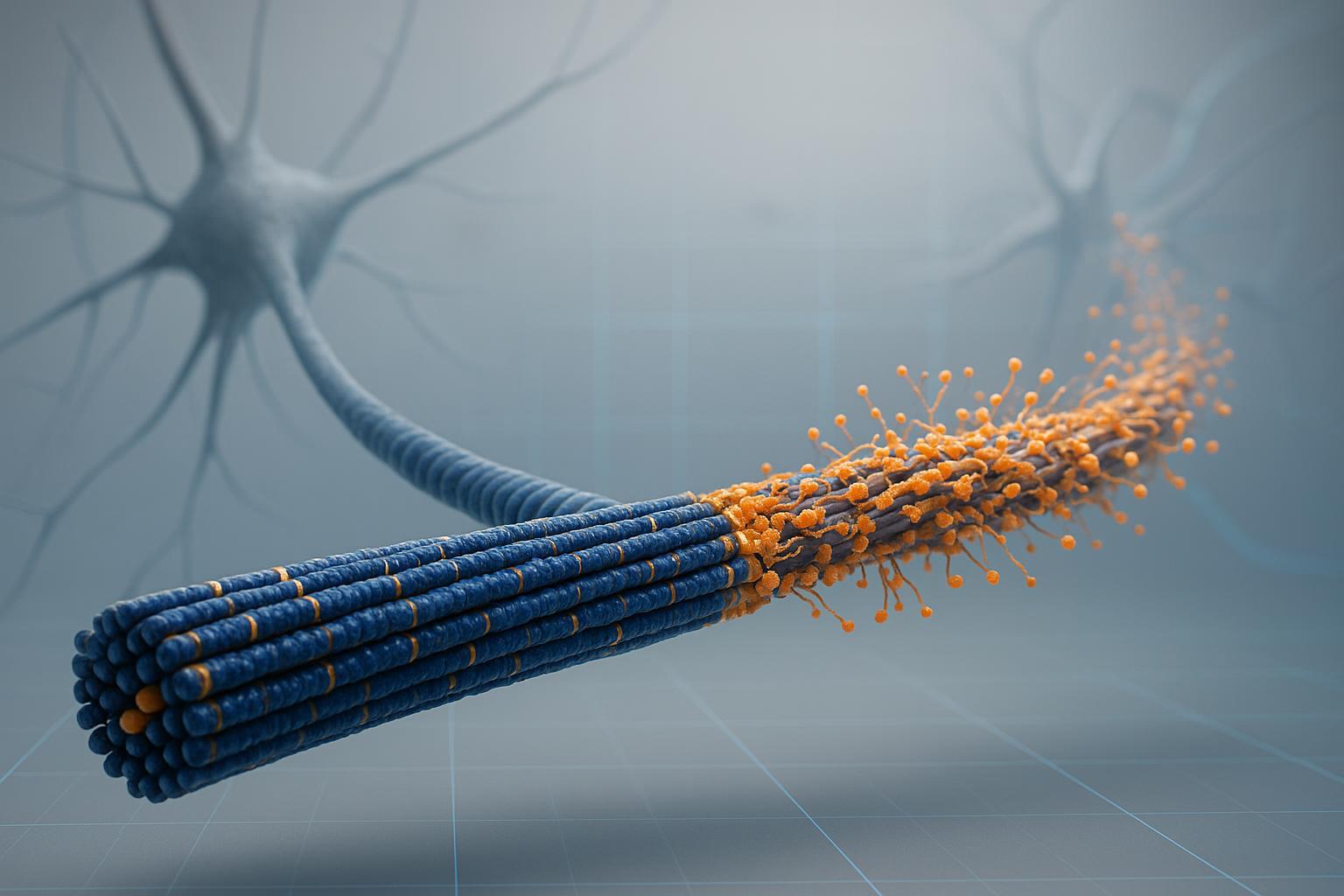
p-Tau is more than a biomarker label—it's a set of discrete phosphorylation events that alter tau's structure, seeding propensity, and microtubule engagement. When you quantify those events at specific sites (for example, pThr181, pThr217, pSer396, pSer404), patterns emerge that map to disease stage, therapeutic response, and cohort stratification. This article is a practical guide to high-precision, site-specific tau phosphorylation analysis in CSF and plasma using immunoenrichment and Orbitrap-based PRM, with a focus on auditable LOD/LOQ, CV%, and linearity.
