Polysaccharide methylation analysis precisely reveals glycosidic linkage patterns, branching, and terminal residues in complex carbohydrates. At Creative Proteomics, we transform challenging carbohydrate matrices into actionable linkage maps that support structure–function studies, product consistency, and advanced material characterization.
Why Choose This Service?
- Linkage-level resolution: Identify 1→2, 1→3, 1→4, 1→6 linkages, branch points, and terminals.
- Neutral & acidic polysaccharides: Optional carboxyl reduction ensures reliable linkage calling in uronic-acid–rich samples.
- Fit-for-purpose reporting: Clear PMAA tables, diagnostic ions, and semi-quantitative mol% suitable for comparability, release testing, and research dossiers.
- Cross-validated results: Methylation data can be integrated with composition, FT-IR/NMR, and SEC-MALS on request for higher structural confidence.
What Is Polysaccharide Methylation Analysis?
The method exhaustively methylates all free hydroxyls in a polysaccharide, then hydrolyzes, reduces, and acetylates the fragments to form partially methylated alditol acetates (PMAAs). Each PMAA has a characteristic retention time and EI-MS fingerprint that indicates which hydroxyls were involved in glycosidic bonds before derivatization. Pattern recognition of these PMAAs reconstructs backbone linkages, branch frequencies, and terminal residues.
Key outputs
- Linkage assignments for each monosaccharide (e.g., 2,3,4-Me3-Hex → terminal Hex; 2,3,6-Me3-Hex → 4-linked Hex; 2,4,6-Me3-Hex → 3-linked Hex; 2,3-Me2-Hex → 4,6-linked Hex branch, etc.).
- Branching ratio and distribution of linkages across detected sugar types.
- Semi-quantitative mol% of PMAAs (relative response), enabling batch comparison.
When to Use This Service
- You need glycosidic linkage evidence to complement monosaccharide composition or HPSEC profiles.
- Your sample contains uronic acids, sulfation, or complex branching and requires robust interpretation.
- You are comparing batches, sources, or processing conditions and must quantify structural shifts at the linkage level.
- You are correlating structure with rheology, bioactivity, or formulation behavior.
Key Advantages of Our Polysaccharide Methylation Analysis Service
- Resolve specific glycosidic linkages including 1→2, 1→3, 1→4, 1→6, and branch points
- Compatible with acidic polysaccharides through carboxyl reduction and NaBD4 labeling
- Detect terminal residues and infer polymer branching architecture
- Enable semi-quantitative comparison of linkage types across samples
- Identify linkage-level shifts induced by processing, fermentation, or extraction
- Integrate seamlessly with structural confirmation workflows (e.g., NMR, FT-IR)
- Offer optional desulfation or deacetylation prep steps for modified glycans
- Deliver batch-ready linkage distribution charts for comparability studies
- Include internal reference controls to ensure run-to-run reproducibility
Analytical Workflow for Neutral and Acidic Polysaccharides

Custom Options and Related Glycan Profiling Services
- Acidic polysaccharides: Standard carboxyl reduction workflow with NaBD4 labeling for robust linkage calls.
- Sulfated polysaccharides: Advisory on desulfation-before-methylation trials; orthogonal sulfate mapping by LC-MS/MS.
- Monosaccharide composition by HPAEC-PAD or GC-MS alditol acetates to anchor PMAA interpretation.
- Molar-mass profiling by SEC–MALS to relate linkage architecture to size distribution.
- NMR (1H/13C, HSQC/HMBC) for site-specific confirmation in advanced studies.
GC–MS Instrumentation and Method Parameters for PMAA Linkage Analysis
Instrumentation
- System: Capillary GC with EI–quadrupole MS
- Column: Low-polarity (e.g., DB-5MS, 30 m × 0.25 mm, 0.25 μm film)
- Carrier Gas: Helium, ~1.0 mL/min
- Injection Mode: Split/splitless, 1 μL
Oven Program
- Start: 140 °C (2 min hold)
- Ramp: 3 °C/min to 280 °C (10–15 min hold)
- Total Runtime: ~60–70 min
MS Settings
- Ion Source: EI at 70 eV
- Scan Range: m/z 50–650 (full scan or SIM)
- Standards: Internal retention markers or reference PMAAs
Method QC
- Methylation Check: Optional IR/NMR verification
- Internal Control: myo-Inositol or spiked PMAA
- Fragment Matching: Diagnostic EI ions matched to library for linkage assignment

Agilent 7890B-5977A (Figure from Agilent)
Integrated QC Strategy and Method Validation
Completeness of permethylation assessed; re-methylation performed if residual –OH signatures are detected.
Process controls & blanks included to track background and carryover.
Retention-index alignment to ensure run-to-run comparability.
Replicate derivatizations available for critical samples or comparative studies.
Result plausibility checks: PMAA patterns reconciled with expected sugar inventories and known biosynthetic constraints.
What You Receive: Comprehensive and Interpretable Results
- Comprehensive report with methods summary and QC checkpoints.
