Absolute Quantification of Histone H3 Epigenetic Marks by LC-MS/MS
What is Precise Quantification of Histone H3?
Unveiling the Epigenetic Landscape
Histone H3 is a fundamental structural component of eukaryotic chromatin, forming one-half of the core tetramer within the nucleosome octamer around which DNA is wrapped. While its globular domain is essential for nucleosome stability and DNA packaging, its biological significance is predominantly defined by its unstructured N-terminal tail, which protrudes from the nucleosome core.
This tail serves as a dynamic signaling hub, subject to a vast array of covalent post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation. These modifications constitute a "Histone Code" that regulates the interaction between DNA and nuclear proteins, thereby controlling the physical accessibility of the genome.
The importance of Histone H3 extends to the regulation of nearly all DNA-templated processes, including transcription, replication, and repair. By recruiting specific "reader" proteins, H3 modifications dictate the transition between tightly packed, transcriptionally silent heterochromatin (e.g., marked by H3K9me3) and accessible, active euchromatin (e.g., marked by H3K4me3 or H3K27ac). Consequently, Histone H3 acts as a critical epigenetic determinant of cell fate, governing stem cell differentiation and developmental timing. Dysregulation of H3 PTM stoichiometry is a primary driver in oncology and metabolic diseases, highlighting its central role in maintaining genomic integrity and cellular homeostasis.
In pathological states like cancer or metabolic dysfunction, the global stoichiometry of these H3 marks shifts. However, because H3 tails often carry combinatorial modifications (e.g., phosphorylation adjacent to methylation), traditional antibodies frequently fail due to epitope occlusion or cross-reactivity. Absolute quantification via mass spectrometry is the only method capable of resolving these complex proteoforms with stoichiometric accuracy, enabling researchers to accurately decipher the "Histone Code" and its dynamic role in transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, and epigenetic inheritance.
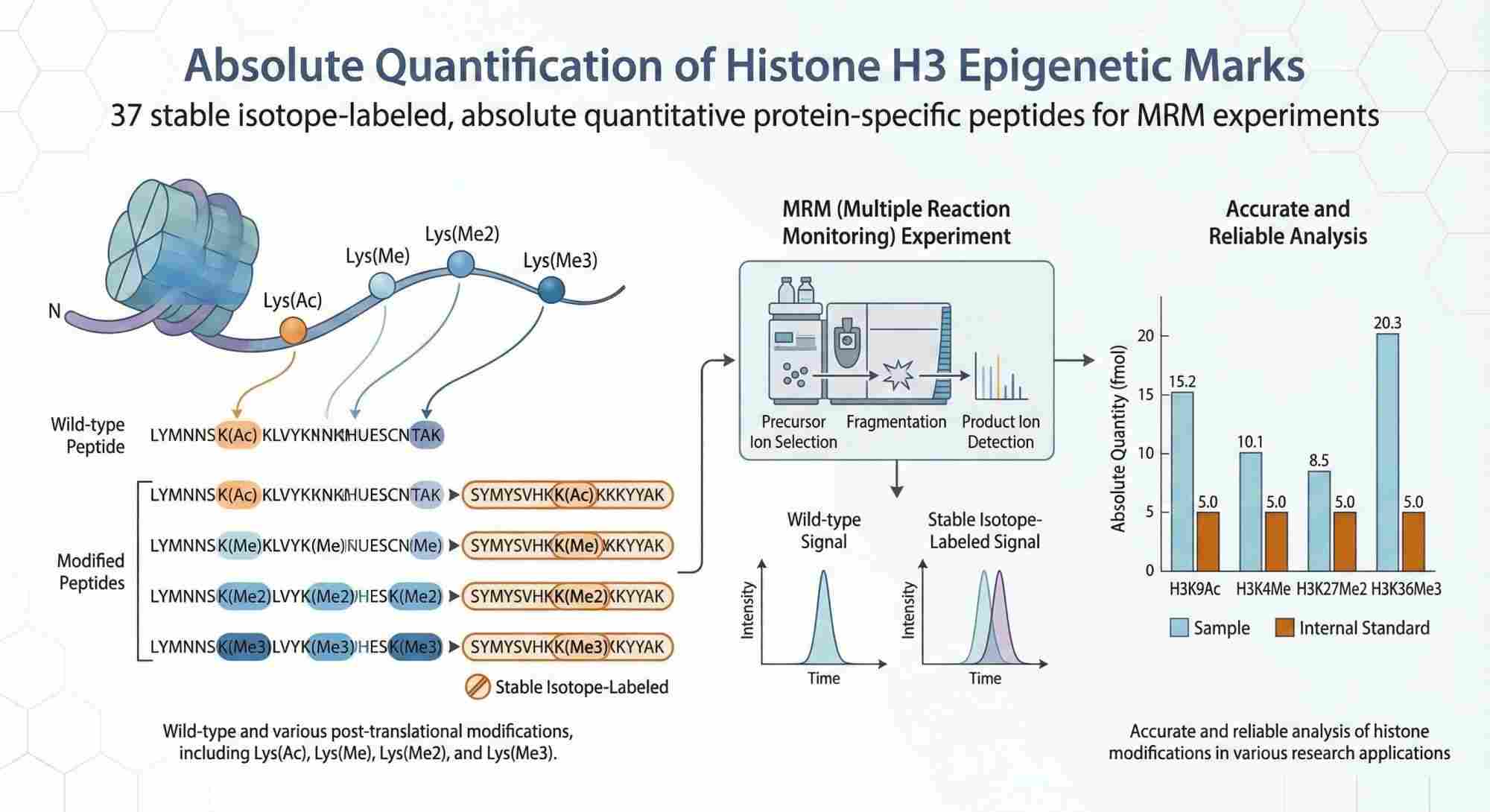
Why Choose MRM-Based Histone Quantification?