The biological significance: why site-specific phosphorylation matters
Tau's role in microtubule stability
Tau stabilizes axonal microtubules and tunes transport. Physiological phosphorylation modulates this binding, allowing neurons to adapt to signaling and metabolic states. Loss of appropriate regulation weakens microtubule integrity and axonal trafficking—an early thread in the Alzheimer's tapestry.
The shift to pathological reversible phosphorylation
Under disease pressure, reversible phosphorylation shifts toward multi-site, higher-occupancy states that reduce microtubule binding and increase tau's conformational flexibility. Over time, hyperphosphorylated tau becomes primed for misfolding and seeding, contributing to neurofibrillary pathology.
From physiological regulation to toxic hyperphosphorylation
Hyperphosphorylation at disease-associated sites (such as Ser396/Ser404) correlates with filament formation and later-stage pathology, whereas earlier changes (Thr181/Thr217) track with preclinical and MCI phases across multiple cohorts. These stage-dependent signatures are why site resolution matters.
Dynamic balance: phosphorylation and dephosphorylation mechanisms
Kinase activity (e.g., PKA, GSK-3β, CDK5) and phosphatase activity (e.g., PP2A) set the dynamic range of tau phosphorylation. Dysregulation—whether by kinase overactivity, phosphatase inhibition, or both—shifts tau toward states that detach from microtubules and accumulate.
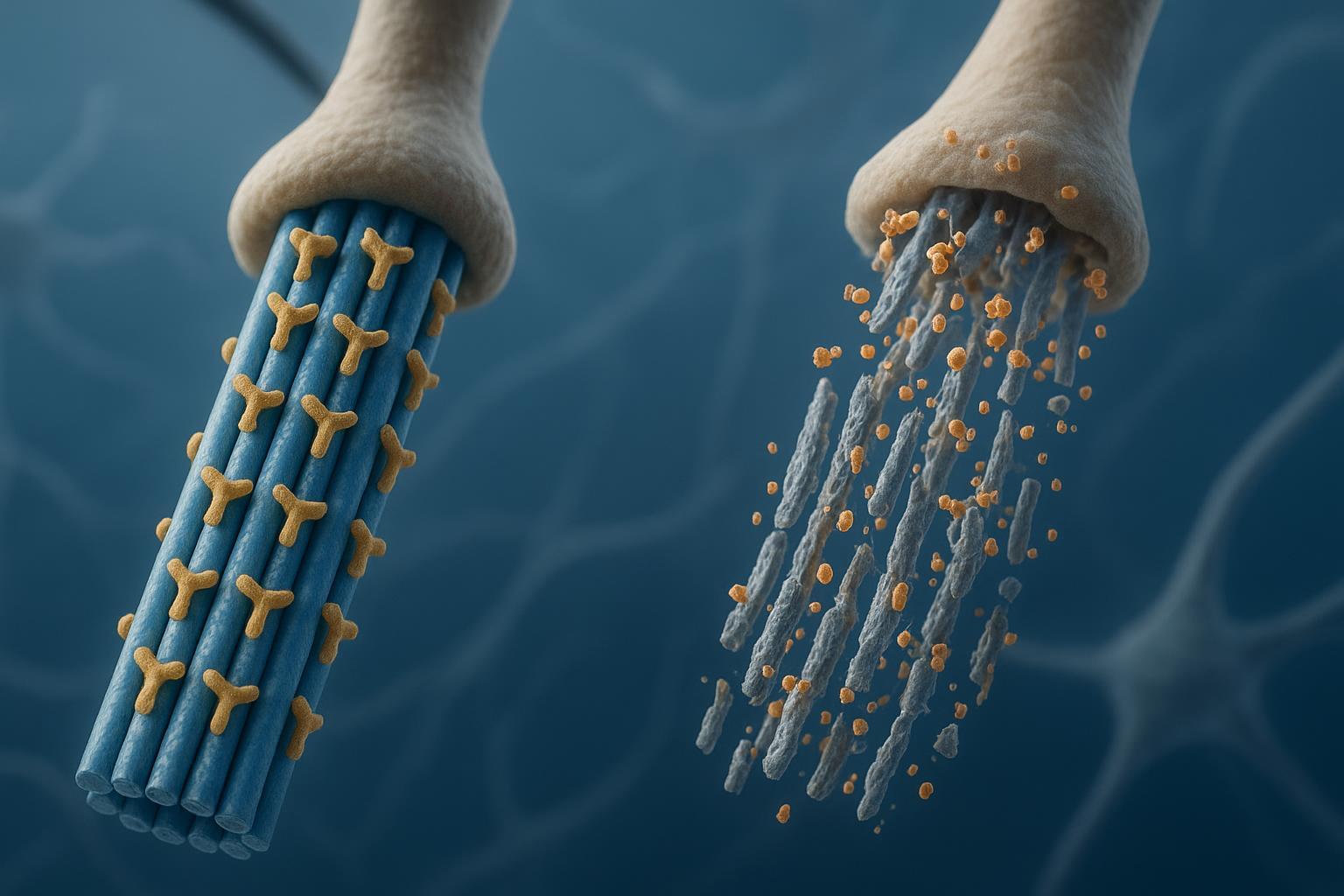 Figure 1: The molecular mechanism showing how tau phosphorylation triggers microtubule detachment and neurodegeneration.