- PMAA identification table: RT, key ions, inferred linkage, assigned sugar t4ype, mol% (relative).
- Linkage distribution chart (backbone vs branch vs terminals).
- Interpretation memo: Structural implications, comparison across groups/batches, and recommendations for orthogonal confirmation (e.g., 1D/2D NMR, SEC-MALS, HPAEC-PAD).
- Raw data files and processed chromatograms/MS spectra (on request).
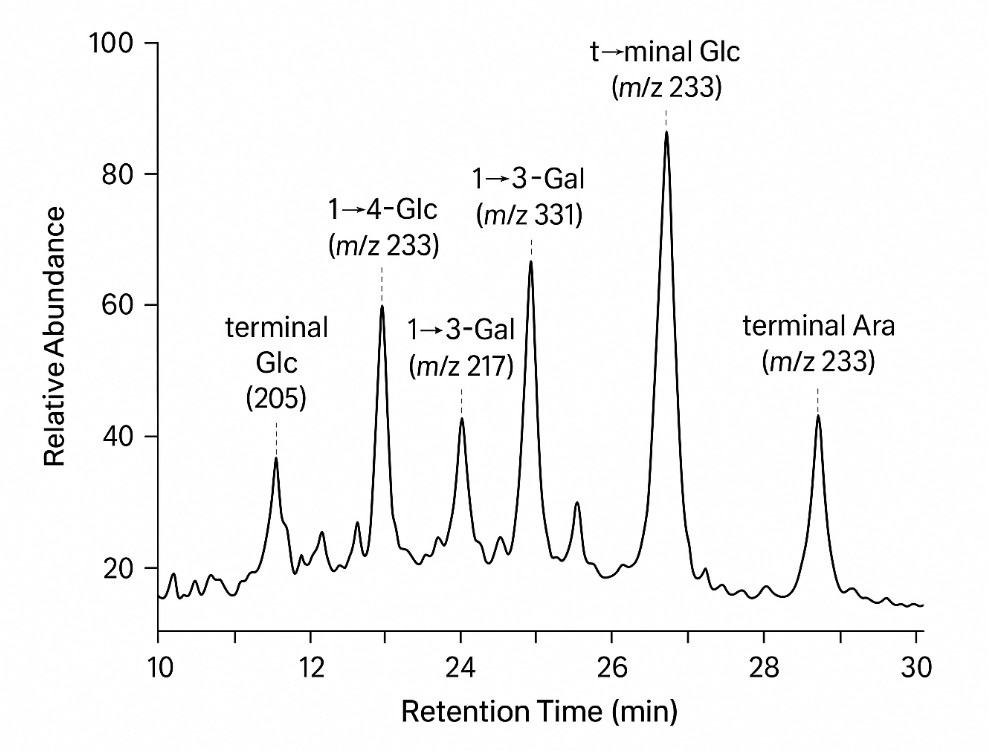
GC–MS Total Ion Chromatogram (TIC)
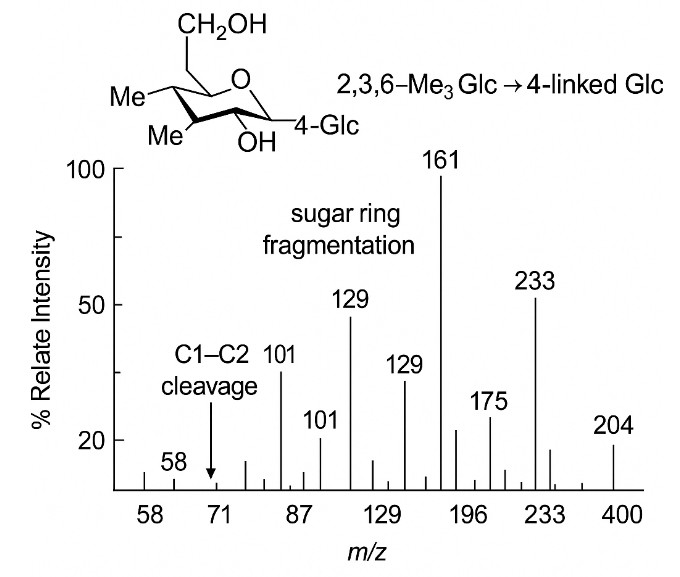
Diagnostic EI-MS Fragmentation Pattern of PMAA
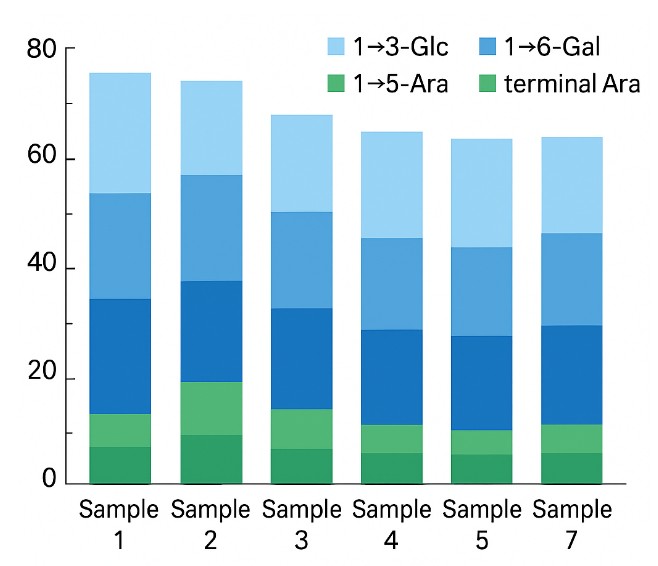
Linkage Composition Across Samples
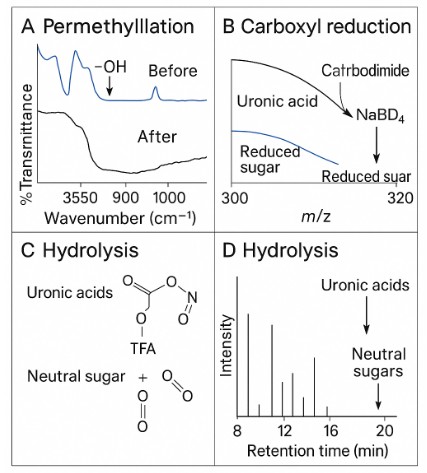
Workflow Overview with Quality Control Snapshots
Sample Submission Guidelines and Matrix Requirements
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Sample Type | Purified polysaccharide (plant, microbial, marine, or synthetic origin) |
| Minimum Amount | ≥ 1 mg preferred per condition; contact us for micro-scale projects |
| Physical Form | Dry powder strongly preferred; aqueous accepted if concentration is known |
| Buffer Components | Avoid buffers with salts, EDTA, citrate, or Tris; desalting available on request |
| Protein/Phenolic Removal | Remove interfering components (e.g., proteins, polyphenols, pigments) beforehand |
| Uronic Acid Content | Please indicate if present; we apply optional carboxyl reduction if needed |
| Other Modifications | Specify sulfation, phosphorylation, acetylation, etc., for tailored preprocessing |
| Storage & Shipping | Store dry at –20 °C; ship with desiccant in sealed tube or vial |
Use Cases: When Methylation Analysis Drives Decision-Making
![]()
Batch comparability
Detect subtle linkage variations across production lots, extraction batches, or natural sources to ensure structural consistency.
![]()
Process optimization
Evaluate how purification, degradation, or enzymatic modification impacts linkage architecture and branching patterns.
![]()
Botanical or microbial characterization
Differentiate plant gums, fungal β-glucans, or microbial exopolysaccharides based on linkage fingerprints.
![]()
Structure–function correlation
