Glycopeptide analysis has important applications in biomedical and drug discovery to investigate the effects of glycosylation on protein function and to develop quality control methods for novel protein therapeutics. Glycopeptide analysis services are offered by Creative Proteomics to assist clients throughout the world in adhering to ICH Q6B guidelines.
Background
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain one or more attached glycan (sugar) molecules. These glycan moieties can be covalently attached to the peptide backbone via N-glycosidic or O-glycosidic bonds. Glycopeptides are commonly found in glycoproteins, which are proteins that have undergone post-translational glycosylation. Glycopeptides play important roles in various biological processes, including protein folding, stability, cellular recognition, and immune response.
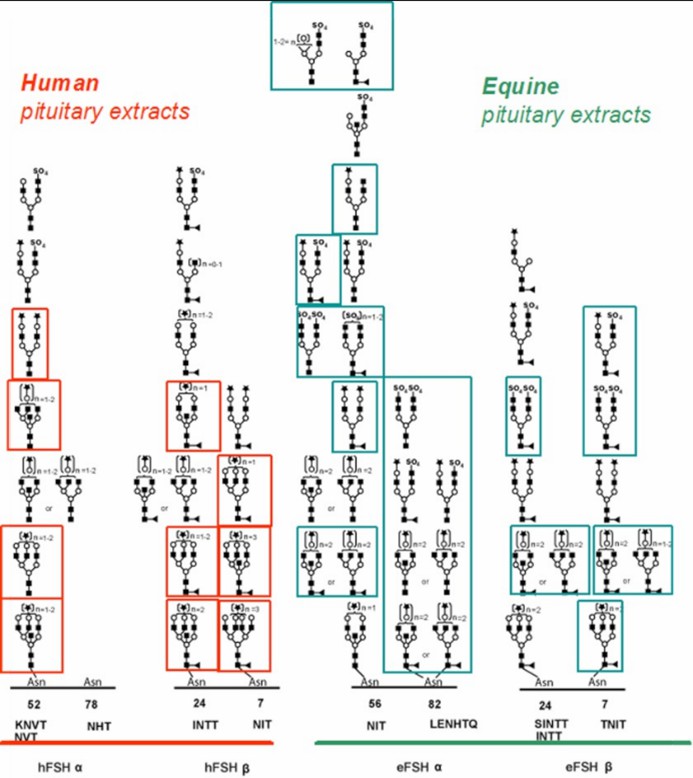 Fig 1. Comparison of the glycopeptides identified from human and equine FSH. (Desaire, H.; 2013)
Fig 1. Comparison of the glycopeptides identified from human and equine FSH. (Desaire, H.; 2013)
Application of Glycopeptides
- Because the glycosylation pattern of proteins changes under pathological situations, glycopeptides have the potential to be used as biomarkers for a variety of disorders. Novel biomarkers for disease early detection and diagnosis can be found by studying glycopeptides.
- In the creation of glycoprotein-based therapies, glycopeptides are essential. Designing and improving pharmacological candidates requires an understanding of their structure and function.
- To improve the immune response, glycopeptides can be employed in the production of vaccines. Vaccines can stimulate a more potent immune response and increase the generation of antibodies by conjugating antigens to glycans.
- In the research field of glycoproteomics, which entails the extensive identification and analysis of glycoproteins, glycopeptides are also employed. Understanding the function of glycosylation in many biological processes is made easier by this.
What Can We Provide for Glycopeptides Analysis?
Mass spectrometry (MS) analysis: This technique is widely used for glycopeptide analysis. It involves ionizing the glycopeptides and measuring their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). MS can provide information on glycan composition, glycan branching pattern, and peptide sequence. Various MS techniques, such as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI-TOF), electrospray ionization (ESI), and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), are used for glycopeptide analysis.

Liquid chromatography (LC) analysis: LC techniques, such as reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) or hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC), can be coupled with MS for the separation and analysis of glycopeptides. LC helps in resolving complex mixtures of glycopeptides and enhances the sensitivity of MS analysis.

Lectin affinity chromatography: Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that specifically recognize glycan structures. Lectin affinity chromatography involves binding glycopeptides to lectins immobilized on a chromatography column, followed by elution and subsequent analysis of the captured glycopeptides. This method provides information about glycan structures and their distribution in glycopeptides.
Enzymatic digestion: Glycopeptides can be enzymatically digested using specific glycosidases or proteases to release the glycans or peptides, respectively. This digestion can facilitate the analysis of glycan structures and peptide sequences separately using various analytical techniques, including MS and LC.
Antibody-based methods: Antibodies specific for glycopeptides or glycan epitopes can be used for the targeted analysis of glycopeptides. Techniques like enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or immunoprecipitation can be employed using these antibodies for glycopeptide detection and quantification.

Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: NMR spectroscopy can provide valuable information on the three-dimensional structure and dynamics of glycopeptides. This technique offers insights into the conformational properties of both the peptide and glycan components of glycopeptides.
Our Advantages
- Unmatched project management capability
- Tailored R&D solutions
- Decreasing development risk and improving the overall success rate for drug research
Want to Learn More?
Our main objective at Creative Proteomics is to offer our clients precise and trustworthy protein drug characterization services. We are devoted to assisting our customers in ensuring the efficacy and security of their protein-based treatments. We work to provide thorough, rigorous analyses using cutting-edge equipment, skilled scientists, and strict quality control procedures. Our team is dedicated to provide practical insights to help the R&D efforts of our clients since we recognize the importance of glycopeptide analysis in the development and characterization of protein medicines. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions about our services.
Reference
- Desaire, H. Glycopeptide Analysis, Recent Developments and Applications. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2013, 12(4), 893–901.
Related Sections
Services
Applications
For research use only, not intended for any clinical use.

 Fig 1. Comparison of the glycopeptides identified from human and equine FSH. (Desaire, H.; 2013)
Fig 1. Comparison of the glycopeptides identified from human and equine FSH. (Desaire, H.; 2013)