Figure 1: The molecular mechanism showing how tau phosphorylation triggers microtubule detachment and neurodegeneration.
Deciphering the tau phosphorylation cascade: from sites to symptoms
Understanding the multistage phosphorylation cascade
Evidence across clinical cohorts suggests a sequence: early increases in pThr217 and pThr181 align with amyloid positivity and cognitive decline risk; later, elevations in pSer396 and pSer404 coincide with tangle burden and symptomatic progression. These are not binary switches but graded, site-specific shifts.
Kinase-driven modification: PKA phosphorylation in neurodegeneration
PKA contributes to tau regulation and can modulate pathways that influence phosphorylation stoichiometry (including interactions with PP2A). By contrast, GSK-3β has stronger, more direct links to seed formation and paired helical filament epitopes.
The impact of GSK-3β and PKA on tau seed formation
GSK-3β targets multiple disease-relevant residues and is frequently implicated in pathological seeding, including sites within the PHF-1 epitope. PKA's influence appears more indirect, shaping the phosphorylation landscape that permits aggregation.
Downstream effects: how phosphorylation triggers tau aggregation
Accumulated multi-site phosphorylation decreases microtubule binding, exposes aggregation-prone regions, and promotes template-driven fibrillization. In biofluids, these events are mirrored by increasing concentrations of site-specific phosphopeptides.
Mapping critical sites: pThr181, pThr217, and the meaning of tau hyperphosphorylation
Diagnostic significance of early-stage sites
pThr217 and pThr181 in CSF and plasma consistently associate with amyloid/tau PET and can separate preclinical and MCI groups in multiple studies. Early-stage sensitivity makes them attractive for stratification and for tracking target engagement in trials.
Late-stage markers: pSer396 and pSer404 in fibril formation
pSer396 and pSer404 increase predominantly in later disease, aligning with neurofibrillary tangle burden rather than early conversion risk. Their presence complements early markers to describe trajectory and severity.
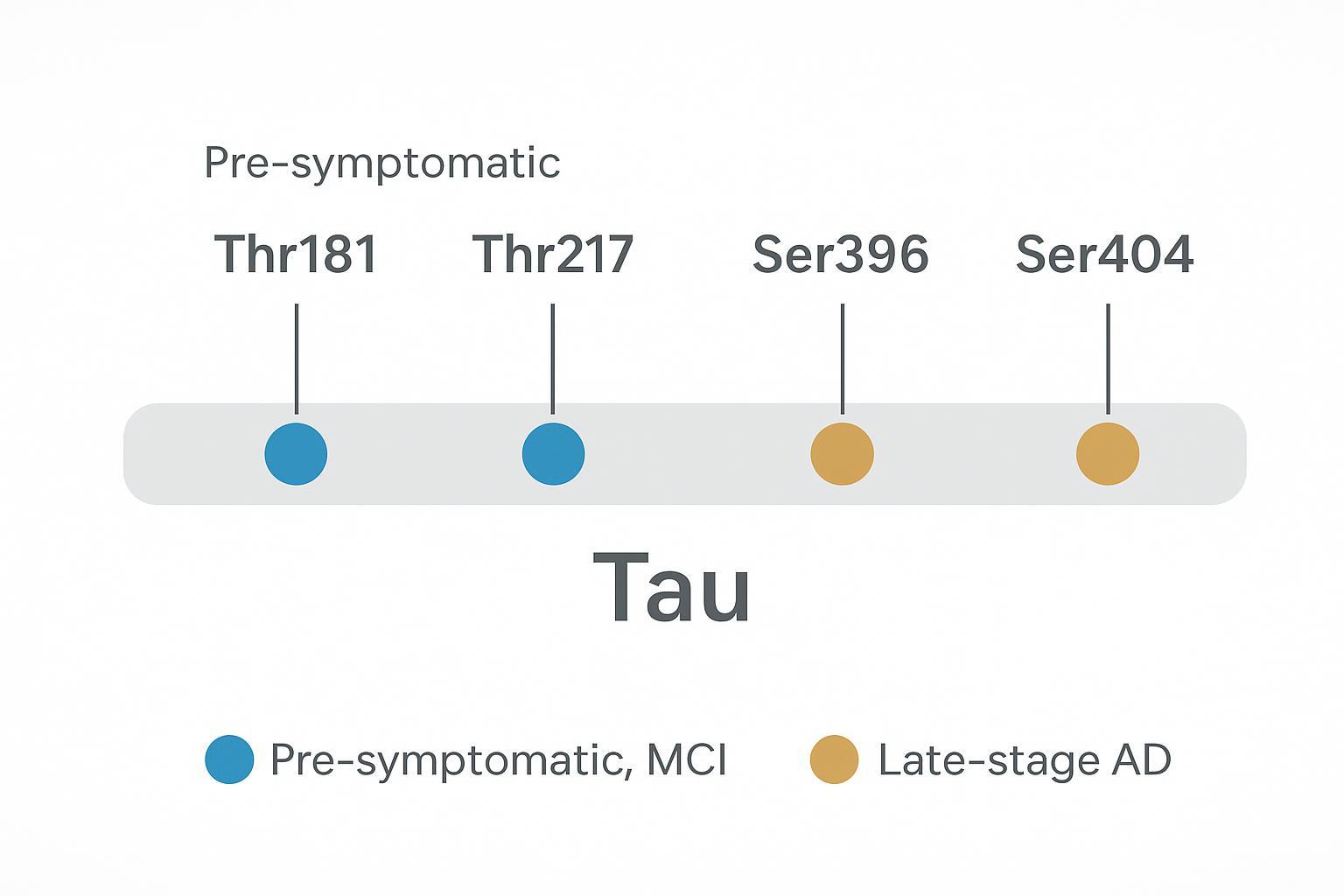 Figure 2: Mapping key tau phosphorylation sites to progressive stages of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.