Overcoming the Limitations of Antibody-Based Epigenetics
In the field of chromatin biology, the precise mapping of histone modifications is often hindered by the limitations of Western Blotting and ELISA. Our targeted proteomics workflow addresses these challenges to provide data of superior fidelity.
- Elimination of Antibody Cross-Reactivity
Antibodies raised against specific histone PTMs frequently suffer from significant cross-reactivity, particularly between closely related states (e.g., distinguishing H3K9me2 from H3K9me3) or when adjacent residues are modified (epitope occlusion).
The Solution: Mass spectrometry distinguishes analytes based on mass-to-charge (m/z) ratios. Our method definitively identifies specific PTM states without the ambiguity of epitope masking or non-specific binding.
- Absolute Stoichiometry over Relative Fold-Change
Understanding the biological impact of a histone mark requires knowing its occupancy—what percentage of nucleosomes carry a specific modification? Relative quantification cannot provide this.
The Solution: By using heavy-labeled internal standards of known concentration, we calculate the absolute molar abundance of each PTM. This allows for the determination of occupancy rates, providing a quantitative link between chromatin state and phenotype.
- Comprehensive Analysis of Combinatorial PTMs
Histone tails are often decorated with multiple simultaneous modifications that influence "reader" protein binding.
The Solution: Our panel of 37 peptides is designed to detect and quantify these specific modified sequences, capturing the complexity of the combinatorial histone code in a single analytical run.
Absolute Quantification of Histone H3 at Creative Proteomics
This Sample-to-Data Absolute Histone H3 Quantification Service is designed for epigenetics and chromatin biology researchers who require rigorous, quantitative insight into histone modification landscapes without the need to develop or optimize analytical workflows in-house. The service enables precise absolute quantification of Histone H3 and its key post-translational modifications (PTMs) using validated LC-MS/MS workflows on triple-quadrupole or high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms. By moving beyond relative measurements, this approach provides biologically interpretable data on histone modification stoichiometry, which is critical for understanding chromatin regulation and epigenetic mechanisms.
The analytical panel covers 37 Histone H3 proteotypic peptides, including wild-type sequences and major regulatory PTMs such as acetylation and mono-, di-, and tri-methylation. These modifications are central to transcriptional control, chromatin remodeling, and epigenetic inheritance. The service supports cell pellets or purified histone extracts from human and commonly used mammalian research models, with sample input requirements compatible with standard chromatin workflows. Our laboratory performs all experimental steps, including nuclei isolation, acid extraction, chemical derivatization (propionic anhydride method, when applicable), enzymatic digestion, and LC-MS/MS analysis.
Researchers receive a comprehensive data package that includes absolute abundance values for individual H3 PTMs, normalized occupancy ratios, and raw mass spectrometry files for downstream analysis. This service is widely used for high-throughput screening of epigenetic drugs such as HDAC and histone methyltransferase inhibitors, validation of ChIP-seq results, clinical biomarker discovery, and mechanistic studies in oncology and developmental biology. Its popularity stems from the combination of quantitative rigor, standardized workflows, and full outsourcing convenience, enabling researchers to focus on biological interpretation rather than analytical method development.
Technical Specifications
The CP Histone H3 Panel Capabilities
| Feature | Specification |
| Target Protein | Histone H3 |
| Quantification Method | Targeted Proteomics (LC-MRM/MS) with Stable Isotope Dilution (SID) |
| Peptide Count | 37 Unique Proteotypic Peptides |
| Modification Types | Acetylation (Ac), Methylation (Me1, Me2, Me3) |
| Target Residues | Focus on N-terminal tail Lysines (e.g., K4, K9, K27, K36, etc.) |
| Data Output | Absolute Concentration (fmol) and Relative Occupancy (%) |
FAQs
-
Q: Why is mass spectrometry preferred over Western Blotting for histone analysis?
A: Western blotting is semi-quantitative and relies on antibodies that often cross-react with neighboring modifications (crosstalk). Mass spectrometry measures the physical mass of the peptide, allowing for the distinct separation and absolute quantification of specific methylation states (e.g., distinguishing Trimethylation from Dimethylation with 100% specificity).
-
Q: Does this service cover histone variants (e.g., H3.3)?
A: The proteotypic peptides are selected based on the sequence of Histone H3. Some peptides are conserved across variants (H3.1, H3.2, H3.3), while others may be specific. Please refer to the CP Histone Proteins Quantification Service Target Peptide List.xlsx to determine specificity regarding histone variants.
-
Q: Can this method quantify combinatorial marks (e.g., K9me3 and K14ac on the same tail)?
A: Yes. If the two modifications occur on the same tryptic peptide (the same cleaved segment of the protein), MRM can detect and quantify the specific peptide species carrying both modifications simultaneously, providing a direct view of combinatorial regulation.
-
Q: How does this data complement ChIP-Seq?
A: ChIP-Seq determines where on the genome a modification is located. Our MRM quantification determines the global abundance of that modification. Together, they provide a complete picture: MRM tells you the total cellular "budget" of an epigenetic mark, while ChIP-Seq tells you how that budget is distributed across the genome.
Sample Submission Guidelines
To ensure the stability of histone modifications (which are sensitive to demethylases and deacetylases), please adhere to the following:
- Cell Culture: Wash cells with PBS containing Sodium Butyrate (or a broad-spectrum histone deacetylase inhibitor cocktail) to prevent PTM loss.
- Tissue: Snap-freeze tissue immediately upon dissection.
- Shipping: All samples must be shipped on Dry Ice.
- Buffer Note: Avoid lysis buffers containing high detergents (SDS) if you are performing the extraction yourself, as these interfere with histone recovery and MS analysis.