Link specific backbone or branch motifs with material properties such as gelling, viscosity, bioadhesion, or immunomodulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What does polysaccharide methylation reveal that composition or HPSEC cannot?
It resolves glycosidic linkages—backbone, branch points, and terminals—with relative proportions for batch comparability and structure–function insight, not just sugar types or size.
Q2. Can you analyze uronic-acid–rich (acidic) polysaccharides?
Yes. We perform carboxyl reduction with NaBD₄, converting acidic residues to neutral forms so linkage positions are called reliably.
Q3. How are sulfated or acetylated glycans handled without losing information?
Through fit-for-purpose pretreatments (controlled desulfation/deacetylation) and, when needed, LC–MS/MS sulfate mapping to preserve interpretability.
Q4. Are the reported linkage values quantitative?
They are semi-quantitative (mol% by response) and robust for relative comparisons across batches or process conditions.
Q5. Which linkages are typically resolved?
Terminals and common 1→2 / 1→3 / 1→4 / 1→6 linkages for hexoses and their derivatives, plus branch indicators (e.g., 3,6-disubstituted residues) via diagnostic EI ions.
Q6. Can results be integrated with other techniques in one report?
Yes—monosaccharide composition (HPAEC-PAD or GC-MS), SEC–MALS, and 1D/2D NMR can be cross-referenced to raise structural confidence.
Q7. What most impacts data quality: sample or instrument settings?
Sample cleanliness (low salts, proteins, phenolics, detergents) is the primary driver; acquisition is then optimized to the matrix.
Q8. How do you verify complete methylation?
By method controls and optional IR/NMR screens for residual –OH; re-methylation is performed if incompleteness is detected.
Q9. Can you work with crude extracts?
Yes. We offer cleanup/fractionation to remove interferents and enrich target polysaccharides before methylation.
Q10. Is methylation analysis suitable for release or COA-style comparability?
Yes. We deliver standardized linkage tables, diagnostic ions, and distribution charts suitable for internal specifications and dossiers.
Q11. How are ambiguous peaks resolved?
Using retention indices, diagnostic EI fragments, selective ion monitoring when helpful, and orthogonal confirmation (e.g., NMR, targeted LC-MS/MS).