Figure 2: Mapping key tau phosphorylation sites to progressive stages of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.
Methodology that stands up to audit: CSF/plasma immunoenrichment with Orbitrap PRM
The limitations of in-silico site prediction
In-silico phosphorylation site prediction and motif scoring are valuable for hypothesis generation, but they do not capture matrix effects, peptide chemistry, or interference patterns in CSF/plasma. For clinical translation and decision-making, experimental, site-specific tau phosphorylation analysis remains the standard.
Mass spectrometry readout: PRM as a high-specificity choice
Parallel Reaction Monitoring (PRM) on quadrupole-Orbitrap platforms combines quadrupole isolation with high-resolution MS2, providing mass accuracy and improved interference control. Typical starting settings for phosphopeptides in complex matrices include MS2 resolution at 60,000–120,000 (m/z 200), isolation windows of 0.7–1.6 m/z, maximum injection times of 100–400 ms to secure 8–12 points per peak, and HCD collision energies around 25–32% (stepped when needed). Scheduling targets reduces duty cycle load and improves sensitivity. When site localization proves challenging, consider complementary ETD/EThcD on selected peptides.
Optimizing phosphopeptide enrichment (immunoaffinity vs TiO2/IMAC)
- Immunoaffinity enrichment (antibody capture against phospho-epitopes or tau domains) offers high specificity and can deliver superior S/N in CSF/plasma for low-abundance sites.
- TiO2/IMAC can enrich broader phospho-peptide pools but require careful cleanup to mitigate non-specific binding and acidic peptide bias.
- Practical tip: run method scouting on pooled CSF/plasma to compare recovery and background for your peptides of interest before locking the assay.
Quantitative accuracy: SIS calibration; TMT vs label-free quantification
Absolute or ratio-based quantification hinges on stable isotope–labeled (SIL) phosphopeptides. Spike heavy counterparts across 3–4 orders of magnitude in matrix-matched backgrounds to establish linearity, calculate LOD/LOQ, and monitor recovery. TMT multiplexing is attractive for discovery and batch throughput, but isobaric interference and ratio compression can complicate low-level phosphopeptide quant. For targeted, site-specific tau phosphorylation analysis in CSF/plasma, PRM with SIL peptides is typically favored over LFQ/TMT for auditable precision.
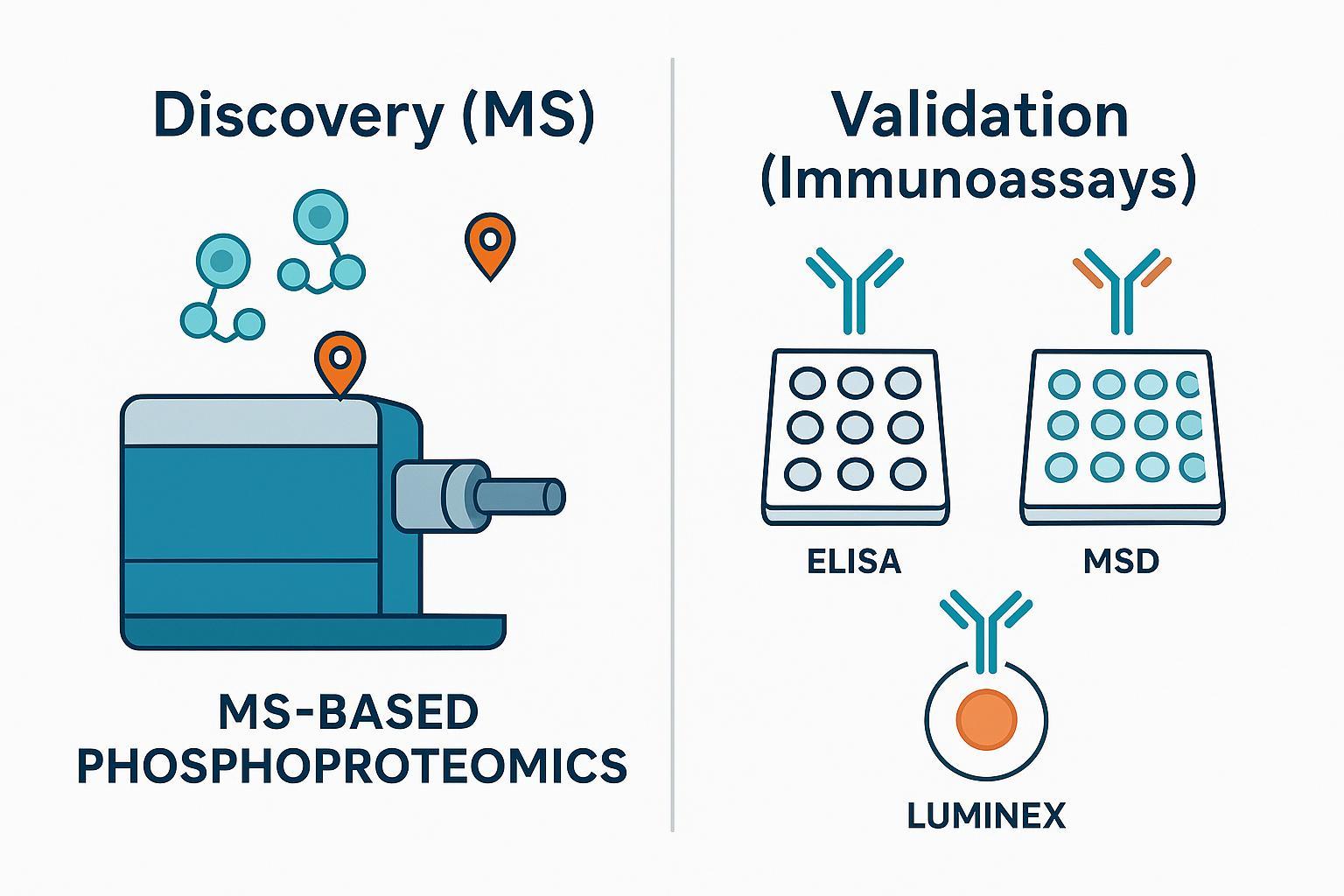
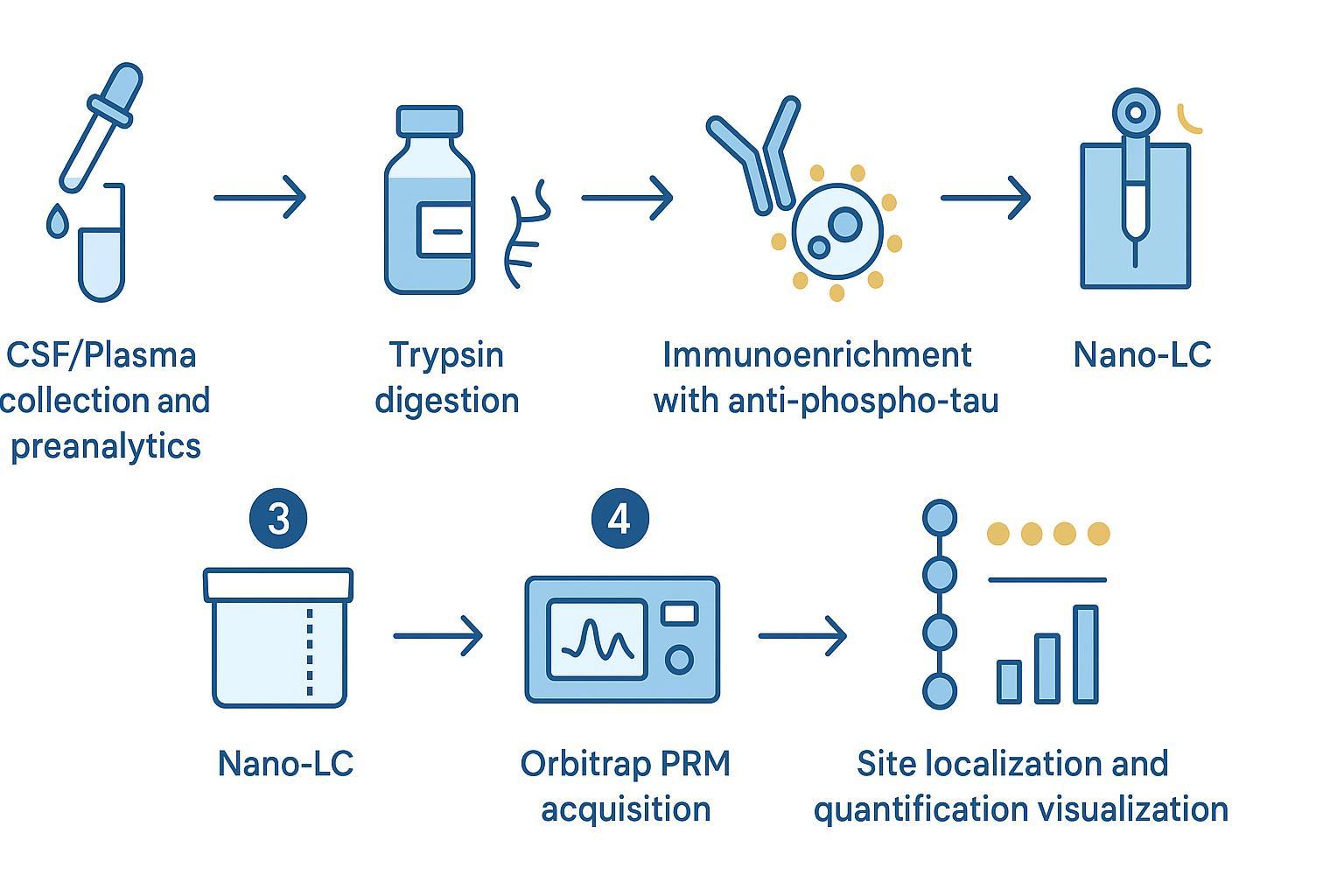 Figure 3: High-throughput workflow for quantitative phosphorylation analysis and site-specific validation.
Figure 3: High-throughput workflow for quantitative phosphorylation analysis and site-specific validation.
Site-specific tau phosphorylation analysis: validation plan and QC metrics you can trust
LOD/LOQ determination in matrix, linearity, and recovery
Define LOD/LOQ with matrix-matched calibrators (e.g., pooled CSF/plasma post-enrichment). Fit weighted (1/x or 1/x²) calibration curves over 3–4 orders of magnitude and verify back-calculated accuracies within 80–120% at all levels; accept ≤20% at the LLOQ. Perform spike-recovery tests by adding known amounts of SIL and native peptides into pre- and post-enrichment samples to separate capture and ionization contributions. Document dilution linearity to confirm assay robustness across clinical ranges. For regulatory-aligned definitions, see the 2018 FDA guidance on Bioanalytical Method Validation and ICH M10 (adopted 2022).
Precision targets and stability studies
Aim for intra- and inter-assay precision with CV ≤15% at mid/high QC levels (≤20% at LLOQ), assessed across days, operators, and instruments. Stability work should include bench-top, freeze–thaw, long-term storage, and processed autosampler stability, all performed in matrix. CLSI frameworks for LC–MS peptide measurements (e.g., C64; EP06 linearity, EP15 precision, EP17 LoD/LoQ) offer useful acceptance structures.
Site-localization confidence and false localization rate control
For each phosphopeptide, report localization confidence using algorithms such as AScore/ptmRS and, where possible, verify with synthetic standards. Target an empirical phosphosite FLR of 1–5% using decoy strategies or orthogonal confirmation.
- Validation checklist (adapt for your lab):
- Define targets (pThr217, pThr181, pSer396, pSer404) and peptide sequences/charge states.
- Verify preanalytical handling (collection tubes, processing times, freeze–thaw tolerance).
- Select enrichment (immunoaffinity vs TiO2/IMAC) based on pooled-matrix scouting.
- Build PRM method: resolution, isolation width, CE optimization, scheduled inclusion list.
- Establish matrix-matched calibration with SIL peptides; determine linearity (R²), LOD/LOQ.
- Assess recovery and matrix effects; confirm dilution linearity.
- Quantify precision (intra/inter-assay CV%) and accuracy (80–120% criteria).
- Perform stability studies (bench-top, freeze–thaw, long-term, processed).
- Report site localization with FLR control and document acceptance thresholds.
- Define batch QC scheme and run acceptance rules.
| Component | Practical target | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Linearity | 3–4 orders; R² ≥ 0.99 | Weighted 1/x or 1/x² in matrix-matched curves |
| LLOQ accuracy/precision | 80–120% / ≤20% CV | Define per peptide in CSF/plasma |
| Precision (mid/high QC) | ≤15% CV | Inter-day, inter-operator |
PTM crosstalk: phosphorylation and ubiquitination in tau proteostasis
The co-regulatory model and proteasomal degradation
Phosphorylation can gate ubiquitination patterns on tau, altering recognition by E3 ligases and routing toward the proteasome or autophagy-lysosome pathways. In models, selective degradation of phosphorylated tau species is feasible, supporting dual-PTM therapeutic strategies.
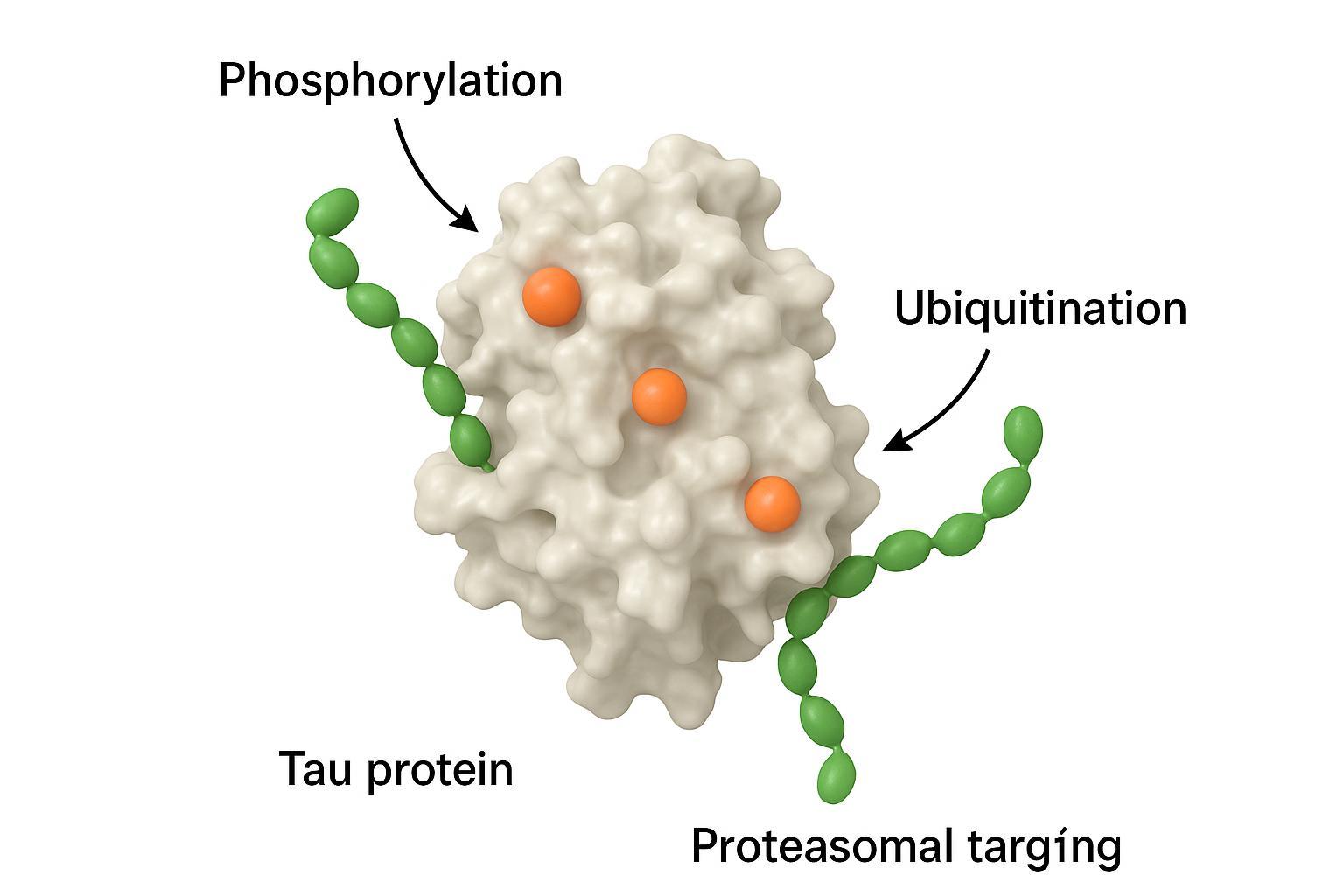 Figure 4: The interplay between phosphorylation and ubiquitination in tau proteostasis regulation.
Figure 4: The interplay between phosphorylation and ubiquitination in tau proteostasis regulation.
Data resources and database support for study design
Authoritative resources can strengthen site selection and interpretation. PhosphoSitePlus curates site-level evidence for MAPT (tau), including Thr181, Thr217, Ser396, and Ser404; see the MAPT (P10636) page for a consolidated view. Public cohorts and portals such as ADNI and AMP-AD provide cross-cohort comparators and SOPs for biofluid handling and biomarker analysis. A targeted PRM method paper describing antibody-free CSF tau measurement offers practical parameter references.
According to the curated MAPT entry in PhosphoSitePlus (accessed 2026), site-level experimental evidence is available for Thr181, Thr217, Ser396, and Ser404. For validation constructs like LLOQ accuracy/precision and stability, refer to the FDA's 2018 Bioanalytical Method Validation guidance and the ICH M10 guideline (adopted 2022). For study planning and cross-validation datasets, the ADNI data portal and the AMP-AD Knowledge Portal provide protocols and multi-omics resources. For Orbitrap PRM parameterization in CSF, an antibody-free tau PRM study (PLoS One, 2022) details acquisition settings aligned with the recommendations above.
Practical example: SIS-based PRM calibration on Orbitrap
Disclosure: Creative Proteomics is our product. As a practical example, consider a CSF assay targeting pThr217, pThr181, pSer396, and pSer404. Heavy, phosphorylation-matched SIL peptides are spiked into pooled, post-enrichment CSF at 8 levels spanning ~4 orders of magnitude. Scheduled PRM (MS2 resolution 60,000–120,000; isolation 0.7–1.0 m/z) acquires ≥3 interference-free fragments per peptide. A matrix-matched, weighted 1/x calibration is fit in Skyline, achieving R² ≥0.99 over the working range. LLOQ is defined as the lowest level with accuracy within 80–120% and precision ≤20% CV; mid/high QCs target ≤15% CV. Dilution linearity and spike-recovery experiments are run to partition capture vs ionization effects. Site localization is confirmed with ptmRS and by comparing synthetic peptide spectra. For readers who need a transfer-ready starting point, explore the PTM services and enrichment options on the Creative Proteomics PTM hub.
- PhosphoSitePlus MAPT page: Curated tau phosphorylation sites and evidence
- FDA (2018) guidance: Bioanalytical Method Validation for Industry
- ICH M10 (2022): Bioanalytical Method Validation guideline
- ADNI data portal: Longitudinal imaging and biofluid biomarker resources
- AMP-AD portal: Multi-omics datasets and methods
- PRM CSF tau method: Antibody-free targeted PRM study (PLoS One, 2022)
- Creative Proteomics PTM hub: MS-based PTM analysis services
Next steps
If you need a validated, site-specific tau phosphorylation workflow or a transfer-ready PRM method, visit the Creative Proteomics PTM services overview to discuss study design and QC expectations.
Our products and services are for research use only.